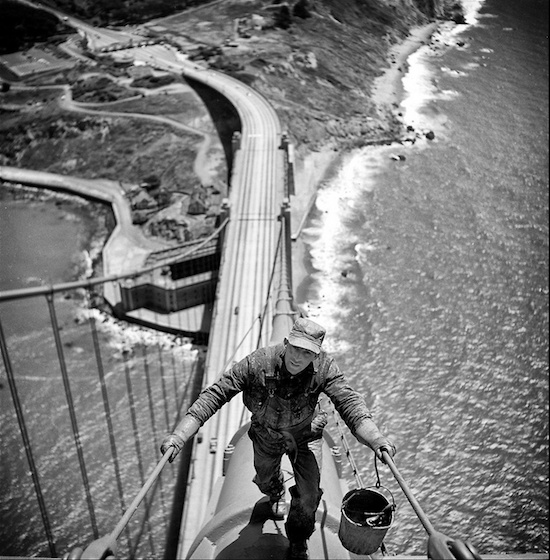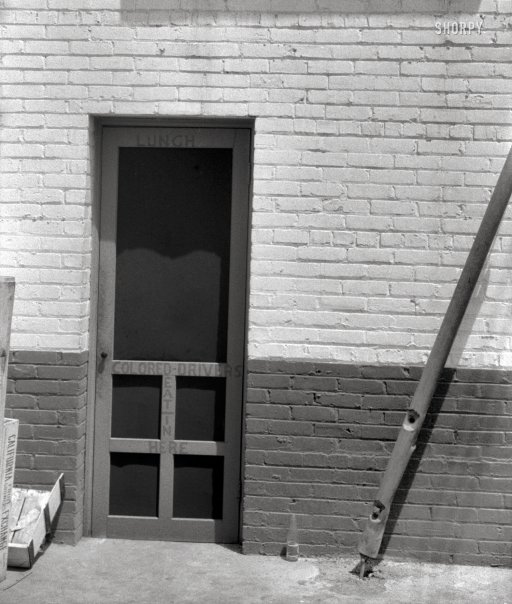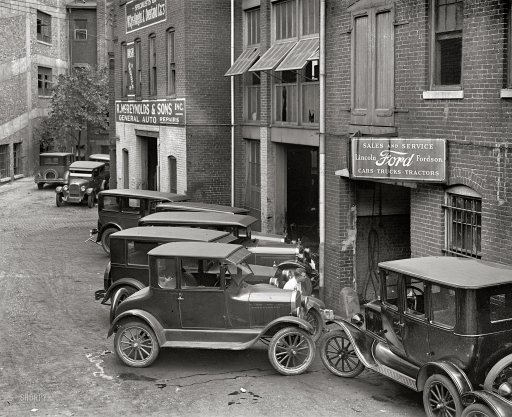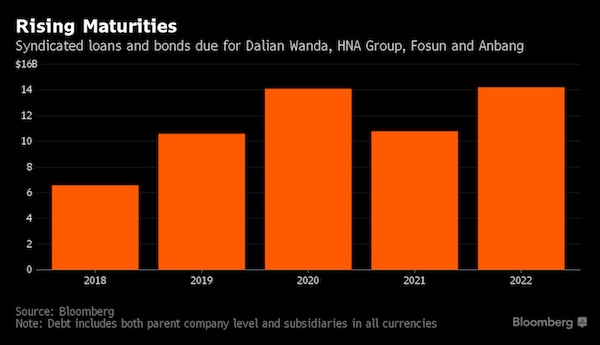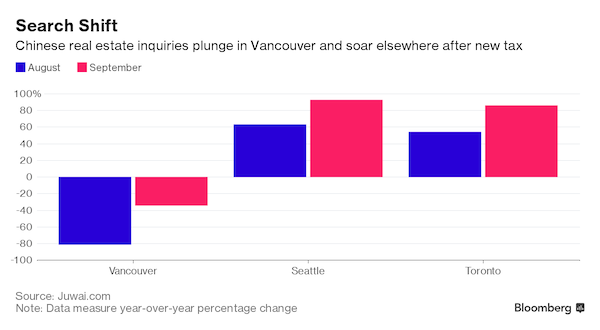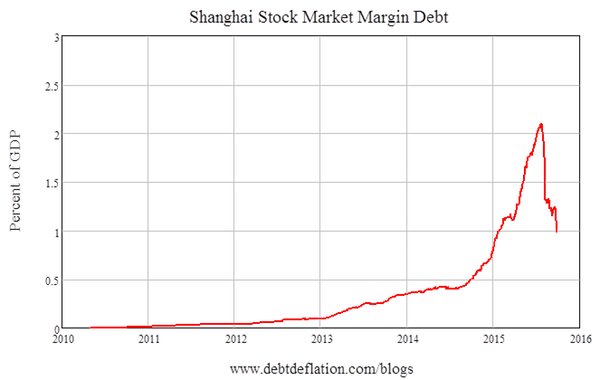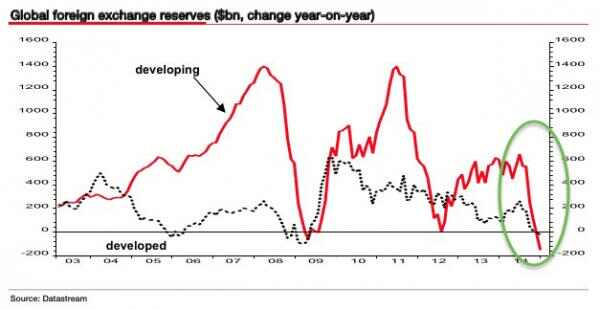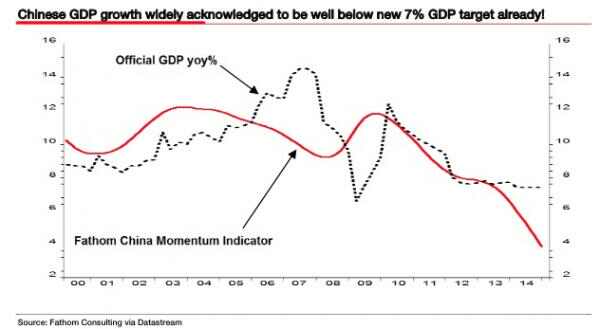
Piet Mondriaan Composition in color A 1917

Funny but very serious. Recommend the whole article.
• Tesla Shareholders: Are You Drunk On Elon Musk’s Kool-Aid? (Lewitt)
Tesla shareholders (and bullish Wall Street analysts) are either geniuses or delusional and I am betting on the latter. Typical of the lack of gray matter being applied to this investment is a recent post on Seeking Alpha, often a place where amateurs go to pump stocks they own. Someone calling himself “Silicon Valley Insights” issued an ungrammatical “Strong Buy” recommendation on October 11 based on the following syllogism: (1) “Tesla CEO Elon Musk has stated very firmly that they can and will reach his goal of producing 5,000 cars per week by the end of this year.” (2) “Musk has a history of setting aggressive targets (more for his staff than investors) [Editors’s Note: That is a lie.] and then missing them on initial timing but reaching them later. [Editor’s Notes: That is another lie–Musk has NEVER reached a production target.]
(3) “Reaching anything [sic] significant portion of that 5K target (say 1-2K) by the end of December could drive TSLA shares significantly higher.” This genius then suggests that investors stay focused on the Model 3 ramp as the key price driver over the coming weeks and months and argues that the announcement that only 260 Model 3s were produced in the third quarter leaves “much of the risk…now in the stock price.” He is correct – there is a great deal of risk embedded in a stock trading at infinity-times earnings with no prospect of profitability , a track record of breaking promises, a reluctance to sell equity to fund itself even at price levels above the targets of most analysts, and a market cap larger than rivals that are pouring tens of billions of dollars into putting it out of business.
Undeterred, he offers two investment strategies. The first he terms a “reasonable and conservative” one that waits to invest in TSLA shares until the early November third quarter earnings call. In my world, a reasonable and conservative strategy would be to run for the hills or short the stock (as I am doing). A “more aggressive and risky strategy” (compared to skydiving or bungee jumping) would be “to buy shares before that third quarter report and call on the bet that the Model 3 production update will be taken positively.” No doubt investors like Mr. Silicon Valley Insights will put a positive spin on whatever fairy tales Elon Musk spins on that call, but that is a big bet indeed.

Bankers involved in LIbor and other scandals regulate themselves. This is the exact opposite of an independent central bank. It’s a criminal racket.
• ECB Suffers from “Corporate Capture at its Most Extreme” (DQ)
No single institution has more influence over the lives of European citizens than the European Central Bank. It sets the interest rates for the 19 Member States of the Eurozone, with a combined population of 341 million people. Every month it issues billions of euros of virtually interest-free loans to hard-up financial institutions while splashing €60 billion each month on sovereign and corporate bonds as part of its QE program, thanks to which it now boasts the biggest balance sheet of any central bank on Planet Earth. Through its regulatory arm, the Single Supervisory Mechanism, it decides which struggling banks in the Eurozone get to live or die and which lucky competitor gets to pick up the pieces afterwards, without taking on the otherwise unknown risks. In short, the ECB wields a bewildering amount of power and influence over Europe’s financial system.
But how does it reach the decisions it makes? Who has the ECB’s institutional ear? The ECB has 22 advisory boards with 517 seats in total that provide ECB decision-makers with recommendations on all aspects of EU monetary policy. A new report by the non-profit research and campaign group Corporate Europe Observatory (CEO) reveals that 508 of the 517 available seats are assigned to representatives of private financial institutions. In other words, 98% of the ECB’s external advisors have some sort of skin in the game. Of the nine seats not taken by the financial sector, seven have gone to non-financial companies such as German industrial giant Siemens and just two to consumer groups, according to the CEO report. In response to questions by CEO, the ECB said that its advisory groups help it to gather information, effectively “discharge its mandate”, and “explain its policy decisions to citizens.”
[..] Many of the above institutions were implicated in two of the biggest financial crimes of this century, the Forex and Libor scandals. In fact, according to CEO, banks involved in a separate forex manipulation scandal that emerged in 2013 have been heavily represented on the ECB’s Foreign Exchange Contact Group. In other words, these banks are supposed to be under direct ECB supervision, and yet they have been repeatedly caught committing serious financial crimes. And now it turns out that they enjoy more influence over ECB decision making than anyone else..

Spot the nonsense: ”..already bought over 2 trillion euros worth of bonds to cut borrowing costs and induce household and corporate spending..”
They buy bonds and magically households will start spending. They don’t belive that themselves either.
• ECB Still Believes In Eventual Inflation, Wage Rise: Draghi (R.)
Wages and inflation in the 19-country euro zone will eventually rise but more slowly than earlier thought, requiring continued patience from policymakers, European Central Bank President Mario Draghi said on Saturday. Wage growth has failed to respond to stimulus for a list of reasons but the ECB remains convinced that labor markets and not a structural change in the nature of inflation is the chief culprit behind low prices, Draghi told a news conference on the sidelines of the International Monetary Fund annual meeting. Having fought low inflation for years, the ECB is due to decide at its Oct. 26 meeting whether to prolong stimulus, having to reconcile rapid economic expansion with weak wage and price growth.
Sources close to the discussion earlier told Reuters that the ECB will likely extend asset purchases but at lower volumes, signaling both confidence in the outlook but also indicating that policy support will continue for a long time. “The bottom line in terms of policy is that we are confident that as the conditions will continue to improve, the inflation rate will gradually converge in a self-sustained manner,” Draghi said. “But together with our confidence, we should also be patient because it’s going to take time.” Even as the euro zone has enjoyed 17 straight quarters of economic growth, wage growth has underperformed expectations, due in part to hidden slack in the labor market and low wage demands from unions.
Some policymakers also argue that globalization and technological changes have made value chains more international, making low inflation a global phenomenon and limiting central banks’ ability to control prices in their own jurisdiction. Draghi acknowledged the debate but said the ECB was convinced the main problem was the labor market and even if there was a broader issue, it would not lead to policy change. The ECB has kept interest rates in negative territory for years and already bought over 2 trillion euros worth of bonds to cut borrowing costs and induce household and corporate spending.

They say one thing and do another.
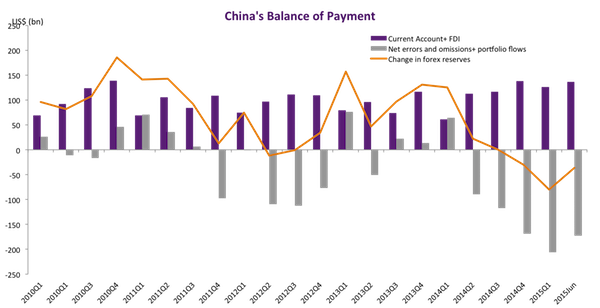
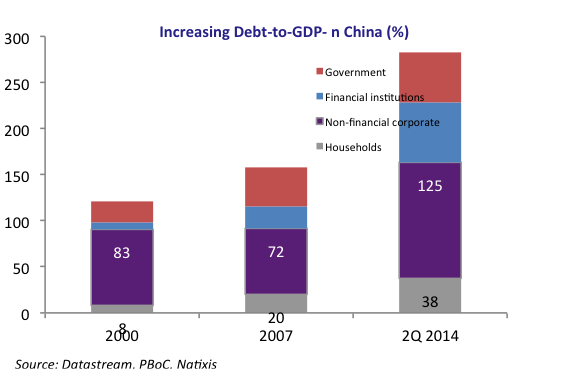
• China Credit Growth Exceeds Estimates Despite Debt Curb Vow (BBG)
China’s broadest gauge of new credit exceeded projections, signaling that the funding taps remain open even as the government pushes to curb excessive borrowing. Aggregate financing stood at 1.82 trillion yuan ($276 billion) in September, the People’s Bank of China said Saturday, compared with an estimated 1.57 trillion yuan in a Bloomberg survey and 1.48 trillion yuan the prior month. New yuan loans stood at 1.27 trillion yuan, versus a projected 1.2 trillion yuan. The broad M2 money supply increased 9.2%, exceeding estimates and picking up from the prior record low. Policy makers have been clamping down on shadow banking while also working to keep corporate borrowing intact to avoid impeding growth.
The central bank said Sept. 30 it will reduce the amount of cash some banks must hold as reserves from next year, with the size of the cut linked to lending to parts of the economy where credit is scarce. “Momentum continues to be very strong,” said Kenneth Courtis, chairman of Starfort Investment Holdings and a former Asia vice chairman for Goldman Sachs. “Loan demand of the private sector has finally turned up in recent months.” “This means that there is little hope of further policy easing in the fourth quarter as the monetary policy is very accommodative,” said Zhou Hao, an economist at Commerzbank in Singapore. “There could be even a tightening bias.”
“Household short-term loans have increased too rapidly, with some funds being invested in stock and property markets,” said Wen Bin, a researcher at China Minsheng Banking Corp. in Beijing. “Regulators have started to pay attention to the sector and required banks to strengthen credit review. I think the momentum will show signs of slowing in the fourth quarter.” “Deleveraging is not happening if we look at any measure of credit growth,” according to Christopher Balding, an associate professor at the HSBC School of Business at Peking University in Shenzhen. “Lending in 2017 has actually accelerated significantly from 2016.”

Yeah. Financed by debt.
• PBOC Governor Zhou Says China’s 6.9% Growth ‘May Continue’ (BBG)
Economic indicators show “stabilized and stronger growth” and the momentum of a 6.9% expansion in the first six months of 2017 “may continue in the second half,” People’s Bank of China Governor Zhou Xiaochuan said. Imports and exports increased rapidly, fiscal income grew, and prices have been steady, Zhou said, according to a statement the central bank released Saturday after he attended meetings of global finance chiefs this week in Washington. The effects of a campaign to rein in leverage are showing, and China will monitor and prevent shadow banking and real estate risk, he said. China’s broadest gauge of new credit, released Saturday, exceeded projections, signaling that the funding taps remain open even as the government pushes to curb excessive borrowing. “Positive progress has been achieved in economic transformation,” the statement said.
“China will continue to pursue a proactive fiscal policy and a prudent monetary policy, with a comprehensive set of policies to strengthen areas of weakness.” Zhou’s comments, delivered before a gathering of Group of 20 finance ministers and central bankers, come before the release of third-quarter GDP, scheduled for Oct. 19. Economists project a moderation to 6.8% growth from the 6.9% pace in the second quarter amid government efforts to reduce overcapacity and ease debt risk. Steady growth in the world’s second-largest economy gives policy makers additional room to push ahead with reforms. Zhou recently made a fresh call to further open up the financial sector, warning that such an overhaul will become more difficult if the window of opportunity is missed. Some analysts say they expect reforms will pick up should President Xi Jinping further consolidate power after the 19th Party Congress starting next week.
The IMF this week increased its global growth forecast amid brightening prospects in the world’s biggest economies. It also raised its China growth estimate to 6.8 percent this year and 6.5 percent in 2018, up 0.1 percentage point in each year versus July. “We expect that the authorities can and will maintain a sufficiently expansionary macro policy mix to meet their policy target of doubling 2010 GDP by 2020,” Changyong Rhee, the fund’s Asia and Pacific director, said at a briefing Friday in Washington. “However, as this expansionary policy comes at the cost of a further large increase in debt, it also implies that there’s more downside risk in the medium-term due to this rapid credit expansion.”

Beijing seems to be getting scared of people’s reactions. Still, when you think about it, closing down 50% of steel production says something about the country’s needs for steel.
• In China, The War On Coal Just Got Serious (SMH)
Beijing: In Australia, politicians continue to debate the existence of climate change. Donald Trump’s Environment Protection Agency declared this week that the “war on coal is over”. In China, the outlook could not be more different. The war on coal reached fever pitch here this month. As a deadline looms to achieve clean air targets by the end of 2017, October has seen unprecedented measures come into force to curb air pollution and reduce emissions. Steel production has been halved in major steel cities, coal banned in China’s coal capital, factories closed down for failing pollution inspections, and hundreds of officials sacked for failing to meet environmental targets. The complete shutdowns, or 50% production cuts, will stay in place for an unprecedented five months.
The winter heating season in China is approaching, when coal use has traditionally spiked, worsening northern China’s notorious air pollution. But cities are under pressure to meet important domestic targets for clean air, set five years ago by the State Council in response to a public outcry over pollution. China can’t allow a repeat of last winter, when, after several years of improvement, air quality suddenly worsened in some cities. For a few days in January 2016, the sky darkened and it looked possible that the “airpocalypse” of 2013 – which first drew global attention to Beijing’s severe air pollution – was back. Social media went into overdrive. Fighting air pollution is a matter of social stability, Environment Protection Minister Li Ganjie said a fortnight ago. So now the Chinese government has brought out the “iron fist”.
That was the phrase used by the environment protection bureau in China’s most polluted province, Hebei, as 69 government officials were sacked and 154 handed over to police for investigation last month for failing to implement pollution control measures. Meeting emissions targets has become a key performance indicator for local Communist Party bosses and mayors alike. Local governments that don’t enforce the pollution controls will have environmental assessments for new property developments suspended by the Ministry for Environment Protection, effectively blocking deals. A battle plan has been drawn up by the ministry to cover 28 northern cities, including Beijing and Tianjin, where 7000 pollution inspectors will be deployed to expose violations and look for data fraud. The curbs on industry, particularly steel making, are hitting world resources prices, including Australia’s biggest exports, as demand for iron ore and coal fall.

Let me guess. They want more reforms.
• IMF Steering Committee Warns Global Growth Is At Risk Of Faltering (BBG)
The IMF’s steering committee warned that global growth is at risk of faltering in coming years given uncomfortably low inflation and rising geopolitical risks, injecting a cautious note into an otherwise improving economic outlook. “The recovery is not yet complete, with inflation below target in most advanced economies, and potential growth remains weak in many countries,” the International Monetary and Financial Committee said in a communique released Saturday in Washington. “Near-term risks are broadly balanced, but there is no room for complacency because medium-term economic risks are tilted to the downside and geopolitical tensions are rising.” The panel didn’t specify which geopolitical risks it was most concerned about.
In the past few weeks the U.S. and North Korea have engaged in shrill rhetoric about Pyongyang’s nuclear weapons. And on Friday, U.S. President Donald Trump took steps to confront Iran and renegotiate a 2015 multinational accord to curb Tehran’s nuclear program. At the same time, the U.K. is in the middle of negotiations on the terms of its exit from the EU. The panel nonetheless described the global outlook as strengthening, with rising investment, industrial output and confidence – conditions that make it ripe for nations to “tackle key policy challenges” and enact policies that boost the speed limit of their economies. “It’s when the sun is shining that you need to fix the roof,” IMF Managing Director Christine Lagarde said at a press briefing to discuss the statement.

The best part of the iMF is not the front office, it’s the anonymous workers.
• Corbyn Has A Washington Ally On Taxing The Rich. But No, It’s Not Trump (G.)
The IMF has been on quite a journey from the days when it was seen as the provisional wing of the Washington consensus. These days the IMF is less likely to harp on about the joys of liberalised capital flows than it is to warn of the dangers of ever-greater inequality. The fund’s latest foray into the realms of progressive economics came last week when it used its half-yearly fiscal monitor – normally a dry-as-dust publication – to make the case for higher taxes on the super-rich. Make no mistake, this is a significant moment. For almost 40 years, since the arrival of Margaret Thatcher in Downing Street and Ronald Reagan in the White House, the economic orthodoxy on taxation has been that higher taxes for the 1% are self-defeating.
Soaking the rich, it was said, would punish initiative and lead to lower levels of innovation, investment, growth and, therefore, reduced revenue for the state. As the Conservative party conference showed, this line of argument is still popular. Minister after minister took to the stage to warn that Jeremy Corbyn’s tax plans would lead to a 1970s-style brain drain. The IMF agrees that a return to the income tax levels seen in Britain during the 1970s would have an impact on growth. But that was when the top rate was 83%, and Corbyn’s plans are far more modest. Indeed, it is a sign of how difficult it has become to have a grown-up debate about tax that Labour’s call for a 50% tax band on those earning more than £123,000 and 45% for those earning more than £80,000 should be seen as confiscatory.
The IMF’s analysis does something to redress the balance, making two important points. First, it says that tax systems should have become more progressive in recent years in order to help offset growing inequality, but have actually become less so. Second, it finds no evidence for the argument that attempts to make the rich pay more tax would lead to lower growth. There is nothing especially surprising about either of the IMF’s conclusions: in fact, the real surprise is that it has taken so long for the penny to drop. Growth rates have not picked up as taxes have been cut for the top 1%. On the contrary, they are much weaker than they were in the immediate postwar decades, when the rich could expect to pay at least half their incomes – and often substantially more than half – to the taxman.
If trickle-down theory worked, there would be a strong correlation between growth and countries with low marginal tax rates for the rich. There is no such correlation and, as the IMF rightly concludes, “there would appear to be scope for increasing the progressivity of income taxation without significantly hurting growth for countries wishing to enhance income redistribution”. With a nod to the work of the French economist Thomas Piketty, the fiscal monitor also says that countries should consider wealth taxes for the rich, to be levied on land and property.

Why am I thinking it’s the Brit(on)s themselves who’ve done that?
• Brexit Has Made The UK The Sick Man Of Europe Once More (NS)
Though it didn’t feel like it at the time, the years preceding 2017 now resemble an economic golden age for the UK. After the damage imposed by the financial crisis and excessive austerity, Britain recovered to become the fastest growing G7 country. Real earnings finally rose as wages increased and inflation fell (income per person grew by 3.5% in 2015). And then the Brexit vote happened. Though the immediate recession that the Treasury and others forecast did not materialise, the UK has already paid a significant price. Having previously been the fastest growing G7 country, Britain is now the slowest. Real earnings are again in decline owing to the inflationary spike caused by the pound’s depreciation (the UK has the lowest growth and the highest inflation – stagflation – of any major EU economy).
Firms have delayed investment for fear of future chaos and consumer confidence has plummeted. EU negotiator Michel Barner’s warning of a “very disturbing” deadlock in the Brexit talks reflects and reinforces all of these maladies. While Leavers plead with Philip Hammond to set money aside for “a no-deal scenario”, the referendum result is daily harming the public finances. The Office for Budget Responsibility has forecast a £15bn budgetary hit (the equivalent of nearly £300m a week). To the UK’s existing defects – low productivity, low investment and low pay – new ones have been added: political uncertainty and economic instability. The Conservatives, to annex former Chancellor George Osborne’s phrase of choice, failed to fix the roof when the sun was shining.
Rather than taking advantage of record-low borrowing rates to invest in infrastructure (and improve the UK’s dismal productivity), the government squandered money on expensive tax cuts. The Sisyphean pursuit of a budget surplus (now not expected until at least 2027) reduced the scope for valuable investment. Productivity in quarter two of this year was just 0.9% higher than a decade ago – the worst performance for 200 years. Having softened austerity, without abandoning it, the Conservatives are now stuck in a political no man’s land.

Cross-party action against May. It’s quite something. But it’ll just be more fighting.
• UK MPs Move To Block May From Signing ‘No Deal’ Brexit (G.)
A powerful cross-party group of MPs is drawing up plans that would make it impossible for Theresa May to allow Britain to crash out of the EU without a deal in 2019. The move comes amid new warnings that a “cliff-edge” Brexit would be catastrophic for the economy. One critical aim of the group – which includes the former Tory chancellor Kenneth Clarke and several Conservative ex-ministers, together with prominent Labour, SNP, Liberal Democrat and Green MPs – is to give parliament the ability to veto, or prevent by other legal means, a “bad deal” or “no deal” outcome. Concern over Brexit policy reached new heights this weekend after the prime minister told the House of Commons that her government was spending £250m on preparations for a possible “no deal” result because negotiations with Brussels had stalled.
Several hundred amendments to the EU withdrawal bill include one tabled by the former cabinet minister Dominic Grieve and signed by nine other Tory MPs, together with members of all the other main parties, saying any final deal must be approved by an entirely separate act of parliament. If passed, this would give the majority of MPs who favour a soft Brexit the binding vote on the final outcome they have been seeking and therefore the ability to reject any “cliff-edge” option. A separate amendment tabled by Clarke and the former Labour minister Chris Leslie says Theresa May’s plan for a two-year transition period after Brexit – which she outlined in her recent Florence speech – should be written into the withdrawal bill, with an acceptance EU rules and law would continue to apply during that period. If such a transition was not agreed, the amendment says, exit from the EU should not be allowed to happen.

Some nice history, but a weird anti-Islam stance. And a somewhat dubious conclusion.
• Forget Catalonia, Flanders Is The Real Test Case Of EU Separatism! (OR)
To concisely summarize, there’s a very distinct possibility that the EU’s liberal-globalist elite have been planning to divide and rule the continent along identity-based lines in order to further their ultimate goal of creating a “federation of regions”. Catalonia is the spark that could set off this entire process, but it could also just be a flash in the pan that might end up being contained no matter what its final result may be. Flanders, however, is much different because of the heightened symbolism that Belgium holds in terms of EU identity, and the dissolution of this somewhat artificially created state would be the clearest sign yet that the EU’s ruling elite intend to take the bloc down the direction of manufactured fragmentation. Bearing this in mind, the spread of the “Catalan Chain Reaction” to Belgium and the inspiration that this could give to Flanders to break off from the rest of the country should be seen as the true barometer over whether or not the EU’s “nation-states” will disintegrate into a constellation of “Balkanized” ones.
{..] It’s important to mention that the territory of what would eventually become Belgium had regularly been a battleground between the competing European powers of the Netherlands, the pre-unification German states, France, the UK, and even Spain and Austria during their control of this region, and this new country’s creation was widely considered by some to be nothing more than a buffer state. The 1830 London Conference between the UK, France, Prussia, Austria, and Russia saw the Great Power of the time recognize the fledgling entity as an independent actor, with Paris even militarily intervening to protecting it during Amsterdam’s failed “Ten Day’s Campaign” to reclaim its lost southern province in summer 1831.
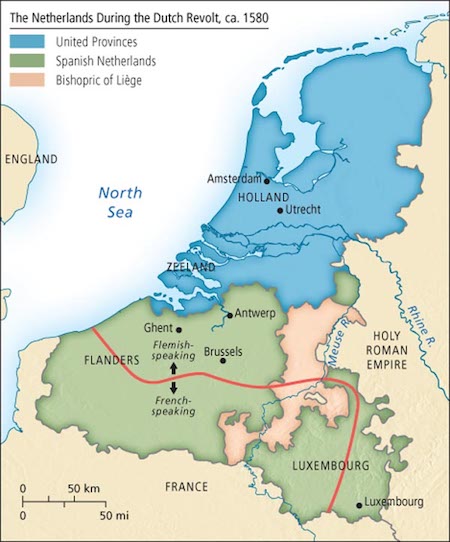
[..] Flanders contributes four times as much to Belgium’s national economy as Catalonia does to Spain’s, being responsible for a whopping 80% of the country’s GDP as estimated by the European Commission, and it also accounts for roughly two-thirds of Belgium’s total population unlike Catalonia’s one-sixth or so. This means that Flemish independence would be absolutely disastrous for the people living in the remaining 55% of the “Belgian” rump state, which would for all intents and purposes constitute a de-facto, though unwillingly, independent Wallonia.

Austria is as much of a threat to the EU as Flanders is. The Visograd anti-migrants idea is moving west. This worries Germany, which shares quite a long border with Austria.
• Europe’s Migration Crisis Casts Long Shadow As Austria Votes (R.)
Austria holds a parliamentary election on Sunday in which a young conservative star hopes to beat the far right at its own game with a hard line on refugees and pledging to prevent a repeat of Europe’s migration crisis. Foreign Minister Sebastian Kurz, who is just 31, propelled his conservative People’s Party (OVP) to the top of opinion polls when he became its leader in May, dislodging the far-right Freedom Party from the spot it had held for more than a year. He is now the clear favorite to become Austria’s next leader. Kurz has pledged to shut down migrants’ main routes into Europe, through the Balkans and across the Mediterranean. Many voters now feel the country was overrun when it threw open its borders in 2015 to a wave of hundreds of thousands of people fleeing war and poverty in the Middle East and elsewhere.
Chancellor Christian Kern’s Social Democrats (SPO) are currently in coalition with Kurz’s OVP, but Kurz called an end to the alliance when he took over the helm of his party, forcing Sunday’s snap election. Opinion polls have consistently shown the OVP in the lead with around a third of the vote, and second place being a tight race between the Social Democrats and the Freedom Party (FPO), whose candidate came close to winning last year’s presidential election. “We must stop illegal immigration to Austria because otherwise there will be no more order and security,” Kurz told tabloid daily Oesterreich on Friday night. Campaigning has been dominated by the immigration issue. Kurz plans to cap benefit payments for refugees at well below the general level and bar other foreigners from receiving such payments until they have lived in the country for five years.

Now or never