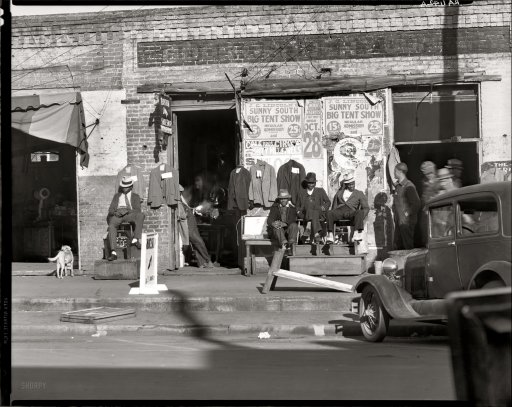
Walker Evans “Sidewalk scene in Selma, Alabama.” 1935



That’s precisely the risk.
• ECB Fears ‘Abrupt Reversal’ For Global Assets On Fed Tightening (AEP)
The global asset boom is an accident waiting to happen as the US prepares to tighten monetary policy and the Greek crisis escalates, the ECB has warned. The ECB’s financial stability report described a “fragile equilibrium” in world markets, with a host of underlying risks and the looming threat of an “abrupt reversal” if anything goes wrong. Europe’s shadow banking nexus has grown by leaps and bounds since the Lehman crisis and has begun to generate a whole new set of dangers, many of them beyond the oversight of regulators. While tougher rules have forced the banks to retrench, shadow banking has picked up the baton. Hedge funds have ballooned by 150pc since early 2008.
Investment funds have grown by 120pc to €9.4 trillion with a pervasive “liquidity mismatch”, investing in sticky assets across the globe while allowing clients to withdraw their money at short notice. This is a recipe for trouble in bouts of stress. “Large-scale outflows cannot be ruled out,” it said. The ECB warned that a rush for crowded exits could set off a wave of forced selling and quickly spin out of control. “Initial asset price adjustments would be amplified, triggering further redemptions and margin calls, thereby fueling such negative liquidity spirals,” it said. Adding to the toxic mix, the shadow banks are taking on large amounts of “implicit leverage” through swaps and derivatives contracts that are hard to track. The issuance of high-risk “leveraged loans” reached €200bn last year, nearing the extremes seen just the before the Lehman crisis.
Half of all issues this year had a debt/EBITDA ratio of five or higher, implying extreme leverage. The number of junk bonds sold reached a record pace of €60bn in the first quarter. “A deterioration in underwriting standards is evident in the increasing proportion of highly indebted issuers, below-average coverage ratios and growth in the covenant-lite segment,” the report said, warning that this nexus of debt is primed for trouble if there is an interest rate shock. While banks are in better shape than five years ago, their rate of return on equity has dropped to 3pc, far lower than their cost of equity. They remain damaged. The immediate trigger for any market rout is the nerve-racking crisis in Greece, with just a week left until the Greek authorities must repay the IMF €300m.
Vitor Constancio, the ECB’s vice-president, said it is impossible to rule out a default since Greek officials themselves have openly threatened to do so, and this in turn could set off bond market contagion across southern Europe. The ECB’s report said the former crisis states still have extremely high levels of public and private debt and have yet to clean up government finances. “Fiscal positions remain precarious in some countries,” it said. “Financial market reactions to the developments in Greece have been muted to date, but in the absence of a quick agreement, the risk of an upward adjustment of the risk premia on vulnerable euro area sovereigns could materialise,” it said.

Not going to happen.
• US And China Can Avoid Collision Course – If US Gives Up Its Empire (Guardian)
To avoid a violent militaristic clash with China, or another cold war rivalry, the United States should pursue a simple solution: give up its empire. Americans fear that China’s rapid economic growth will slowly translate into a more expansive and assertive foreign policy that will inevitably result in a war with the US. Harvard Professor Graham Allison has found: “in 12 of 16 cases in the past 500 years when a rising power challenged a ruling power, the outcome was war.” Chicago University scholar John Mearsheimer has bluntly argued: “China cannot rise peacefully.” But the apparently looming conflict between the US and China is not because of China’s rise per se, but rather because the US insists on maintaining military and economic dominance among China’s neighbors.
Although Americans like to think of their massive overseas military presence as a benign force that’s inherently stabilizing, Beijing certainly doesn’t see it that way. According to political scientists Andrew Nathan and Andrew Scobell, Beijing sees America as “the most intrusive outside actor in China’s internal affairs, the guarantor of the status quo in Taiwan, the largest naval presence in the East China and South China seas, [and] the formal or informal military ally of many of China’s neighbors.” (All of which is true.) They think that the US “seeks to curtail China’s political influence and harm China’s interests” with a “militaristic, offense-minded, expansionist, and selfish” foreign policy.
China’s regional ambitions are not uniquely pernicious or aggressive, but they do overlap with America’s ambition to be the dominant power in its own region, and in every region of the world. Leaving aside caricatured debates about which nation should get to wave the big “Number 1” foam finger, it’s worth asking whether having 50,000 US troops permanently stationed in Japan actually serves US interests and what benefits we derive from keeping almost 30,000 US troops in South Korea and whether Americans will be any safer if the Obama administration manages to reestablish a US military presence in the Philippines to counter China’s maritime territorial claims in the South China Sea.

People are not rational creatures. “To an economist, these findings are somewhere between puzzling and preposterous.”
• The Economist Who Realized How Crazy We Are (Michael Lewis)
For a surprisingly long time behavioral economics wasn’t much more than a bunch of weird observations made by Richard Thaler, more or less to himself. What he calls his “first heretical thoughts” occurred in graduate school, while writing his thesis. He’d set out to determine how to value a human life – so that, say, the government might decide how much to spend on some life-saving highway improvement. It sounds like a question without a clear answer but, as Thaler points out, people answer it clearly, if implicitly, every day, when they accept money for a greater chance of dying on the job. “Suppose I could get data on the death rates of various occupations, including dangerous ones like mining, logging and skyscraper window washing, and safer ones like farming, shop keeping and low rise window washing,” recalls Thaler.
“The risky jobs should pay more than the less risky ones: otherwise why would anyone do them?” Using wage data, and an actuarial table of mortality rates in those jobs, he was able to work out what people needed to be paid to risk their life. (The current implied value of an American life is $7 million.) Only he didn’t stop there. He got distracted by a funny idea. This willingness to allow oneself to be distracted from one’s assigned task would later turn out to be a chief characteristic of behavioral economists, along with a bunch of other traits not normally found in economists, though often found in children: a sense of wonder, a tendency to ask embarrassing questions, and a mistrust of grown-ups’ ideas about what’s worth spending time thinking about and what is not.
They’re the sort of people whose day is made when they discover that health club members are most likely to hit the gym the day after they have received their monthly bill, or that race track gamblers are a lot more likely to bet on the longshot the last race of the day than the first. At any rate, in addition to calculating the market’s price for a human life, Thaler got distracted by how much fun he might have if he asked actual human beings how much they needed to be paid to run the risk of dying. He began with his own students, telling them to imagine that by attending his lecture, they had exposed themselves to a rare fatal disease. There was a 1 in 1,000 chance they had caught it. There was a single dose of the antidote: How much would they be willing to pay for it?
Then he asked them the same question, in a different way: How much would they demand to be paid to attend a lecture in which there is a 1 in 1,000 chance of contracting a rare fatal disease, for which there was no antidote? The questions were practically identical, but the answers people gave to them were – and are – wildly different. People would say they would pay two grand for the antidote, for instance, but would need to be paid half a million dollars to expose themselves to the virus. “Economic theory is not alone in saying that the answers should be identical,” writes Thaler. “Logical consistency demands it. … To an economist, these findings are somewhere between puzzling and preposterous.”

To what extent are EU and ECB blind to the euro’s inherent weakness?
• Euro-Sclerosis (Alasdair Macleod)
if Greece defaults we would at least expect the validity of this relatively new euro to be challenged in the foreign exchange markets. Even if the ECB decided to rescue what it could from a Greek default by rearranging the order of bank creditors in its favour through a bail-in, it would still have to make substantial provisions from its own inadequate capital base. For this reason, rather than risk exposing the ECB as undercapitalised, it seems likely that Greece will be permitted to win its game of chicken against the Eurozone, forcing the other Eurozone states to come up with enough money to pay off maturing debt and cover public sector wages. So will that save the euro?
Perhaps it will, but if so maybe not for long. If the Eurozone’s finance ministers give in to Greece, it will be harder for other profligate nations to impose continuing austerity. Anti-austerity parties, such as Podemas in Spain, are increasingly likely to form tomorrow’s governments, and Spain faces a general election later this year. Prime Minister Renzi and President Hollande in Italy and France respectively are keen to do away with austerity and increase government spending as their route to economic salvation. Unfortunately for both the undercapitalised ECB and its young currency, they are increasingly likely to be caught in the crossfire between the Northern creditors and the profligate borrowers in the South.
Even if Greece is to be saved from default, the ECB will need to strengthen the Greek banks. This is likely to be done in two ways: firstly by forcing them to recapitalise with or without bail-ins, and secondly to restrict money outflows through capital controls and harsh limits on depositor withdrawals if need be. Essentially it is back to the Cyprus solution. Whichever way Greece is played, Eurozone residents will see themselves having a currency that is becoming increasingly questionable. The bail-in debacle that was Cyprus is still etched in depositors’ minds. Cyprus certainly has not been forgotten in Greece, where ordinary people are now resorting to buying mobile capital goods that can be easily sold, such as German automobiles, with the bank balances that cannot be withdrawn in cash and are otherwise at risk from a Cyprus-style bail-in.
Greek depositors have realised that euro balances held in the banks are not reliably money. Folding cash is still money, but that is all, and furthermore the folding stuff is rationed. The next blow for the euro could come from the exchange rate. If the euro continues to lose purchasing power on the foreign exchanges, it is likely to undermine confidence on the ground. And when that happens it will be increasingly difficult for the ECB to retrieve the situation and maintain the euro’s credibility as money. It just doesn’t seem sensible to take such enormous risks with a currency that has existed for only thirteen years.

“They may have no intention of defaulting, but very few government have ever paid off their debts in the end.”
• This Time It Is Different (Martin Armstrong)
For years, I have warned that we will face our worst nightmare – the collapse of socialism. In the death throes of this abomination that even the Ten Commandments listed as a serious sin, equal to “thou shalt not kill”, government will become the ugly beast that will devour society to retain power. Of course, they will never see themselves that way, but they will justify in their minds that stripping us of our freedom, rights, privileges, and immunities, is necessary to maintain socialism for the good of the people. Karl Marx, who sought to change society by sheer force, set all this in motion. What has taken place is really scary, for indeed they have altered society far more than anyone dares to ponder.
Why is this Sovereign Debt Crisis collapse different from 1931? When the governments of the world defaulted on their debts in 1931, there were no pension funds. Government has exempted itself from all prudent reason for you take the state operated pension funds, like Social Security in the USA, where 100% of the money is in government bonds. They may have no intention of defaulting, but very few government have ever paid off their debts in the end. Then there are states who regulate pension funds requiring more than 80% to be in government bonds. A Sovereign Debt Default this time around will wipe out socialism, yet the bulk of the people are clueless not merely about the risk, but the ramifications.
Younger generations do not save to support their parents for that was government’s job post-Great Depression. Socialism has altered thousands of years of family structure following the ranting of Karl Marx. This has been one giant lab experiment that ended badly in China and Russia and is coming to a local government near you. So this time it is SUBSTANTIALLY DIFFERENT. Government is now on the hook, which is part of the reason why they are moving to eliminate cash to prevent bank runs and to force society to comply with their demands.
This time it is very different. They have wiped out society placing the entire scheme of socialism as a terrible nightmare that will end badly, and they have ruined the social family structure disarming people that for thousands of years was our very means of self-sufficient survival. These clown have set the tone for wiping out the dreams they sold the elderly, all while hunting taxes and causing job creation to implode as the youth has been converted into the lost generation. All this with pretend good intentions. Can you imagine the damage to society if they had actually intended this mess? They have lied to themselves and to the people. We have to crash and burn – that part is inevitable. Only when the economy turns down will we then argue over solutions.

“It is a deliberate policy that aims to take away from the poor and give to the rich.”
• Austerity and Balanced Budgets Doomed To Fail (Rochon)
In its April budget, the federal government announced it had succeeded in balancing the budget. Such an achievement, however, will prove to be at best a Pyrrhic victory. History shows austerity and balanced budgets never work and only doom our economies to more misery. The Austerians, as American economist Rob Parenteau calls them, are clearly winning the policy war. In Canada, as in many other places around the world, governments are turning once again to austerity policies in order to reign in public spending believed to be out of control. These cuts, however, are usually done in vital social programs, such as health care, education, social housing and unemployment benefits. As is the case with other policies, austerity has both winners and losers.
The victims of austerian economics are often the disenfranchised and the unemployed, whereas those who benefit from austerity invariably tend to be wealthier Canadians, through reduced tax rates and, in Canada specifically, through a panoply of boutique tax policies such as the recent doubling of tax-free savings accounts and income splitting. In this sense, austerity is not a haphazard policy but a well-crafted approach to rewriting the Canadian social contract. It is a deliberate policy that aims to take away from the poor and give to the rich. Those who disagree with the statement have the burden to show how austerity is a success, but they will have great difficulty proving it. Academic research has come down against austerity. In fact, austerity has zero empirical support, and it has been completely discredited and proven to be the result of questionable research.
The most famous case was a landmark 2010 paper written by Carmen Reinhart and Kenneth Rogoff (both from Harvard University, no less), which argued debt-GDP ratios over 90% would result in considerable damage to national economies, notably a marked decline in economic growth. Their paper had a huge impact on policy and accounted in many respects for the great policy U-Turn of 2010 when countries reversed their previous Keynesian spending policies and reverted to austerity. This was a policy fiasco, with the inevitable result that our economies stalled and have remained in this zombie state ever since.
Yet, the paper was completely discredited. Nobel Laureate Paul Krugman went even further and stated unequivocally, “All of the economic research that allegedly supported the austerity push has been discredited. Widely touted statistical results were, it turned out, based on highly dubious assumptions and procedures – plus a few outright mistakes – and evaporated under closer scrutiny. It is rare, in the history of economic thought, for debates to get resolved this decisively.” Bucknell University economist Matias Vernengo has publicly called for the paper to be officially retracted or “unpublished.”

Uncooperative games.
• John Nash’s Game Theory Doesn’t Bode Well For Greece (El-Erian)
Economics and finance suffered two tragedies in the past week: the death of the Nobel laureate John Nash and his wife in a horrible car accident, and more delays from Greece and its creditors in reaching an agreement on a path out of the costly and protracted crisis. At first sight there seem to be little to link the two tragedies. Yet the game theory insights that John Nash pioneered – including the concept of a “cooperative game” – shed important light on what is happening in Greece, and help explain why the drama is unlikely to have a happy ending anytime soon. In a cooperative game, players coordinate to achieve better outcomes than the ones that would likely prevail in the absence of such coordination. If the game is played uncooperatively, however, the result is unfortunate for all players.
There are at least four ways to transform uncooperative games into cooperative ones. Unfortunately, these approaches would be ineffective in the case of Greece. One involves using two-sided and mutually supportive conditionality as the transformation agent: for example, by rewarding the implementation of economic reforms with the ready availability of external financing. This has been tried in Greece, but the results have fallen short, which has diminished the effectiveness of this tool. Specifically, Greece’s record on making good on its policy-reform promises has been far from perfect; and its creditors have been too hesitant in providing the extent of debt relief and cash the country needs.
A second way involves a decisive external impetus. In the case of Greece and its creditors, this role has been played by fear, particularly the fear that the Greek economy would implode, which would force it out of the euro zone. This has stoked the additional fear that such an outcome would destabilize other euro zone economies, threaten the integrity of the single currency group and disrupt the global economy. And fear is an inconsistent transformation agent because its impact is hard to sustain. As soon as it dissipates, all sides revert to uncooperative behavior. And this is what has happened in this case since at least 2010.
A third alternative involves the entry of new players that are willing and able to put aside uncooperative legacies. In today’s Europe, however, the political reality is that new players tend to be even more skeptical than their predecessors. The electoral victory of Syriza in Greece is a case in point. Finally, mutually beneficial developments could convince both sides to work together more closely. Regrettably, this hasn’t been the case of Greece and its European partners, given the limited progress on the ground. Assessing the Greek drama through the lens of game theory explains why the crisis – and the question of Greece’s continued euro-zone membership – are no closer to being resolved.
Applying Nash’s theory shows that the best we can realistically expect is yet another attempt to postpone painful decisions. But even this inadequate outcome is proving increasingly difficult to deliver, and if it materializes, the resulting delay will lead to an even more difficult situation, unless the players decide to stop their uncooperative game very soon.

Finally, some wise words. “When you make a mistake of this depth, the worst thing in the world is not to admit it and not to change it.”
• Stiglitz Tells EU to Admit Mistakes and Ease Up on Greece (Bloomberg)
Nobel laureate Joseph Stiglitz said the European Union should admit the mistake it made imposing austerity on Greece and soften its stance or bear the consequences if the country exits the euro area. “For the wellbeing of Europe and for the betterment of the world, I think the European Commission should soften,” Stiglitz said Tuesday in an interview in Split, Croatia. “Greece has done an enormous amount of work.” Stiglitz’s comments echo calls from economists including fellow Nobel laureate Paul Krugman for EU leaders to compromise to avoid a messy Greek exit from the euro that could send shock waves deeper through the currency bloc. “Europe bears a lot of responsibility as there were fundamental flaws in the design of the euro zone,” Stiglitz said.
“They created a system of divergence, not convergence, and when you combine that with austerity, that’s a recipe for the disaster we’ve seen.” The EU “should help Greece,” Stiglitz said, by starting “fundamental reforms” in the euro zone, shifting policy from austerity to promoting growth and allowing governments to temporarily assist struggling companies. As growth begins to be restored, governments should take actions to improve the efficiency of the public sector, he said. “Europe should admit that it made a mistake,” said Stiglitz, who was in the Croatian Adriatic resort town to receive an honorary degree from the University of Split. Croatia, which joined the European Union in 2013, “shouldn’t rush to the euro,” Stiglitz said.
While the country is set to exit a six-year recession this year, it’s under pressure from the EU to narrow its budget deficit and lower public debt now at 85% of output. “It doesn’t make sense to focus on the deficit when you are in recession,” Stiglitz said. Another option would be to devalue its currency, which is tied to the euro in a managed float, Stiglitz said. And while President Kolinda Grabar-Kitarovic said in an April interview that Croatia may join the euro zone by 2020, Stiglitz said the currency’s troubles had undermined the entire project. “If European voters 20 years ago were told what the consequences of the euro would be, would anybody have voted for it?” he asked. “I think the answer would be, knowing what they know now, that nobody would have voted for it.”

I agree. Plus, Greece can bundle its June IMF payments. It has just won an entire extra month.
• ‘Pots of Money’ to Be Found for Greece to Pay IMF, Roubini Says (Bloomberg)
Economist Nouriel Roubini said he expects “pots of money” to be found to allow Greece to meet its payment commitments to the IMF. “Radical decisions like capital controls, like deposit freezes, like IOUs that have a lot of collateral damage, not just financially but also economic, can be prevented,” Roubini, chairman of Roubini Global Economics, said in an interview in Dresden, Germany, where he’s attending a meeting of G-7 finance chiefs.
Greece is scheduled on June 5 to make the first of about €1.6 billion in IMF payments coming due in the next three weeks. Talks between Greek officials and the country’s international creditors over unlocking aid remain stalled. If Greece fails to meet its payments, “everybody realizes that’s the beginning of a Greek accident that has lots of other collateral damage, not just for Greece but potentially contagion also in financial markets,” Roubini said in the Bloomberg Television interview on Thursday.

“Korkidis told MPs taking part in the inquiry that IMF official Poul Thomsen had argued that Greeks should earn around €300 per month.”
• Greek Commerce Chief Slams Troika Over Bailouts (Kathimerini)
The head of the National Confederation of Commerce (ESEE), Vassilis Korkidis said on Thursday to a parliamentary committee investigating Greece’s bailouts that representatives of the troika had only spoken to the organization once since Athens signed its first bailout in 2010 and that during the discussion visiting officials suggested that Greek wages needed to drop to levels similar to other Balkan countries. Korkidis told MPs taking part in the inquiry that IMF official Poul Thomsen had argued that Greeks should earn around €300 per month. Korkidis was also critical of how previous governments handled the bailouts. “Some people rushed to get us involved in this ordeal, while others were in a rush to get us out,” he said.

“..the effect could be dramatic if it left the euro and prices in euro terms fell sharply.”
• Greece Owes Drugmakers $1.2 Billion – And Counting (Reuters)
Cash-strapped Greece has racked up mounting debts with international drugmakers and now owes the industry more than €1.1 billion, a leading industry official said on Wednesday. The rising unpaid bill reflects the growing struggle by the nearly bankrupt country to muster cash, and creates a dilemma for companies under moral pressure not to cut off supplies of life-saving medicines. Richard Bergstrom, director general of the European Federation of Pharmaceutical Industries and Associations, told Reuters his members had not been paid by Greece since December 2014. They are owed money by both hospitals and state-run health insurer EOPYY.
Drugmakers and EU officials are now discussing options in the event Greece defaults on its debt or leaves the euro zone, disrupting imports of vital goods, including medicines. “We have started a conversation in Brussels with the European Commission,” Bergstrom said. “We want the Commission to know that our companies are in this for the long run and are committed to Greece.” There is a precedent for the pharmaceutical industry to agree exceptional supply measures during a financial crisis. It happened in Argentina in 2002, when some firms agreed to continue to supply drugs for a period without payment. But the situation is complicated in Europe, given EU competition rules. They mean the Commission would need to take the initiative in approving any special scheme.
Drugmakers want any emergency program to include steps to mitigate spillover effects on other markets, including curbs on re-exports of drugs and a block on other governments referencing Greek prices when setting their own drug prices. Although Greece represents less than 1% of world drugs sales, it can have a bigger impact because of such reference pricing – and the effect could be dramatic if it left the euro and prices in euro terms fell sharply. Some drugs imported into Greece are already re-exported to other European countries under EU free-trade rules. The drugs industry has been here before. Greece also ran up large debts for its medicines in 2010-12, although they have since been repaid, with some companies receiving payment in government bonds that were subsequently written down in value.

Beppe time.
• As Greece Leads The News, Italy’s Problems Mount On Eve Of Elections (CNBC)
While Greece has been hitting the headlines recently, Matteo Renzi has quietly had a tough few months. The Italian prime minister has had to tackle difficulties both abroad and at home – including a slow economic recovery. All this presents a difficult backdrop for Renzi as he faces 22 million voters with elections in 7 regions and over 1,000 municipalities this weekend. On the domestic front, we’ve seen protests over education reform and a court ruling that pension cuts were unconstitutional, a decision that will require €13 billion in repayments. On top of that, there are accusations of political corruption and organised crime links within Renzi’s Democratic Party (PD). When I spoke to Renzi earlier this year, he said he was declaring war on corruption.
That war hasn’t stopped criticism of how contracts were awarded at the Milan Expo, never mind the backlash over mounting costs and delayed completion. On the international scene, Renzi’s much-touted plan to deal with the EU migrant crisis suffered as several governments refused to participate. Awkward. Having said that, let’s not ignore the positives. Early efforts with labor and bank reform show progress and Italy’s economy is showing signs of life, expanding 0.3 percent in the first quarter – the first uptick since the third quarter of 2013 – as a weaker euro and lower oil prices help push the country out of its longest recession on record. The economic figures tie with recent business confidence data and yet unemployment is still ticking higher – hitting 13% in March. As one Italian worker told me in Milan: “If recovery is happening, it isn’t happening fast enough.”

Oil poised to take a big step down again. US production at record levels, OPEC to increase exports.
• Everyone Is Fleeing Oil’s Biggest Fund (Bloomberg)
The biggest U.S. exchange-traded fund that tracks oil is heading for the largest two-month outflow in six years, raising concern that crude’s 30% rally may stall. Holders of the United States Oil Fund, known as USO, have withdrawn almost $1 billion so far in April and May, according to data compiled by Bloomberg. Crude dropped about $12 a barrel after a $1.4 billion exodus from the fund in the two months ended June 2009. Oil has rebounded from a six-year low in mid-March on speculation that the falling number of drilling rigs will reduce output. U.S. crude stockpiles near the highest level in 85 years and OPEC’s refusal to cut production will continue to weigh on prices, according to Goldman Sachs, Deutsche Bank and Citigroup.
“The oil rebound has run out of gas and now you are seeing nervous investors with itchy trigger fingers bailing out of USO,” Eric Balchunas, a Bloomberg Intelligence analyst, said May 27. “They don’t want to get burned by another drop in oil.” Futures rallied 25% in April, the biggest monthly gain since May 2009, and have fallen 2.4% so far in May. Crude’s recovery has slowed this month. U.S. production climbed to 9.57 million barrels a day last week, the most in Energy Information Administration data going back to 1983.
Inventories were 479.4 million, 86 million above the previous year’s level. OPEC, which supplies about 40% of the world’s oil, meets June 5 in Vienna to discuss output policy. The group will maintain its production target, Mohammad Oun, Libya’s deputy vice prime minister for energy, said Thursday, joining Kuwait in predicting no policy change. “We do not think that the bulls have enough supporting fundamental factors to make a case for a higher oil price,” Harry Tchilinguirian, BNP Paribas SA’s London-based head of commodity markets strategy, said Thursday. The supply surplus will push oil down to “$55 and then possibly lower,” he said.

Austerity is designed to target the weak.
• British Women Disproportionately Affected By Austerity (Guardian)
The UK risks widening gender inequality because of austerity policies that disproportionately affect women, a coalition of charities has warned. Cuts to social security, the public sector and legal aid will only worsen women’s position in British society, the charities say, while proposals for a five-year lock on tax raises will benefit men over women. Those factors in combination mean that women will bear the brunt of measures to pay off the deficit, they argue. The warning comes from A Fair Deal for Women, an umbrella group of 11 women’s rights charities, including Women’s Aid, the Fawcett Society, the Women’s Resource Centre, and Rape Crisis . They point out that last year Britain fell to 26th place on the World Economic Forum’s Gender Gap Index – lower than almost all its European neighbours.
“Without swift action to address women’s inequality in all areas, we could see the UK falling even lower,” said Florence Burton, a spokeswoman for the group. A Fair Deal for Women raised the alarm after Wednesday’s Queen’s speech launched the first stage of the Tories’ austerity agenda. Caroline Lucas, Green MP for Brighton Pavilion, said: “What we are increasingly seeing is that austerity perpetuates gender inequality. We ought to be tackling inequality head-on to build a strong, fair and successful economy; indeed equality and economic policy should go hand in hand. “Nobody who advocates the kinds of public-spending cuts we’ve been served up, with their disproportionately negative impact on women in particular, can justifiably claim to be an advocate of equal rights for men and women or of an economy that works for all.”
Money-saving proposals in the Queen’s speech included reducing the household benefits cap to £23,000 a year, freezing most benefits and tax credits for two years, and removing housing support from 18-to-21-year-olds. The government sweetened the pill with a five-year lock on tax rises including VAT, income tax and national insurance, as well as the extension of right to buy to housing association tenants. But Burton said the government had put forward economic policies that don’t work for women. “Putting a five-year lock on raising taxes is a policy that benefits men over women, whilst further austerity measures – like cutting benefits – are detrimental to women and their children, placing them in high risk of poverty,” she said.

Predictable. And stupid.
• Borrowing to Replenish Depleted Pensions (NY Times)
Facing a shortfall of more than $50 billion in his state’s pensions, and with no simple solution at hand, Gov. Tom Wolf of Pennsylvania is proposing to issue $3 billion in bonds, despite the role that such bonds have already played in the fiscal woes of other places. And he is not alone. Several states and municipalities are considering similar action as they struggle with ballooning pension costs. Interest in so-called pension obligation bonds is expected to intensify in the wake of a recent Illinois Supreme Court decision that rejected the state’s attempt to overhaul its severely depleted pension system. The court ruled unanimously that Illinois could not legally cut its public workers’ retirement benefits to lower costs, forcing lawmakers to scramble for the billions of dollars it will take to keep the system intact.
While the Illinois ruling is not binding on other states, analysts think it may influence lawmakers elsewhere to look to alternatives to cutting public pensions. The Illinois justices offered a list of all the times since 1917 that state lawmakers had ignored expert warnings and diverted pension money to other projects. They said, in effect, that the lawmakers had to restore the money. Pennsylvania and other states and cities fear similar restrictions. “My reaction was, ‘Yeah, that’s going to play here,’ “ said John D. McGinnis, a lawmaker in Pennsylvania, which has also been diverting money from its pension system, setting the stage for a crisis as more and more public workers retire. The state has no explicit constitutional mandate to protect public pensions, as Illinois does, but that is irrelevant, said Mr. McGinnis, a Republican and former finance professor at Pennsylvania State University.
“The judiciary in Pennsylvania has been solidly of the belief that there are ‘implicit contracts,’ and you can’t deviate from them,” he said. If lawmakers in Harrisburg were to unilaterally cut pensions now, he said, they could be taken to court and be dealt a stinging rebuke, like their counterparts in Illinois. Against that backdrop, pension obligation bonds may appear tempting, even though such deals have contributed to financial crises in Detroit, Puerto Rico, Illinois and other places. The deals are generally pitched to state and local officials as an arbitrage play: The government will issue the bonds; the pension system will invest the proceeds; and the investments will earn more, on average, than the interest rate on the bonds. The projected spread between the two rates makes it look as if the government has refinanced its pension shortfall at a lower interest rate, saving vast sums of money.

They fit the model. In fact, they probably are the model.
• Wall Street Banks Are Being Drawn Into The FIFA Bribery Probe (MarketWatch)
Major global banks — including Wall Street giants Citigroup and J.P. Morgan — could be drawn into the sweeping probe into alleged racketeering, wire fraud and corruption in the soccer world, as investigators trawl through evidence tied to the FIFA bribery scandal. A raft of banks have been named in the 164-page indictment that the U.S. Department of Justice released Wednesday, alleging that nine soccer officials from the sport’s top governing body, FIFA, and five sports executives were part of a 24-year corruption scheme involving more than $150 million in bribes. Among major financial institutions allegedly used to facilitate payments and wire transfers are J.P. Morgan, Citigroup, Bank of America, HSBC, UBS, and Julius Baer, according to indictment.
“Part of our investigation will look at the conduct of the financial institutions to see whether they were cognizant of the fact they were helping launder these bribe payments,” Kelly T. Currie, acting U.S. attorney for the Eastern District of New York, said. “It’s too early to say whether there’s any problematic behavior, but it will be part of our investigation.” None of the banks has been accused of wrongdoing. According to the FIFA indictment, the U.S. banking sector played a central role in the alleged bribery scheme. As early as the 1990s, but increasingly in the 2000s and 2010s, “the defendants and their co-conspirators relied heavily on the United States financial system,” the charges state. “This reliance was significant and sustained and was one of the central methods and means through which they promoted and concealed their schemes.”
Many of the transactions involved millions of dollars that would pass through U.S. bank accounts before allegedly being redirected to personal accounts. In one example, transactions totaling $10 million were alleged to have been wired from a FIFA account in Switzerland to a Bank of America account in New York to be credited to accounts held by the Caribbean Football Union (CFU) and CONCACAF, the continental confederation under FIFA headquartered in the United States.

Devastation on a planetary sclae.
• The Tar Sands Sell-Out (Guardian)
Amid the strip mines and steam plants sprawled across the northern Alberta wilderness, Fort McKay is just a tiny dot on the map. It is also one of the single biggest source sites of the carbon pollution that is choking the planet. This tiny First Nations community grew rich on oil, and was wrecked by oil. Local Cece Fitzpatrick grabbed what she saw as a last chance for Fort McKay and decided to run for chief, promising to stand up to the industry which came here 50 years ago. Within a 25-mile radius of Fort McKay, 21 projects with a capacity of up to 3.3m barrels a day have been approved or are in production. Another 20 with a combined capacity of about 1.6m barrels a day are in the planning stage, according to Fort McKay First Nation.
Locals can hear, smell, feel and taste the evidence of extraction, even inside their homes. On bad days, it smells like cat piss, according to Cece Fitzpatrick. The tar sands here are one of the single biggest source sites of the carbon pollution that is choking the planet. Mine out all the thick black petroleum, as the Canadian government proposes, ship it out by proposed pipelines such as the Keystone XL and oil trains, and abandon all hope of avoiding a climate catastrophe. Even with the drop in oil prices, Canadian crude exports hit an all-time high this year, and the government expects a significant increase in tar sands production.
While oil made some people here rich, it is also poisoning the waters of the Athabasca River. Researchers last year confirmed high rates of cervical cancers and a rare bile duct cancer among First Nations communities who fish from the Athabasca and hunt off the land. Which was why Cece decided to run for chief, challenging a leader in power almost continuously since 1986, and who long ago gave up trying to keep the industry out. The worst thing is my grandkids, Cece said. Enough is enough. When do we stop and say: ‘Let’s look at the future of our kids?’ Because really I don’t want people to have kids any more because our future here is so bleak. We don’t want to live here anymore.

As many die in the Sahara as do in the Mediterranean.
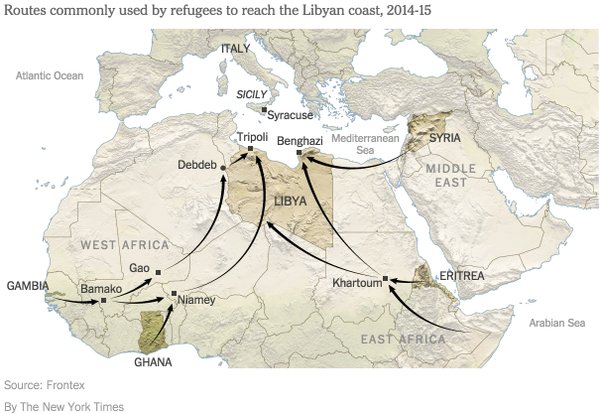
• African Migrants Risk All In Sahara To Reach Europe (Reuters)
Some 2,000 migrant deaths in Mediterranean waters between the Libyan and Italian coasts this year have prompted alarmed European governments to tighten maritime patrols to stem an influx of migrants in boats from Libya, which has been in widespread chaos since rebels toppled Muammar Gaddafi in 2011. Yet the International Organization for Migration (IOM) warns that at least as many migrants may die during the long desert crossing from Niger, the main staging post for West Africans seeking to cross the Mediterranean. Despite Niger’s passage of a tough new law against people trafficking, some 100,000 migrants fleeing desperate poverty at home in hopes of a better life in Europe are expected to cross the West African state’s borders this year. Many will pass through smugglers compounds known as “ghettos”.
“It’s a bit frightening but I have to deal with it because in life you have to be brave,” said migrant Fousseni Ismael, 16, wearing a blue headscarf to protect him from the sun as he waits to board a truck. As night falls, the pickup rolls out of the metal gates of the compound and snakes through the sandy backstreets of Agadez, passing groups of Muslim men knelt in the evening prayer. It drives unhindered past a police checkpoint on the outskirts of town and into the blackness of the vast desert. The risks are high. Mohamed, a driver, said he was attacked last week by Touareg bandits wielding AK-47 assault rifles who opened fire on his pickup when he refused to stop, wounding a migrant in the leg.
For protection, scores of trucks follow a military convoy that heads north each Monday toward the oasis town of Dirkou. The death of 92 migrants from thirst – mostly women and children – when their vehicle broke down en route to Algeria, to Libya’s west, in 2013 prompted Nigerien authorities to briefly crack down on the corridor — but the lucrative trade quietly returned. “The desert has always been a cemetery for immigrants, in silence and complete indifference. Travelers tell us they often find bodies – skeletons ravaged by the sands,” said Agadez Mayor Rhissa Feltou.

Cattle country.
• New Zealand, the Land of Disappearing Sheep (Bloomberg)
Once upon a time there were 20 sheep to every Kiwi. Now it’s more like seven to every New Zealander. Blame cows, which are now bringing home the bacon. Huge tracts of flatland once used for sheep farming were converted to dairy pastures as the global price for butter and cheese increased, while demand for sheep meat and wool waned, said Susan Kilsby, a dairy analyst at AgriHQ in Wellington. “Returns for dairy have been substantially better than for a traditional sheep and beef farming operation,” she said. There were other factors at play, too. The removal of subsidies for sheep farming in the mid-1980s exposed ranchers to market forces, explained Adrienne Egger, an agriculture analyst at Beef and Lamb New Zealand, an organization representing farmers.
New irrigation projects also made dairy farming possible for the first time in many parts of the country, AgriHQ’s Kilsby said (cows raised to produce milk are real water guzzlers). In the camp horror classic `Black Sheep’ a flock runs amok after some genetic engineering. The tagline read: “There are 40 million sheep in New Zealand and they’re PISSED OFF!” Fact is, there are far fewer sheep than that. What is true is that thanks to some genetic improvements, productivity has improved. For ranchers who stayed the course, it’s paying off.
Lamb prices at the farm-gate rose 85% in real terms and mutton prices more than doubled from 25 year ago. China, once a market for low-value cuts, has rapidly emerged as a major importer of Made in New Zealand — moving up from eighth place to second between 2008 and 2013. “In 2014, China was the largest single country market by volume of lamb,” Eggers said.