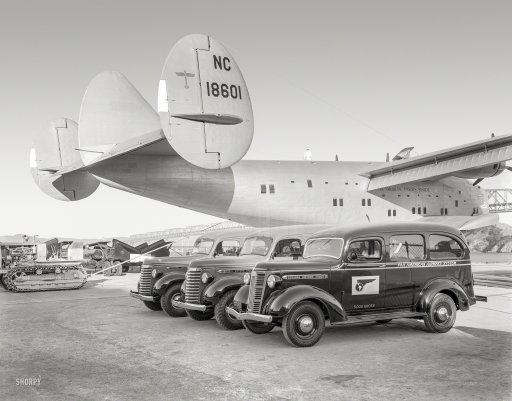
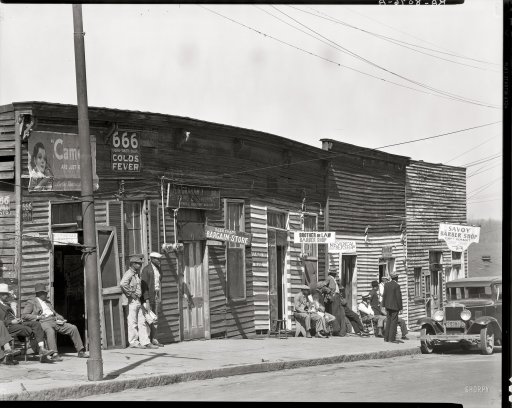
Wyland Stanley Boeing 314 flying boat Honolulu Clipper. 1939



Shanghai Accord to be like Plaza Accord, mass devaluation of the yuan, to “reset global monetary policy stability if only for a few more months”…
• BofA: ‘Shanghai Accord’, Massive Central Bank Intervention Imminent (ZH)
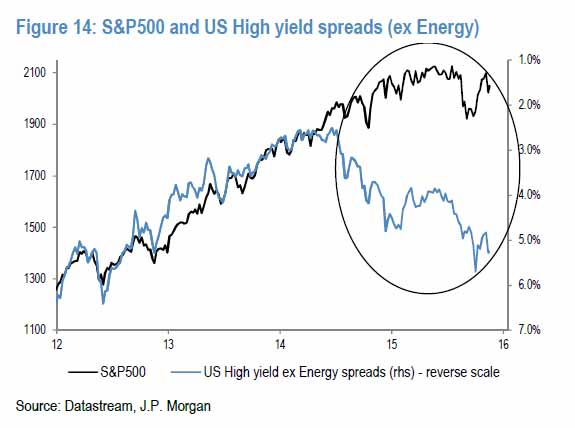
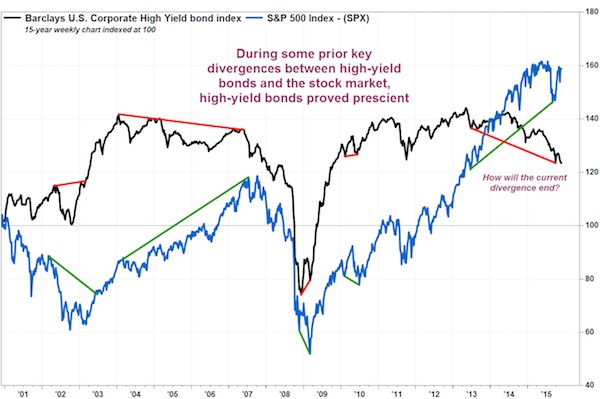
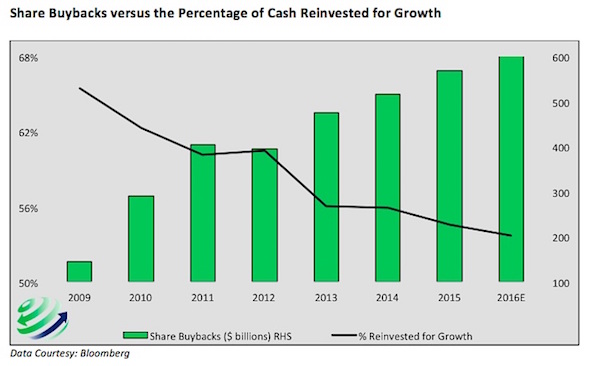
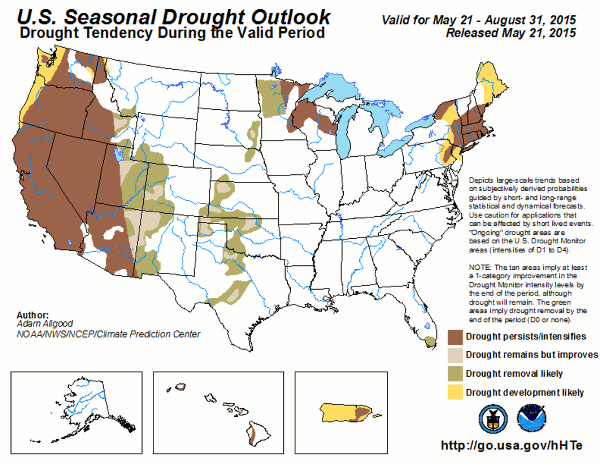
Any time the relative performance of global financials to US Treasuries has stumbled as far as it has, as shown in the chart below, it has meant one thing – a major central bank intervention was imminent. At least that’s the interpretation of BofA’s Michael Hartnett, who shows that in order to provide the kick for the bounce in this all too important “deflationary leading indicator”, central banks engaged in major unorthodox easing episodes, whether QE1-3, or the ECB’s QE.
Why intervene now? Here are the problems according to Hartnett:
• Problem 1: US economy in “bad Goldilocks”, i.e. US economy not hot/strong enough to lift global GDP & EPS; but not cold/bad enough to induce global coordinated response
• Problem 2: global policy-maker rhetoric in recent days shows “coordinated innocence” not stimulus, all blaming global economy for weak domestic economies (“Overseas factors are to blame”…Japan PM Abe; “drag on U.S. economy from greater-than-expected-slowdown in China & other EM economies“…FOMC minutes; “increasing concerns about the prospects for the global economy”…ECB Draghi; “the change in China’s growth rate can be attributed in part to weak performance of the global economy”…PBoC)Problem 2 is static, meant for media propaganda and jawboning; it can easily be removed once the global economy takes the next leg lower. Which incidentally would also resolve the gating factor of Problem 1 – as we have said for months, the Fed and its central bank peers need the political cover to launch more stimulus.
And in a reflexive world, where the “economy is the market”, this means just one thing – a big leg lower in stocks is the necessary and sufficient condition to once again push stocks higher, as policy failure is internalized, and global risk reprises from square 1. This is Bank of America’s summary, warning that unless a major policy intervention is enacted, the market will then sell off to the next support level, below the 1,812 which has proven so stable since August. Stabilization of “4C’s” (China, Commodities, Credit, Consumer) allowed SPX 1800 to hold/bounce to 1950-2000; weak policy stimulus in coming weeks could end rally/risk fresh declines to induce growth-boosting policy accord.
Here is a summary of the near-term events which stocks are betting on do not disappoint: G20 Shanghai (February 26-27); ECB (March 10), BoJ (March 15) & FOMC (March 16). And as documented previously, the one main near-term event Hartnett is focusing on is the Shanghai meeting next weekend. Recall: “We remain sellers into strength in coming weeks/months of risk assets at least until a coordinated and aggressive global policy response (e.g. Shanghai Accord) begins to reverse the deterioration in global profit expectations (currently heading sharply south – Chart 1) and credit conditions.”
In other words, Hartnett expects a “Shanghai Accord” to be unveiled next weekend, one where like the Plaza Accord three decades earlier, the Yuan will be massively depreciated, which ironically would halt all piecemeal Yuan devaluation on expectation of future devaluation (as it will have already happened), and reset global monetary policy stability if only for a few more months. Said otherwise, if next weekend the G-20 disappoints and unveils nothing, the next big leg down in the selloff will have arrived.

“They should have the good graces to resign. They are lost. None of this is helping the economy..”
• I Don’t Know What The Bulls Are Smoking: Stockman (CNBC)
Anyone who believes that the global economy isn’t crashing must be delirious, according to David Stockman. The former director of the Office of Management and Budget argues that a rapidly deteriorating economic environment is going to send stocks and oil prices spiraling even lower than they already have. “I think your traders are smoking something stronger than what I can legally buy here in Colorado,” Stockman said Thursday on CNBC’s “Futures Now.” The S&P 500 has fallen 6% year to date, and crude oil has plunged more than 17%. However, Stockman still sees a long way to go.
He expects the S&P 500 to drop to 1,300 before making any new highs, and sees oil falling below $20. Investors have been too optimistic about the U.S. economy because they are not factoring in global risk, said Stockman, who expects to see a recession by the end of the year. “Everywhere trade is drying up, shipping rates are at all-time lows,” he said. “There is a recession that’s going to engulf the entire world economy, including the United States.” Contributing to the turmoil is the ineptitude of central banks, he said. While Stockman doesn’t expect the Federal Reserve to adopt a negative interest rate policy, he said monetary policymakers have exhausted all other options.
“They should have the good graces to resign. They are lost. None of this is helping the economy,” he said. Add in the 2016 presidential election, and Stockman said the markets will find themselves in a situation similar to that of the global financial crisis. “The out-of-control election process will feed into and create an environment that we haven’t seen since the fall of 2008,” he said. Of course, this isn’t the first time Stockman has been bearish. For years, he has been predicting a crash worse than 2008. Stockman headed the White House OMB during President Ronald Reagan’s first term.

Creative accounting 2.0. Don’t like what you see? Just stop reporting it. The US learned this trick a long time ago.
“..the slide in foreign-currency assets held by Chinese financial institutions “is typically much larger than the decline in foreign reserves..”
• China Lenders’ Foreign-Exchange Holdings Omitted From PBOC Data (BBG)
China’s central bank omitted details of financial institutions’ foreign-exchange holdings from monthly data that sheds light on the scale of its intervention to support the yuan. The change took effect in its report for January, when the currency’s slide to a five-year low roiled global financial markets and prompted the People’s Bank of China to step up efforts to boost the exchange rate amid record capital outflows. While the authority announced a $99.47 billion slide in its foreign-exchange reserves for last month, less than December’s record $107.9 billion drop, the figure may not represent the true extent of dollar sales if state-owned lenders were also used to intervene. “Sometimes it’s the commercial banks that sell a lot of dollars when the PBOC wants to prop up the yuan,” said Zhou Hao at Commerzbank in Singapore.
When this happens, the slide in foreign-currency assets held by Chinese financial institutions “is typically much larger than the decline in foreign reserves,” he said. In September, the assets dropped by a record $117 billion – almost triple the $43.3 billion decline in the nation’s reserves – as large state banks sold borrowed dollars for yuan and used forward contracts with the central bank to hedge those positions. Historically, the numbers tend to be broadly in line with one another. China used intervention, verbal warnings and a tightening of capital controls in its bid to quell speculative attacks on the yuan in the offshore market last month. The measures, which caused overnight borrowing costs for the currency to surge to an unprecedented 66.82% in Hong Kong, enjoyed some success and the offshore exchange rate has strengthened 3.6% to 6.5244 a dollar since sinking to a five-year low on Jan. 7. The onshore rate gained 1.2% to 6.5201 in Shanghai.

More detail on this creative outburst in China. Funny thing is, this will backfire. Analysts have other ways of getting the data, and they will do so now with a lot more scrutiny and suspicion.
• Sensitive Financial Data ‘Missing’ From PBOC Report On Capital Outflows (SCMP)
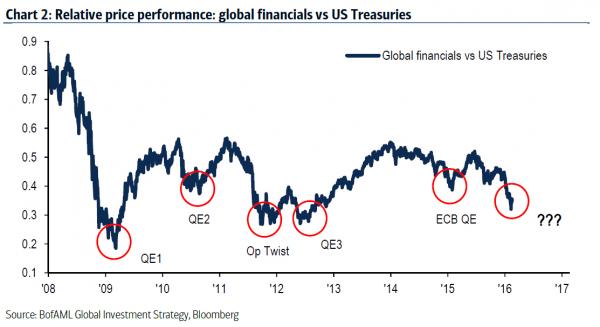
Sensitive data is missing from a regular Chinese central bank report amid concerns about capital outflow as the economy slows and the yuan weakens. Financial analysts say the sudden lack of clear information makes it hard for markets to assess the scale of capital flows out of China as well as the central bank s foreign exchange operations in the banking system. Figures on the “position for forex purchase” are regularly published in the People’s Bank of China’s monthly report on the “Sources and Uses of Credit Funds of Financial Institutions”. The December reading in foreign currencies was US$250 billion. But the data was missing in the central bank s latest report. It seemed the information had been merged into the “other items” category, whose January figure was US$243.9 billion a surge from US$20.4 billion the previous month.
Another key item of potentially sensitive financial data was altered in the latest report. The central bank also regularly publishes data on the forex purchase position in renminbi, which covers all financial institutions including the central bank. The December reading was 26.6 trillion yuan (HK$31.7 trillion). But the January data gave information on forex purchases made only by the central bank, detailing the lower figure of 24.2 trillion yuan. China’s foreign exchange reserves shrank almost US$100 billion last month as the central bank sells dollars and buys renminbi to shore up the country s weakening currency. It followed a record US$108 billion drop in December. Optimism for the yuan has taken a hit from continuous capital outflows amid growing concern about China s economic outlook.
The central bank has been criticised for contributing to the panic through its poor communication with the market and its foreign counterparts. PBOC governor Zhou Xiaochuan last week told Caixin the central bank was “neither a god nor a magician”, though it was very willing to improve communication with the public. This is not the first time the PBOC has tweaked items in its financial reports, but the unannounced changes come at a sensitive time as Beijing tries to stabilise the yuan exchange rate. “Its non-transparent method has left the market unable to form a clear picture about capital flows,” said Liu Li-Gang, ANZ’s chief China economist in Hong Kong. “This will fuel more speculation that China is under great pressure from capital outflows. It will hurt the central bank’s credibility.”

He can bully his own people, unlike foreign investors.
• Xi Jinping Demands ‘Absolute Loyalty’ From Chinese State Media (AP)
The Chinese president, Xi Jinping, has made a rare and high-profile tour of the country’s top three state-run media outlets, telling editors and reporters they must pledge absolute loyalty to the Communist party and closely follow its leadership in “thought, politics and action”. His remarks are the latest sign of Beijing’s increasingly tight control over the media and Xi’s unceasing efforts to consolidate his power as head of the party. Xi overshadowed the propaganda chief, Liu Yunshan, who accompanied him on his visits to the newsrooms of the party newspaper People’s Daily, state-run news agency Xinhua, and state broadcaster China Central Television (CCTV). At CCTV, Xi was welcomed by a placard pledging loyalty. “The central television’s family name is the party,” the sign read, anticipating remarks made by Xi at a later meeting.
“The media run by the party and the government are the propaganda fronts and must have the party as their family name,” Xi told propaganda workers at the meeting, during which he demanded absolute loyalty from state media. “All the work by the party’s media must reflect the party’s will, safeguard the party’s authority, and safeguard the party’s unity,” he said. “They must love the party, protect the party, and closely align themselves with the party leadership in thought, politics and action.” Willy Lam, an expert on elite Chinese politics at the Chinese University of Hong Kong, said Xi is raising standards for state media by requiring they obey the will of the Communist party’s core leadership, which is increasingly defined by Xi himself in another sign of how he has accrued more personal authority than either of his last two predecessors.
“This is a very heavy-handed ideological campaign to drive home the point of total loyalty to the party core,” Lam said. “On one hand, Xi’s influence and power are now unchallenged, but on the other hand, there is a palpable degree of insecurity.” Lam said Xi faces lurking challenges not only from within different party factions but also from among a disaffected public, who are unhappy with the slowing economy and a recent stock market meltdown. Zhang Lifan, a Beijing-based independent historian and political observer, said the tour of state media further added to Xi’s burgeoning personality cult. “I am afraid we will see more personal deification in the media in the future,” Zhang said. “I think Xi is declaring his sovereignty over the state media to say who’s really in charge.”

Gentlemen, count your losses.
• The Only Thing Worse Than Oil? Investing in It (WSJ)
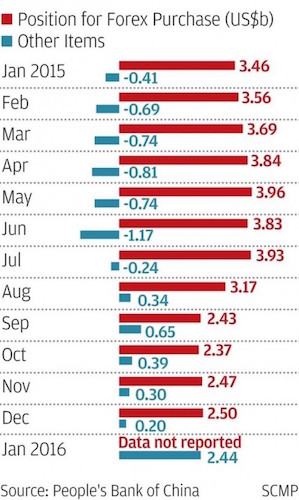
One of the few assets performing worse than oil is a set of products used to bet on it. The $3.86 billion United States Oil Fund LP, an exchange-traded fund that goes by the ticker USO, is down 22% so far this year, while the $575 million iPath S&P GSCI Crude Oil Total Return Index exchange-traded note, known as OIL, is down 26% in that period. In comparison, U.S. crude-oil futures for March delivery settled at $29.64 a barrel on Friday, down 20% this year. The poor returns illustrate the difficulty of making such bets, particularly on oil prices, which have confounded investors by continuing to sink in 2016. Even after oil’s fall over the past year, investors in products that track crude have something else dragging on returns: it’s more costly to make long-term bets.
A glut of oil has shifted the dynamics of the futures market, which reflects the cost of holding oil, and that has further weighed on the performance of some of the products in recent weeks. Many commodity-investment products hold or track the nearest-month futures and regularly rebalance into the following month’s contracts. If the nearer-term contract costs less than the further-dated one, a condition known as contango, the rotation involves getting rid of cheaper contracts to buy more expensive ones. The bigger the difference between the two, the more this so-called roll cost drags on performance. Crude has been in contango since mid-2014, but the differential has risen sharply recently. The difference in the settlement price between March and April oil futures contracts has more than doubled since the end of last year.
At Thursday’s settlement, it cost $2.16 more to buy a barrel of West Texas Intermediate oil for April delivery than oil for March delivery, compared with 96 cents at the end of 2015. The differential was as high as $2.62 on Feb. 11. If left unchanged at Thursday’s settlement prices, the difference between the two contracts implies a monthly loss of 7.02% simply from roll costs, according to FactSet. It “hurts returns,” said Alan Konn at Uhlmann Price Securities, a wealth-management firm in Chicago. The firm has investments tied to the Rogers International Commodity Index, which tracks a basket of 37 commodities. The index is down close to 6% this year and more than 29% over the past 12 months.

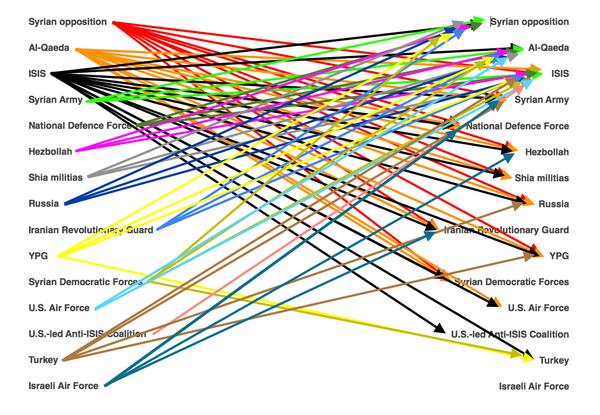
A longer quote than usual for a Debt Rattle of Tyler Durden describing how convoluted the position of the US, EU and NATO is becoming because of their support for Erdogan. Then again, our main export these days is failed states. I added the graph (Who fights what in Syria) from another source.
• A Furious Turkey Says US Is “Acting Like An Enemy” (ZH)
As you might have noticed, Turkish President Recep Tayyip Erdogan is about to lose his mind with the situation in Syria. To be sure, the effort to usurp the Bashar al-Assad government wasn’t exactly going as planned in the first place. Regime change always takes time, but the conflict in Syria was dragging into its fifth year by the time the Russians got directly involved and although it did indeed look as though the SAA was on the verge of defeat, the future of the rebellion was far from certain. But to whatever extent the rebels’ fate was up in the air before September 30, the cause was dealt a devastating blow when Moscow’s warplanes began flying sorties from Latakia and while Ankara and Riyadh were initially willing to sit on the sidelines and see how things played out, once Russia and Hezbollah encircled Aleppo, it was do or die time.
The supply lines to Turkey were cut and without a direct intervention by the rebels’ Sunni benefactors, Moscow and Hassan Nasrallah’s army would ultimately move in on Aleppo proper and that, as they say, would be that. The problem for Turkey, Saudi Arabia, and Qatar is optics. That is, everything anyone does in Syria has to be justified by an imaginary “war on terror.” Turkey can’t say it’s intervening to keep the rebels from being defeated by the Russians, and similarly, Saudi Arabia, Qatar, the US, France and everyone else needs to preserve the narrative and pretend as though this all doesn’t boil down to the West and the Sunnis versus the Russians and the Shiites. Here’s what we said earlier this month: somehow, Turkey and Saudi Arabia need to figure out how to spin an attack on the YPG and an effort to rescue the opposition at Aleppo as an anti-ISIS operation even though ISIS doesn’t have a large presence in the area.
Well it turns out that’s an impossible task and so, Turkey has resorted to Plan B: a possible false flag bombing and the old “blame the Kurds” strategy. The attack on military personnel in Ankara this week was claimed by The Kurdistan Freedom Hawks (an offshoot of the PKK) in retaliation for Turkey’s aggressive campaign in Cizre (as documented here), but Erdogan has taken the opportunity to remind the world that the PKK and the YPG are largely synonymous. That is, they’re both armed groups of non-state actors and if one is a terrorist organization, then so is the other. Erdogan’s anti-Kurd stance is complicated immeasurably by the fact that both the US and Russia support the YPG out of sheer necessity. The group has proven especially adept at battling ISIS and has secured most of the border with Turkey.
As we noted way back in August, it was inevitable that Washington and Ankara would come to blows over the YPG. After all, the US only secured access to Incirlik by acquiescing to Erdogan’s crackdown on the PKK, but some of the missions the US was flying from Turkey’s air base were in support of the YPG. The whole thing was absurd from the very beginning. Well now, Turkey is not only set to use the fight against the YPG as an excuse to intervene in Syria on behalf of the Sunni rebels battling to beat back the Russian and Iranian advance, but Ankara is also demanding that the US recognize the YPG as a terrorist group. If Washington refuses, “measure will be taken.” “If the Unites States is really Turkey’s friend and ally, then they should recognize the PYD — a Syrian branch of the PKK — as a terrorist organization.
If a friend acts as an enemy, then measures should be taken, and they will not be limited to the Incirlik Airbase, Turkey has significant capabilities,” Erdogan advisor Seref Malkoc told Bugun newspaper. So yeah. Turkey just threatened the US. It’s notable that Malkoc specifically said actions would go “beyond Incirlik,” because pulling access to the base would be the first thing any regional observers would expect from Ankara in the event of a spat with Washington. For Turkey to say that measures will go beyond that, opens the door for Erdogan to become openly hostile towards his NATO allies. “The only thing we expect from our U.S. ally is to support Turkey with no ifs or buts,” PM Ahmet Davutoglu told a news conferenceon Saturday. “If 28 Turkish lives have been claimed through a terrorist attack we can only expect them to say any threat against Turkey is a threat against them.”
In other words, Turkey is explicitly asking the US to support Ankara’s push to invade Syria and not only that, Erdogan wants Washington to sanction attacks on the YPG which the US has overtly armed, trained, and funded. “The disagreement over the YPG risks driving a wedge between the NATO allies at a critical point in Syria’s civil war,” Reuters wrote on Saturday. “On Friday, a State Department spokesman told reporters Washington would continue to support organizations in Syria that it could count on in the fight against Islamic State – an apparent reference to the YPG.”
Right. “Washington will continue to support organizations in Syria that it can count on in the fight against Islamic State.” So we suppose that means the US will support Russia. And Iran. And Hezbollah. But most certainly not Turkey, who is the biggest state sponsor of the Islamic State on the face of the planet.

Japan ag works fine, so that should be destroyed.
• TPP, Abe Set To Demolish Japan’s Small Scale Agriculture Model (FT)
It is a source of national angst: why is Japan — culinary superpower and undisputed champion of the Michelin guide — so terrible at exporting food? In 2014, Japan’s food exports were about $5bn. The Netherlands, a country with a fraction of Japan’s population, exported food worth $103bn — with all the delights of sushi, green tea and wagyu beef generating about the same export sales as Edam cheese. For the government of Prime Minister Shinzo Abe, a missed economic opportunity is now colliding with the political imperative to help Japan’s farmers survive the Trans-Pacific Partnership trade deal, which will slash tariffs on ultra-efficient farmers in the US and Australia. The government has set a goal of more than doubling agricultural exports to Y1trn from 2012 to 2020.
Despite an emerging market slowdown that is hurting Japan’s exports overall, this week trade minister Nobuteru Ishihara said there was a chance of hitting the target early. In yen terms, food exports surged by 24.3% to Y599bn last year, even as overall exports rose by a disappointing 3.5%. Masayoshi Honma, professor of agricultural economics at the University of Tokyo, said the reason for low exports is not complicated. “Japanese exports are so low because they’re expensive,” he says. “There’s a huge differential between the Japanese price and the overseas price.” Japan’s obsession with rice production, a longstanding focus on national self-sufficiency in food and the low productivity of its small-scale, highly-subsidised farms all contribute to high prices.
For years, the importance of rural votes to the ruling Liberal Democratic party meant agriculture was sacred, but as the farming population ages — the average farmer is now 70 — it is one area where Mr Abe has proved willing to grasp the nettle on reforms. One of the few measures his government hopes to pass before upper house elections this summer will permit corporate ownership of agricultural land. That is regarded as crucial to allowing more efficient, large-scale agriculture. Mr Honma is cautious about the Y1trn exports target. “It’s not really agricultural exports because it includes marine and processed products,” he says. Most of Japan’s existing agricultural exports are seafood caught by its vast fishing fleet.

And the same goes for France.
• EU-US TTIP Talks Seen By The French Threatening Small Farms (BBG)
For Bruno Dufayet, the latest round of trade talks between the European Union and the U.S. could sound the death knell for France’s small cattle farms. “For a beef farmer in Europe now, the biggest threat is massive imports of U.S. beef produced in feedlots,” said Dufayet, who notes that his 50 beef-cattle farm in south-central France is typical for the country. “The end could be nigh for this type of livestock farm in France.” French farmers and lawmakers fear free-trade talks with the U.S. will pit Europe’s small family operations against intensive American animal farming. Dufayet is a member of French meat lobby Interbev, which hosted senators and members of parliament at a meeting in Paris on Tuesday that finished over beef canapes and red Bordeaux wine.
European farmers would be unable to compete with a “massive opening” of the region’s markets to U.S. operations that handle thousands of animals at a time, the lobby said. The 12th round of negotiations on the Transatlantic Trade Investment Partnership, or TTIP, starts in Brussels on Feb. 22. The contents of any proposed deal are still to be discussed, and there will be no full liberalization for agricultural products, said Daniel Rosario, a spokesman for the EC. The trade concerns come as farmers across France, Europe’s largest agricultural producer, are protesting against plunging prices of everything from pork to milk. The EU needs to protect its family-owned livestock farms based on extensive grazing and beef should be excluded from the talks, Jean-Paul Denanot, a member of the European Parliament and a substitute member on its agriculture committee, said at the Interbev meeting.
“This is a face-off between systems that have nothing in common,” Jean-Pierre Fleury, who heads the beef working group at EU farm lobby Copa-Cogeca. In addition to differences in scale, the EU tracks animals from birth, while U.S. traceability only applies to livestock moving interstate and exempts beef cattle under 18 months. While the EU banned antibiotics as growth promoters in animal feed in 2006, many U.S. states still allow the routine use of the drugs to promote growth in cows, chickens and pigs. There’s also the argument of higher animal welfare standards in the EU than in the U.S., according to the U.S.-based Humane Society International.

The French were ‘only’ some 300% off in their estimates. That tells you something about their priorities.
• Calais ‘Jungle’ Eviction Postponed Because Of Risk To Lone Children (G.)
The forced eviction of thousands of migrants and refugees from the sprawling “Jungle” camp on the outskirts of Calais has been put on hold by the French authorities, the Observer has learned. French courts have postponed Tuesday’s planned eviction after a census conducted by the charity Help Refugees found that far more refugees were living in the area of the camp earmarked for demolition than French authorities had calculated. Researchers for the charity counted 3,455 people living in the southern stretch of the Jungle, which is scheduled to be destroyed. Of these, 445 were children and 315 were without their parents, the youngest was a 10-year-old Afghan boy. By contrast, French authorities had estimated between 800 and 1,000 people were living there.
The eviction has been placed on hold until a judge visits the camp on Tuesday morning to re-assess the situation, with the case being heard in Lille later that afternoon. Under the previous expulsion order, refugees had been ordered to remove their makeshift homes and possessions by 8pm on Tuesday, while camp shops, cafes, churches and mosques would be razed. Josie Naughton, co-founder of Help Refugees, said: “Hopefully it’s all going to be OK. The judge will decide yes or no, so we hope they show compassion. The figures highlight the brutality of destroying these homes before proper child protection schemes have been put in place. These children have post-traumatic stress, you can’t just put them on a bus, they are going to be in danger.”
George Gabriel of Citizens UK, a group involved in the growing campaign calling for children stranded in the jungle to be allowed into the UK said: “It’s great news that the French courts have put the breaks on the demolition of wide sections of the Jungle. Day after day we find more refugee children living in that terrible camp and risking their lives each night as they try to reach their families. “They have a full legal right to do so, and so for as long as the British and French governments refuse to properly implement the law, it’s vital those boys aren’t dispersed away from the legal advice they so badly need.” However Naughton warned that if the judge does decide that the eviction can go ahead as French authorities want, then the bulldozers would arrive at the Jungle on Wednesday morning.

How long does it take to figure this out?
• Razor Wire Fence Fails To Keep Migrants Out Of Hungary (BBC)
Police in Hungary say increasing numbers of migrants are breaching a razor wire fence built to stop them crossing the border from Serbia. In January, 550 people were caught getting through – up from 270 in December. More than 1,200 were caught in the first 20 days of February. Hungary caused controversy with the 4m barrier, completed in September. However, several other countries have since introduced tough border controls to stop the influx of migrants. The number of people crossing from Serbia dropped after Hungary built the fence along the 175km border with its neighbour last year. But police say migrants are now increasingly getting through, mostly by cutting through or climbing over the barrier. Most are from Pakistan, Iran and Morocco, who are no longer admitted through other routes.
It follows moves by Austria, Slovenia, and Balkan countries to limit the nationalities and the numbers of those being allowed through. More than a million people arrived in the EU in 2015, creating Europe’s worst refugee crisis since World War Two. The majority of migrants and refugees have headed for countries like Germany and Sweden via Hungary and Austria after crossing from Turkey to Greece. Many are fleeing the conflict in Syria. Far fewer migrants are entering Hungary than Austria but the sharply increasing trend of people breaching the border fence is alarming the authorities, reports the BBC’s Central Europe correspondent, Nick Thorpe.
More people crossed from Serbia into Hungary in the first 20 days of February than in the same period in 2015, before a fence was even contemplated, our correspondent adds. Once in Hungary, they face criminal charges or deportation. Meanwhile Interior Minister Sandor Pinter has renewed the closure of three railway crossings to Croatia, for fear that migrants and refugees will again start walking down the tracks into Hungary. On Friday Austria introduced a daily cap on the number of migrants and refugees allowed into the country. Just 80 asylum applications will be accepted each day at the country’s southern border, in a move condemned by critics as incompatible with European law.

Oh God almighty… How do we sleep?
• Despite Aegean Rescuers’ Best Efforts, Not All Migrants Are Saved (NPR)
It’s just before midnight on a February night when the crew of the Responder gets word from the Greek coast guard that a boat with migrants aboard is nearby. It’s in trouble somewhere in Greek territorial waters in the Aegean Sea. “There’s a light, a flash,” says Eugenio Miuccio, a 38-year-old Italian doctor, pointing to a flicker in the pitch-black sea. He and an Italian nurse, 27-year-old Roberto Pantaleo, pull on red life jackets as the ship heads toward the light. Iain Brown, a volunteer rescue diver from Scotland, is also ready. He’s listening, trying to make out people’s voices. “We can hear them screaming before we see them,” he says. “The boats they are in are so thin. We can hear them breaking up.” They’re ready to jump into a small speedboat piloted by Dominic “Mimmo” Vella, a 44-year-old father of three from Malta and a member of the Responder’s crew.
“If something happens and people fall in the water,” Vella says, “with the big boat, we cannot go near them, so we go with the small ones.” The Responder arrives where the migrant boat is supposed to be. But there is no boat, no people. Just empty sea. “False alarm,” Brown says. “We found nothing,” Vella says. “So we’re going to keep on patrolling.” The Responder, a 167-ft. search and rescue tug vessel has been patrolling these waters for the past two months. False alarms come with the territory, but the dangers for which the crew remains prepared are real. The boat is leased by a Malta-based nonprofit called the Migrant Offshore Aid Station (MOAS). An American businessman, Christopher Catrambone, and his Italian wife, Regina, started MOAS in early 2014 to help rescue asylum seekers crossing the Mediterranean between Libya and Italy.
Then, last September, 3-year-old Alan Kurdi washed up on a Turkish beach. The Syrian toddler had drowned trying to reach Greece with his family. The image of his lifeless body jolted the world’s empathy. Donations flooded into MOAS. The charity leased the Responder, hired a crew and recruited volunteers. The Responder arrived in the Aegean at the end of December. The two speedboats aboard are named after Alan and his 5-year-old brother, Galip, who also drowned in September. Brown, the diver, heard about MOAS on the news. He’s 51 and volunteers with the Coast Guard back home in Ayr, Scotland. “I couldn’t stand it anymore, sitting at home while kids were drowning here,” he says. “So I [took] time off and came here. I can help. I understand the sea.”
The Responder patrols a stretch of the Aegean Sea between Turkey and the tiny Greek islet of Agathonissi, just south of the larger island of Samos. The distance between Greece and Turkey is relatively short, as close as 8 miles here. But the sea can look deceptively calm to migrants. “They could leave from a sheltered bay,” says MOAS search and rescue operations officer John Hamilton, as he monitors a radar on deck. “Once they get out of this bay, they come across rough seas.” More than 400 people fleeing war and poverty have died or gone missing in the Mediterranean since the beginning of this year, according to the U.N. refugee agency. At least 311 have drowned in the Aegean, according to the International Organization for Migration. The Responder has been backing up the Greek coast guard in the southern Aegean Sea, and has rescued 739 people here so far. And since 2014, MOAS crews have rescued nearly 12,000 people.
But the crew can’t stop thinking about a boat that capsized on January 15. “That night, we got a call that there was a boat,” Vella says. “And when we arrived to where the boat was supposed to be, we didn’t find the boat. But we found the people. They were screaming.” As the boat sank, people hung onto its blue-and-white hull, moaning loudly for help. “It was so cold that night, so very cold,” Vella says. “I prayed there were no kids in the water.” Miuccio, the Italian doctor, did too. He worried about hypothermia. “Children and babies can only stay in such cold water for a few minutes,” he says. A diver jumped into the sea and swam to the people clinging to the hull. “Children? Children?” the diver screamed. “Babies?”
The first baby was a chubby-cheeked little boy, no more than 2-years-old. Miuccio, on the speedboat that night, remembers that the little boy’s face was blue and he was foaming at the mouth. He had no pulse. “I gave him CPR for 15 minutes,” he says. “But nothing worked.” Pantaleo, the nurse, tried to revive another little boy, also to no avail. A third child, a 4-year-old girl, was also found dead. Then two more children, a boy and a girl, arrived — unconscious but with a pulse. “They responded immediately [after] CPR,” Miuccio recalls. “They started crying, which is a good sign. We took off their wet clothes and immediately wrapped them in isothermal blankets.”
[..] The morning after the three children died in January, Mimmo Vella called his own kids back in Malta. He told them he loved them so much. He told them they were lucky to be safe at home. As MOAS begins yet another patrol, he calls them again. His youngest son’s tiny voice rises above the wind and the waves.