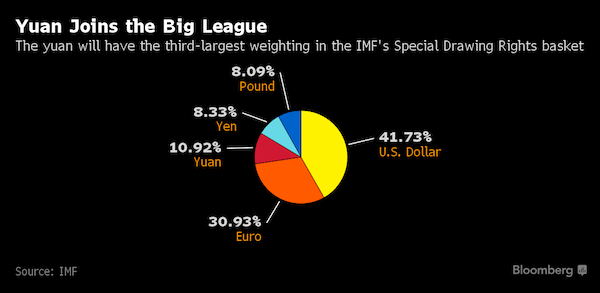
Emanuel Leutze Washington Crossing the Delaware 1851

A very safe bet.
• Morgan Stanley Says Stock Slide Was Just Appetizer for The Real Deal (BBG)
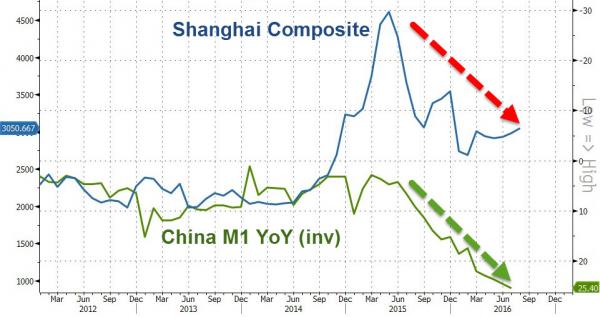
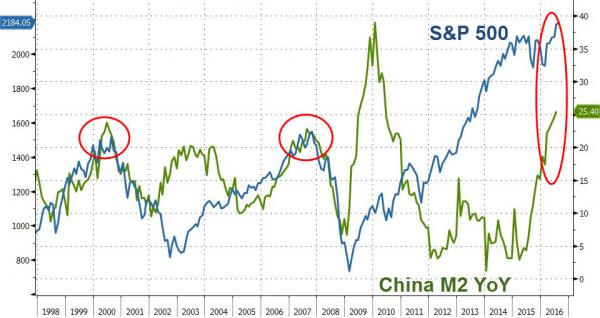
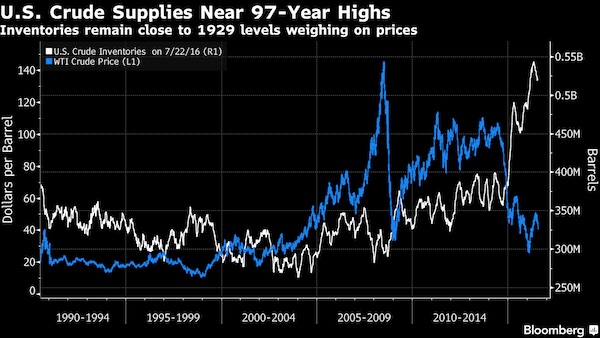
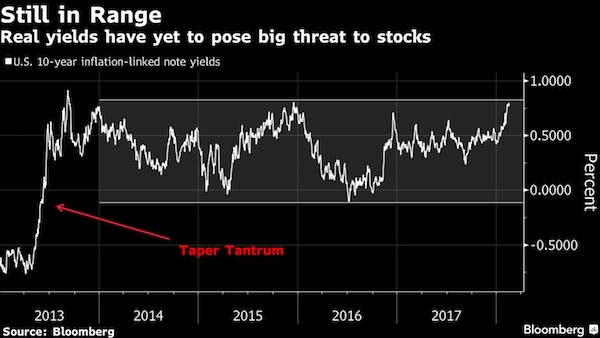
The U.S. stock market only had a taste of the potential damage from higher bond yields earlier this year, with the biggest test yet to come, according to Morgan Stanley. “Appetizer, not the main course,” is how the bank’s strategists led by London-based Andrew Sheets described the correction of late January to early February. Although higher bond yields proved tough for equity investors to digest, the key metric of inflation-adjusted yields didn’t break out of their range for the past five years, they said in a note Monday. uld be at worst neutral, if they boost earnings along the way. Higher real yields, on the other hand, mean a bigger discount rate to value future earnings. Should they break out of the range over the past five years as investors anticipate greater central bank policy normalization, that could hit stocks harder, according to the Morgan Stanley thinking.
Relatively low real yields were a big support for equity valuations, so a break higher would indicate that stocks will have to rely on earnings – not multiple expansion – to drive them higher, Sheets and his colleagues wrote. And the challenge there is that a slowdown may loom starting in the second quarter, they said. “It’s when growth softens while inflation is still rising that returns suffer most,” the strategists wrote. “Strong global growth and a good first-quarter reporting season provided an important offset. We remain on watch for ‘tricky handoff’ in the second quarter, as core inflation rises and activity indicators moderate.”

That’s real growth, right?!
• Weak Dollar Could Bring 3% Boost To Global Trade Growth (BBG)
The weak greenback may prove to be a boon for global trade. On top of the boost already coming from robust global GDP growth, the dollar’s fall over the past year may add over 3% to the level of world trade, according to Gabriel Sterne, global head of macro research at Oxford Economics Ltd. Tipping further dollar weakness, the risks are skewed to the upside for Oxford’s baseline forecast for 5% growth in world trade in 2018. “Falls in the value of the dollar oil the wheels of the global financial system, boosting global liquidity by strengthening balance sheets and alleviating currency mismatches,” Sterne wrote in a note.
“One important channel is variation in the differential between the cost of raising dollars onshore and offshore. Dollar weakness reduces the cross-currency basis, increases cross-border lending and boosts bank equities.” The biggest winners will likely be emerging economies given the weaker dollar will lower the value of their dollar-denominated debt, taking pressure off their balance sheets and from credit conditions more generally. “The seven-year link between dollar strength and U.S. recovery (2009-16) now appears broken, and we think it will remain so, with relatively strong U.S. growth and a weakening dollar providing a significant boost to global activity,” Sterne wrote.

“..As debt levels spread through the system it consumes greater amounts of capital until it eventually kills the host…”
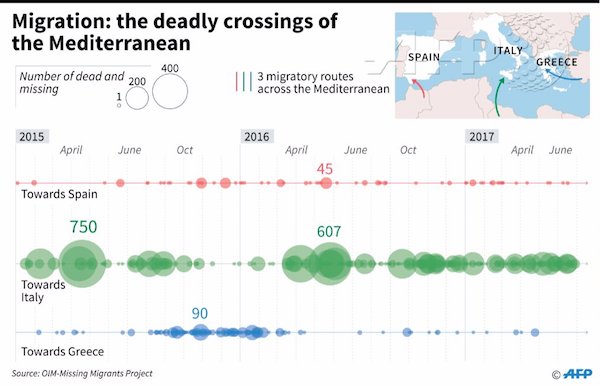
• More Than 80% Of American Adults Owe Somebody Else Money (Snyder)
How long can our debt levels keep growing much, much faster than the overall economy? We haven’t had a year of 3 percent growth for the U.S. economy since the middle of the Bush administration, but we keep borrowing money as if there is no tomorrow. Much of the focus has been on the exploding debt of the federal government, and that is definitely something I plan to address once I get to Washington. But on an individual level, U.S. consumers have been extremely irresponsible as well. In fact, one new survey has found that more than 80 percent of all American adults are currently in debt… It’s no secret that America is a nation that runs on debt, but it may surprise you to learn that the overwhelming majority of U.S. adults owe money in some way, shape, or form. According to new data from Comet, here’s how many Americans have debt at present:
• 80.9% of Baby Boomers • 79.9% of Gen Xers • 81.5% of Millennials For most of us, it starts very early. We were told that going into debt to get a college education would not be a problem because we would be able to pay those loans off with the good jobs we would get after graduation. Unfortunately, those good jobs never really materialized for many of us, and now millions of former college students are absolutely drowning in debt. A study released Friday by the Brookings Institution finds that most borrowers who left school owing at least $50,000 in student loans in 2010 had failed to pay down any of their debt four years later. Instead, their balances had on average risen by 5% as interest accrued on their debt.
As of 2014 there were about 5 million borrowers with such large loan balances, out of 40 million Americans total with student debt. Large-balance borrowers represented 17% of student borrowers leaving college or grad school in 2014, up from 2% of all borrowers in 1990 after adjusting for inflation. Large-balance borrowers now owe 58% of the nation’s $1.4 trillion in outstanding student debt. In addition to owing more than a trillion dollars on student loans, Americans are also now carrying more than a trillion dollars of auto loan debt and more than a trillion dollars of credit card debt. Corporations have been incredibly irresponsible as well. Corporate debt has doubled since the last financial crisis, and corporate bankruptcies have been rising steadily in recent years. All it would take for the dominoes to really start falling is some sort of a major economic downturn.
[..] We can’t keep doing this to ourselves. Our incessant greed is literally destroying the future, but anyone that tries to warn about the collective insanity that has descended upon our society is mocked and ridiculed. Let me ask you a question. Would you willingly choose to give yourself cancer? Of course not, but that is essentially what we are doing to ourselves as a society. Debt is economic cancer, and as Lance Roberts has pointed out, if we continue to allow debt levels to grow like this eventually it will kill our entire economy… Debt is, by its very nature, a cancer on economic growth. As debt levels rise it consumes more capital by diverting it from productive investments into debt service. As debt levels spread through the system it consumes greater amounts of capital until it eventually kills the host.

“..the greatest act of bureaucratic ass-covering in US history.”
• Thirteen Russians and a Ham Sandwich (Jim Kunstler)
Remember that one from 1996? Funny, that was the American mainstream media bragging, after the fact, about our own meddling in another nation’s election.
WASHINGTON — A team of American political strategists who helped [California] Gov. Pete Wilson with his abortive presidential bid earlier this year said this week that they served as Russian President Boris N. Yeltsin’s secret campaign weapon in his comeback win over a Communist challenge. —The Los Angeles Times, July 9, 1996

The beauty in Robert Mueller’s indictment of thirteen Russian Facebook trolls is that they’ll never face trial, so Mr. Mueller will never have to prove his case. In the new misrule of law made popular by the #Me Too movement, accusations suffice to convict the target of an investigation. Kind of sounds like going medieval to me, but that’s how we roll now in the Land of the Free. Readers know, of course, that I’m not a Trump supporter, that I regard him as a national embarrassment, but I’m much more disturbed by the mindless hysteria ginned up Washington’s permanent bureaucracy in collusion with half a dozen major newspapers and cable news networks, who have run a psy-ops campaign to shove the country into a war mentality. The New York Times published a doozy of a lead story on Saturday, the day after the indictments were announced.
The headline said: Trump’s Conspicuous Silence Leaves a Struggle Against Russia Without a Leader. Dean Baquet and his editorial board are apparently seeking an American Napoleon who will mount a white horse and take our legions into Moscow to teach these rascals a lesson — or something like that. I’m surely not the only one to notice how this hysteria is designed to distract the public attention from the documented misconduct among FBI, CIA, NSA, State Department officials and the leaders of the #Resistance itself: the Democratic National Committee, its nominee in the 2016 election, HRC, and Barack Obama’s White House inner circle. You would think that at least some of this mischief would have come to Robert Mueller’s attention, since the paper trail of evidence is as broad and cluttered as the DC Beltway itself. It actually looks like the greatest act of bureaucratic ass-covering in US history.

How to fake democracy.
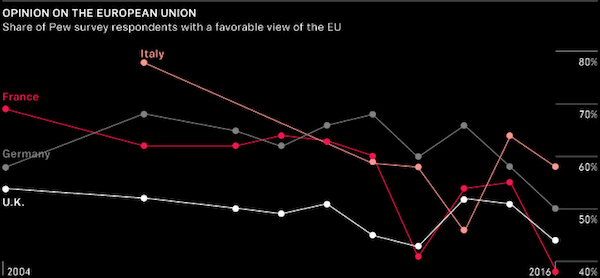
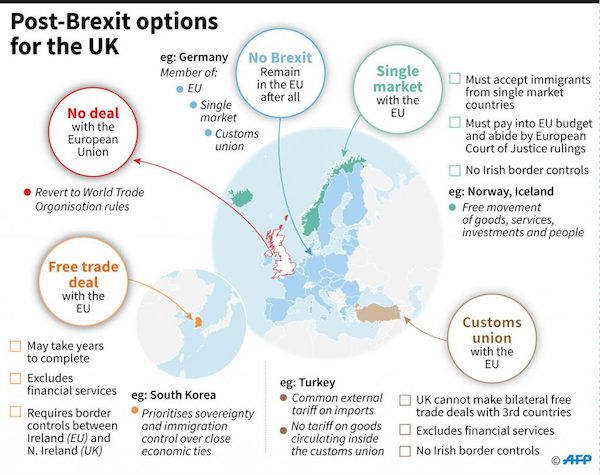
• Seeking Post-Brexit Unity, EU Leaders Find More Fights (AFP)
EU leaders face difficult talks this week on the thorny issues of how to plug holes in the post-Brexit budget and choose a successor for European Commission chief Jean-Claude Juncker. A special one-day summit in Brussels on Friday of the 27 leaders without Britain is meant to be a key step in the roadmap to a leaner and more unified bloc after Britain leaves in just over a year. But cracks have already appeared between French President Emmanuel Macron, leading the charge for a reformed Europe, and Juncker with his federalist vision of how top EU officials should be chosen in future. The row means the EU’s attempts to overcome the shock of losing a major member are running into the classic problems that have bedevilled it for its six decades of existence: money and sovereignty.
Juncker was picked after European elections in 2014 by a controversial “Spitzenkandidat” system — German for “lead candidate” — under which the political group with the most votes gets to nominate its candidate for the job. Both the European Parliament and Juncker back a repeat after the May 2019 European election, saying it gives the public a direct say in who heads the commission, the EU’s powerful executive arm. European Council President Donald Tusk — who coordinates summits and represents the EU member states — is expected to lay out options at the summit, including whether to continue with the Spitzenkandidat system. Leaders are expected to say it is their own “right and obligation” to choose the commission chief, while “taking into account” the views of parliament, as the EU treaties state, an EU source told AFP.

“Formerly” secret?
• UK Has a Secret Plan to Hold Brexit Cash If EU Refuses to Trade (BBG)
Prime Minister Theresa May’s team is eyeing up a contingency plan to hold back billions of pounds in Brexit payments, if the EU refuses to give the U.K. the trade deal it wants. Senior British officials have privately discussed the idea as a fall-back option that could be triggered if negotiations go wrong, three people familiar with the matter said. The plan is not the U.K.’s preferred outcome, but some in May’s administration believe it could be necessary in case the EU tries to renege on a future commitment to a free-trade deal. The proposal comes at a sensitive time, with British ministers seeking in public to build mutual trust with the EU rather than stoke suspicions. The U.K. is trying to persuade the bloc to cooperate on plans for an ambitious trade agreement, which will come into force after the split.
On Tuesday, Brexit Secretary David Davis will outline his idea for collaboration, promising the other 27 member countries that the U.K. won’t try to undercut them by tearing up regulations when it leaves. May is planning to announce her goals for a detailed draft trade accord in a major speech next week, with the aim of having a deal drafted by October to be signed soon after Brexit in March 2019. But the EU says a full trade agreement will be impossible to finish before Brexit. October’s conclusions are likely to form only an outline political declaration rather than a legally binding contract, raising fears among British lawmakers that the U.K. could be vulnerable if the EU backslides on the deal.

It’ll be a steep fall.
• London’s Property Crash Has Begun (Reilly)
The average age of a first time mum at London’s Chelsea and Westminster hospital is 37, a statistic that tells you everything you need to know about the choices supposedly affluent city dwellers are being forced to make in the capital. For the middle classes, the cost of living in London -the cost of getting by- long ago went past insane (£17,040: the cost per year of educating a four year-old child at Thomas’s school in Fulham, not including uniform). It’s the incredible price of property, of course, that’s been the engine driving this madness, ratcheting the pressure ever higher on Londoners who don’t own a home while making very wealthy, on paper at least, those who do.
For the last two decades and more, the capital’s property market to all intents and purposes has behaved like a giant Ponzi scheme played on a global scale. Money from all over the world has poured into London bricks, inflating values unrealistically in relation to wages, while the lavish bonuses paid to European bankers working in the City have also stoked momentum responsible for pushing up, for example, the average price of a London semi-detached house by 553 per cent between January 1995 and November 2017, from £133,820 to £873,603. Over the same period, the average cost of a detached house in the capital went from £257,748 to £1,453,271.
At last, however, the party is over. London property prices, now still flailing cartoonishly in mid-air despite being well over the edge of a cliff, are at the start of what we can call, for want of a better term, a death plunge. Although the carnage is only just beginning in earnest, desperate homeowners looking to sell are already dropping asking prices by tens of thousands of pounds and more. They know the tide is going out quickly. The reasons you would have to be clinically insane to buy property in London today are blessedly easy to understand. Describing a modern financial disaster normally requires some pretence of understanding, say, derivatives markets or the myriad immensely complex ways international banks package and trade debt. Not this time.

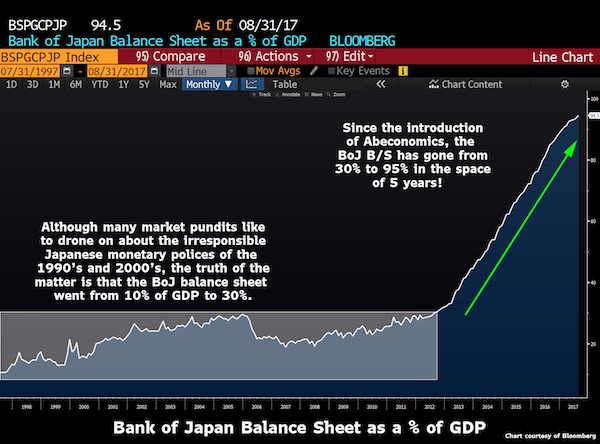
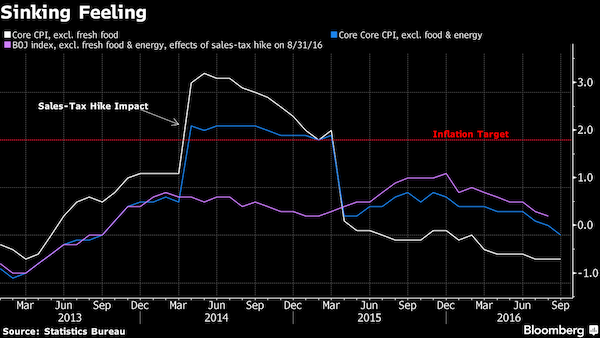
Abenomics continues to its last breath.
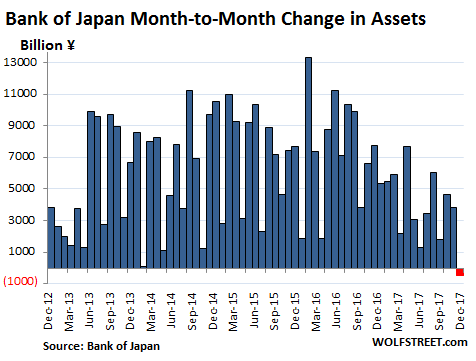
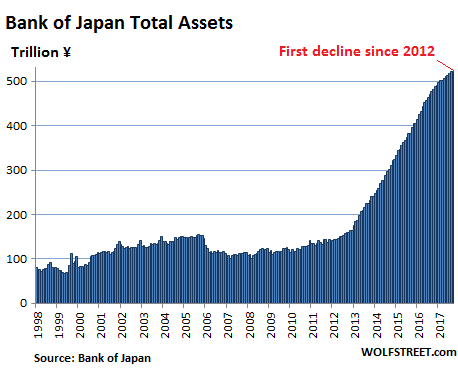
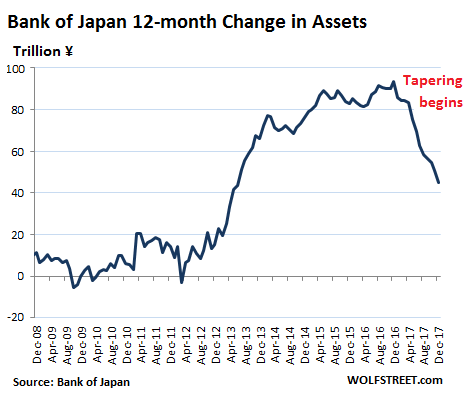
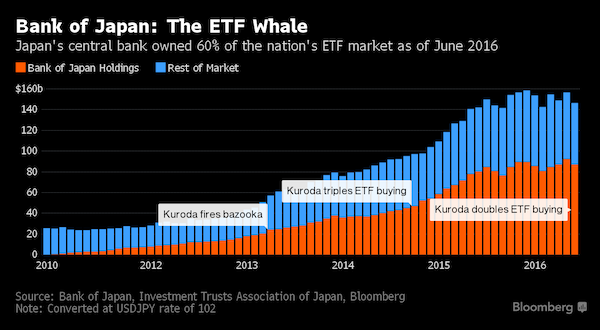
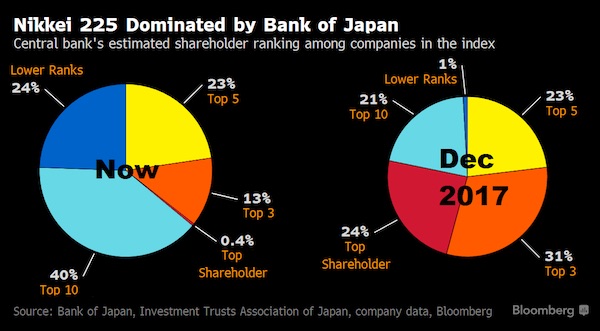
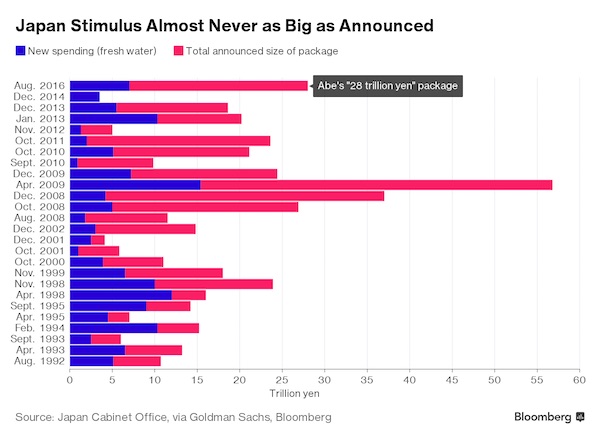
• BOJ To Keep Retreating From Stimulus Under Kuroda (R.)
The reappointment of Bank of Japan Governor Haruhiko Kuroda for another five-year term means the central bank will continue to gradually edge away from crisis-mode stimulus, former BOJ board member Takahide Kiuchi said. Premier Shinzo Abe’s decision to reappoint Kuroda, whose massive easing efforts failed to accelerate inflation to his 2% target since becoming governor in 2013, is a sign the government is no longer insisting that the BOJ meet its price goal quickly, he said. Since abandoning a policy targeting the pace of money printing in 2016, the BOJ is already whittling down its sweeping stimulus program by slowing its bond purchases, Kiuchi said.
“A de-facto normalization of monetary policy is already taking place and will continue under a reappointed Kuroda,” said Kiuchi, who served at the BOJ’s nine-member board until July. “The reappointment was a signal from the government that it wants continuity in monetary policy,” he told Reuters on Monday. The government reappointed Kuroda for another five-year term on Friday, signaling its hope the BOJ will keep up efforts to reflate the economy. During his tenure at the BOJ, Kiuchi has warned of the pitfalls of Kuroda’s monetary experiment and rightly predicted that the bank would be forced to slow its bond buying given the rising costs of its stimulus program. He retains deep insight into the workings of BOJ policy.

Does that come with actual betting?
• Italians Find Way Around Election Poll Ban With ‘Horse Races’ (BBG)
Italians have hit on a way around a ban on publishing polls in the two weeks before March 4 general elections: turn them into horse races. Bloggers Andrea Mancia and Simone Bressan have begun writing up the results of fictitious “underground” races as a means of conveying the performance of various political parties and coalitions without falling foul of the law. Hence, avid politics watchers can check on favorites like Burlesque and his stable — a not-so-thinly veiled reference to former Premier Silvio Berlusconi and his center-right coalition. They can also learn more about the performance of jockeys like Louis le Subjonctif, a reference to Five Star Movement lead candidate Luigi Di Maio and his supposed difficulties in correctly using the subjunctive tense in Italian.
This isn’t the first time the two bloggers have attempted to circumvent blackout legislation and they are not the only ones. Another blog, YouTrend.it, is known for publishing supposed polls with references to papal conclaves and names of imaginary cardinals to indicate the different candidates. During the two-week blackout period, pollsters continue to conduct surveys which circulate among politicians, market analysts and others, but are barred from publishing their findings. Newspapers and other media are also banned from publishing any indications of voting intentions so as not to influence the election.

Jihad. Inside NATO.
• Turkey Threatens to Invade Greece (Bulut)
In an incident that took place less than two weeks after the Greek Defense Ministry announced that Turkey had violated Greek airspace 138 times in a single day, a Turkish coast guard patrol boat on February 13 rammed a Greek coast guard vessel off the shore of Imia, one of many Greek islands over which Turkey claims sovereignty. Most of the areas within modern Greece’s current borders were under the occupation of the Ottoman Empire from the mid-15th century until the Greek War of Independence in 1821 and the establishment of the modern Greek state in 1832. The islands, however, like the rest of Greece, are legally and historically Greek, as their names indicate. Turkey’s ruling Justice and Development Party (AKP), however, and even much of the opposition seem intent on, if not obsessed with, invading and conquering these Greek islands, on the grounds that they are actually Turkish territory.
[..] The Ottoman dynasty and empire was established by a nomadic Turkmen chief sometime around the year 1300. During the more than 600 years of the Ottoman period, the Ottoman Turks, who also represented the Islamic Caliphate, regularly launched wars of jihad, invading and occupying lands across five continents. Neo-Ottomanists in Turkey still proudly embrace the concept of jihad (Islamic holy war) against the kafirs (infidels). The head of the state-funded Directorate of Religious Affairs, the Diyanet, has openly described Turkey’s recent military invasion of Afrin as “jihad.”
This designation makes sense when one considers that Muslim Turks owe their demographic majority in Asia Minor to centuries of Turkish Muslim persecution and discrimination against the Christian, Yazidi and Jewish inhabitants of the area. In the 11th century, Turkic jihadists from Central Asia invaded and conquered the Greek-speaking, Christian Byzantine Empire, paving the way for the gradual Turkification and Islamization of the region through methods such as murder, kidnapping, rape and forced conversions.
The greatest 20th century Turkish assault against Christians took place in the 1914-1923 genocide of Greeks, Armenians and Assyrians (Syriacs/Chaldeans) in Ottoman Turkey. This did not prevent Turkey, which continues to deny the genocide, from becoming a member of NATO in 1952. The assault also did not stop Turkey, three years after joining NATO, from committing a savage anti-Greek pogrom in Istanbul or from forcibly expelling the remaining Greeks from Turkey in 1964. It is precisely because the Turks have never been held accountable for their criminal actions and aggression that they continue to threaten the security and sovereignty of their neighbors. It is high time for the West wake up and take Ankara to task.

The church of science is not objective.
• The Royal Society and the GMO-Agrochemical Sector (CP)
The Royal Society in the UK is a self-governing fellowship of distinguished scientists. Its purpose is reflected in its founding charters of the 1660s: to recognise, promote and support excellence in science and to encourage the development and use of science for the benefit of humanity. Its motto, nullius in verba, is taken to mean ‘take nobody’s word for it’. It is an expression of the determination to withstand the domination of authority and to verify all statements by an appeal to facts based on experiment. In 2015, Steven Druker challenged the Royal Society to justify its outspoken and partisan support of GMO crops and to correct any errors of fact in his book ‘Altered Genes,Twisted Truth’. Not long after the book’s release, he wrote an open letter to the Society calling on it to acknowledge and correct the misleading and exaggerated statements that is has used to actively promote GMOs and in effect convey false impressions.
Druker cited specific instances where members of the Royal Society have at various times made false statements and the Society’s actions were not objective or based on scientific reasoning but biased and stridently pro-GMO. He argued that the Royal Society has misrepresented the case for GMOs and has effectively engaged in a campaign of disinformation. Almost three years later, from what we can gather, the Royal Society has not responded to Druker. [..] In a new, fully-referenced 45-page open letter, environmentalist Dr Rosemary Mason is strident in her criticism of the Royal Society: “The Royal Society of London has thrown its hand in with the agrochemical industry, has received funding from it and accepted its word that GM crops are safe. The scientists who founded The Royal Society (Wren, Boyle, Wilkins and Newton) would turn in their graves.”
Rosemary Mason’s letter is addressed to Venkatraman Ramakrishnan, president of the Royal Society. She sets out in some detail the disturbing effects of the rising use of agrochemicals on human health, the environment, biodiversity and ecology in the UK and beyond. As she notes, many have sounded the alarm over global mass poisoning as a result of tens of thousands of synthetic chemicals entering world markets with no evidence of safety. It has reached the point where we now have an ‘ecological Armageddon’ after a dramatic plunge in insect numbers. Given Mason’s concerns about the Royal Society’s collusion with corporate interests, she refers Ramakrishnan to the reputation of Monsanto and the findings of the Monsanto Tribunal, the Monsanto Papers and the dozens of lawsuits in the US involving that company.

You can try… But French farmers are what they are..
• France To Let Wolf Population Grow By 40% Despite Anger From Farmers (AFP)
The French government has announced it will allow the wolf population to grow 40% despite pressure from farmers in mountain regions who are worried about their sheep flocks. A new strategy unveiled by the centrist government of President Emmanuel Macron will enable the number of wolves to increase from an estimated 360 now to 500 by 2023. Hunting wiped out the grey wolf in France during the 1930s and they only returned in 1992 via Italy – currently home to around 2,000 wolves – before spreading into Switzerland and Germany. The regeneration of the population in France has led to tensions between the government and farmers in the Alps and Pyrenees mountains who complain that attacks on their livestock cause major financial losses.
In a bid to respond to that anger, hunters will be allowed to kill 10% of the population every year, which can be raised to 12% if attacks are more frequent than usual. “We place trust in all of the stakeholders and local lawmakers to calm the debate and enable a co-existence over the long-term,” agriculture minister Stephane Travert and environment minister Nicolas Hulot wrote in a foreword to the report. Hulot, a celebrity environmentalist, spoke recently of how wolf culling “makes me sick to the stomach” but he accepted it was a necessary measure to take farmers’ concerns into account. Hundreds of sheep were let loose on the streets of the city of Lyon last November in one of a number of protests against the wolf, which has protected status.
The 100-page wolf strategy will also enable livestock owners to apply for state funds to shield their animals, but it will make compensation contingent on them installing fencing and taking other protective measures. Wolves eat between 2-4kg (4.4 to 8.8lb) of meat a day on average and the predators have been blamed for an explosion in the number of attacks on livestock in mountainous areas. A total of 10,000 sheep were killed in the Alps region in 2016, according to official figures from the regional government, but the wolf is also known to feast on deer, wild boar or even domestic animals.

When everyone’s guilty, who goes to jail?
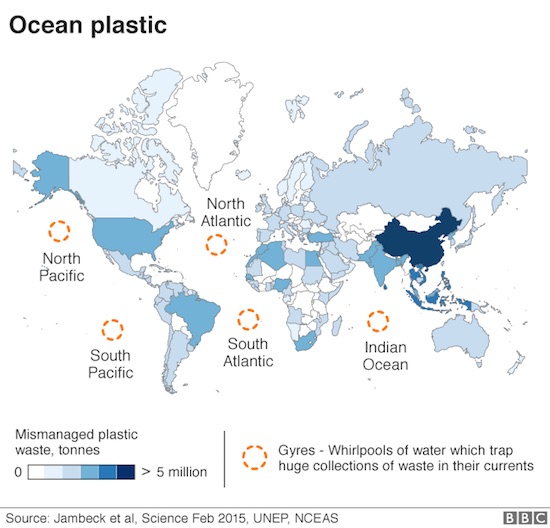
• Ocean Plastic Tide ‘Violates International Law’ (BBC)
The global tide of ocean plastic pollution is a clear violation of international law, campaigners say. They have been urging for a new global treaty to tackle the problem. But a new report – to be presented to a Royal Geographical Society conference on Tuesday – says littering the sea with plastics is already prohibited under existing agreements. The report urges those governments that are trying to tackle the issue to put legal pressure on those that are not. The paper has been written by the veteran environment journalist Oliver Tickell. His conclusions are backed by ClientEarth, the legal group that successfully sued the UK over failures to meet air pollution laws. Tickell says legal action against big polluters such as China, India and Indonesia can be taken only by a nation state.
So he calls for governments and green groups to support small island nations suffering most from plastic pollution. Tickell maintains that marine plastic litter can already be controlled through the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS); the London Convention; the MARPOL Convention; the Basel Convention; Customary Law, and many other regional agreements. Article 194 of UNCLOS, for instance, requires states to “prevent, reduce and control pollution of the marine environment from any source. “Measures shall include, inter alia, those designed to minimize to the fullest possible extent… the release of toxic, harmful or noxious substances, especially those which are persistent, from land-based sources… [and] shall include those necessary to protect and preserve rare or fragile ecosystems as well as the habitat of depleted, threatened or endangered species and other forms of marine life.”