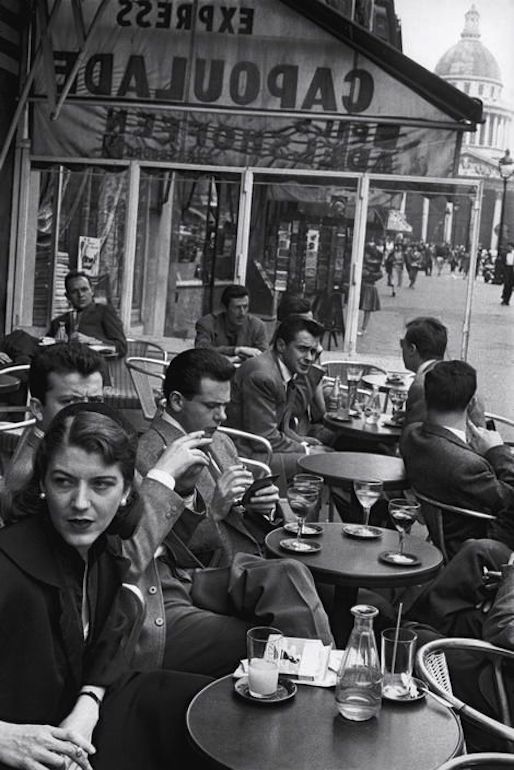
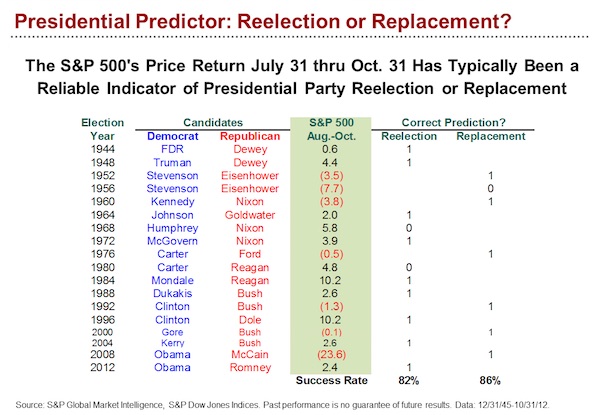
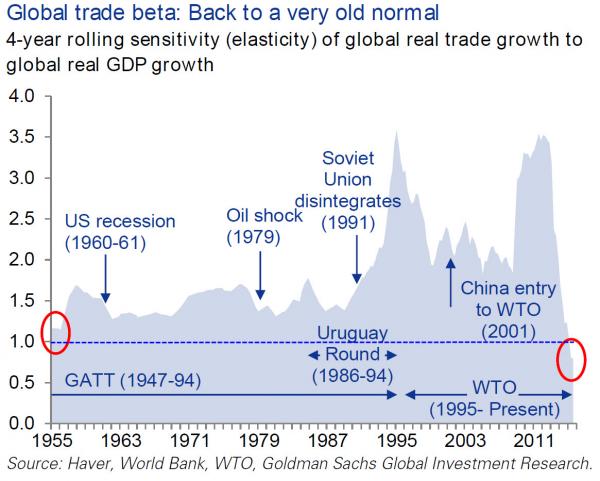
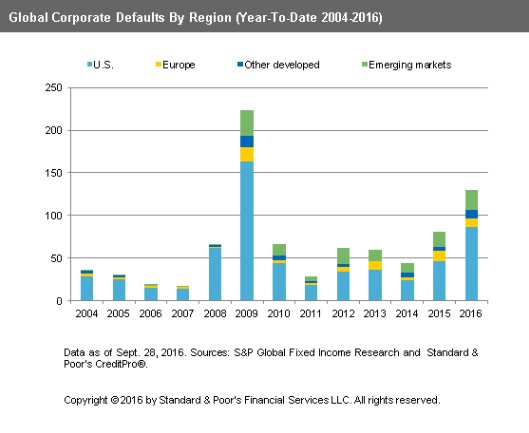
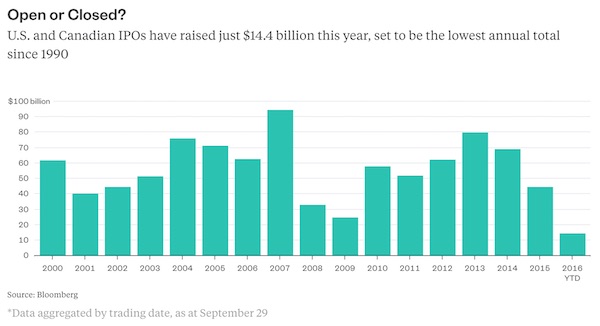
Inge Morath Paris 1954

After having milked the bubble for all it’s worth…
• Australia Hedge Fund Returns Cash To Clients Citing Looming Calamity (SMH)
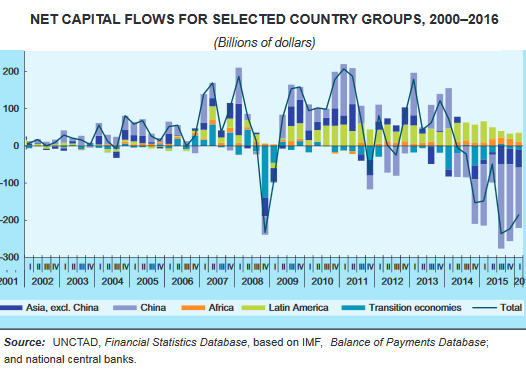
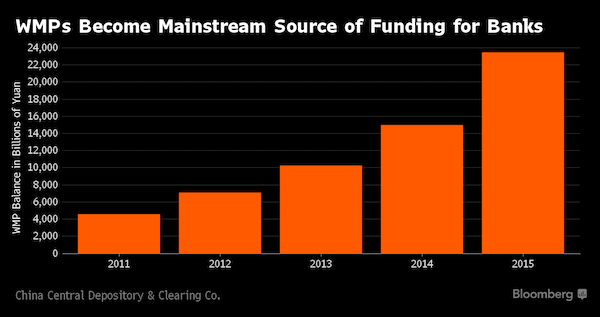
Australian asset manager Altair Asset Management has made the extraordinary decision to liquidate its Australian shares funds and return “hundreds of millions” of dollars back to its clients, citing an impending property market “calamity” and the “overvalued and dangerous time in this cycle”. “Giving up management and performance fees and handing back cash from investments managed by us is a seminal decision, however preserving client’s assets is what all fund managers should put before their own interests,” Philip Parker, who serves as Altair’s chairman and chief investment officer, said in a statement on Monday. The 30-year veteran of funds management said that he had on May 15 advised all Altair clients that he planned to “sell all the underlying shares in the Altair unit trusts and to then hand back the cash to those same managed fund investors”.
Mr Parker said he had “disbanded the team for time being”, including his investment committee of chief economist Steve Roberts, senior healthcare analyst Sally Warneford and independent strategist Gerard Minack. “I would like to make clear this is not a winding up of Altair, but a decision to hand back client monies out of equities which I deem to be far too risky at this point,” Mr Parker’s statement said. “We think that there is too much risk in this market at the moment, we think it’s crazy,” Mr Parker said more candidly. “Valuations are stretched, property is massively overstretched and most of the companies that we follow are at our one-year rolling returns targets – and that’s after we’ve ticked them up over the past year.” “Now we are asking ‘is there any more juice in these companies valuations?’ and the answer is stridently, and with very few exceptions, ‘no there isn’t’.”
Mr Parker outlined a roll call of “the more obvious reasons to exit the riskier asset markets of shares and property”. They included: the Australian east-coast property market “bubble” and its “impending correction”; worries that issues around China’s hot property sector and escalating debt levels will blow up “later this year”; “oversized” geopolitical risks and an “unpredictable” US political environment; and the “overvalued” Aussie equity market. But it was the overheated local property market that was the clearest and most present danger, Mr Parker said. “When you speak to people candidly in the banks, they’ll tell you very specifically that they are extraordinarily worried about the over-leverage of the Australian population in general,” he said.

More looming calamity.
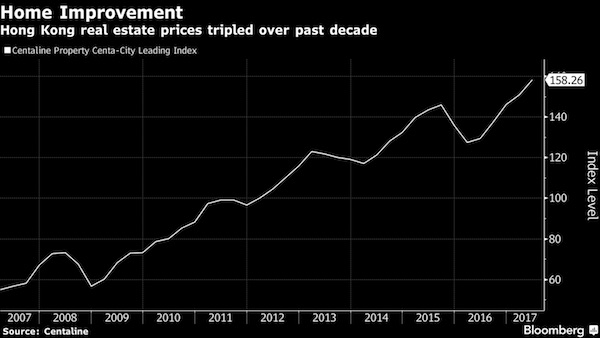
• Hong Kong Throngs of Thousands Defy Bid to Cool Home Market (BBG)
Snaking queues of thousands of prospective apartment buyers in Hong Kong signaled authorities have made no progress in cooling a red-hot property market, where prices are at records. People were lining up on Friday and over the weekend at Victoria Skye, a luxury project at the former airport site of Kai Tak, and at the Ocean Pride development by Cheung Kong Property and MTR. “Successive moves by the government in recent memory to cool the property market only resulted in it becoming crazier,” The Standard newspaper said in an editorial on Monday. “The result is a sea of madness.” The Hong Kong Monetary Authority has been tightening rules for lenders, including restricting levels of lending to developers, as it tries to limit financial risks and take some of the heat out of the market.
The Centaline Property Centa-City Leading Index of existing homes has advanced 23% in the past year, setting new price records week after week. At a Legislative Council meeting on Monday, HKMA Chief Executive Norman Chan said levels of demand were reminiscent of 20 years ago – before Hong Kong suffered a property bust – and he expressed concern that people with limited financial resources were buying just because they thought prices would only keep going up. [..] Developers sold 8,616 homes in the first five months of the year, already more than were sold in any first half since new purchasing rules were introduced in 2013, the Hong Kong Economic Times reported. K&K Property has offered an additional 200 units at Victoria Skye after it sold 306 flats on Saturday, Ming Pao newspaper reported. Cheung Kong will put another 346 up for grabs after selling 496 in a single day, May 26.

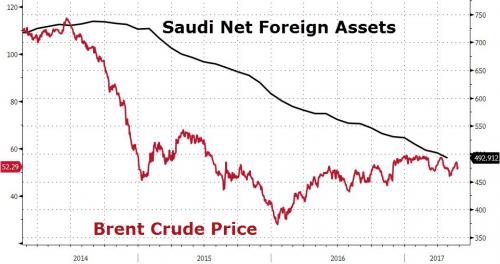
Buying too many weapons. The House of Saud is nervous.
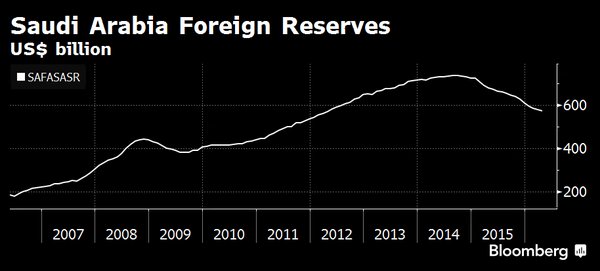
• Saudi Foreign Reserves Dip Below $500 Billion in April (BBG)
Saudi Arabia’s net foreign assets dropped below $500 billion in April for the first time since 2011 even after the kingdom raised $9 billion from its first international sale of Islamic bonds. The Saudi Arabian Monetary Authority, as the central bank is known, said on Sunday its net foreign assets fell by $8.5 billion from the previous month to about $493 billion, the lowest level since 2011. That brings the decline this year to $36 billion. “Didn’t really see any major driver for such a huge drop, especially when accounting for the sukuk sale,” said Mohamed Abu Basha at EFG-Hermes, an investment bank. Even if the proceeds from the sale weren’t included, “the reserve decline remains huge,” he said.
Saudi Arabia’s foreign reserves have dropped from a peak of more than $730 billion in 2014 after the plunge in oil prices, prompting the IMF to warn that the kingdom may run out of financial assets needed to support spending within five years. Authorities have since embarked on an unprecedented plan to overhaul the economy and repair public finances. But the pace of the decline in reserves this year has puzzled economists who see little evidence of increased government spending, fueling speculation it’s triggered by capital flight and the costs of the kingdom’s war in Yemen. Finance Minister Mohammed Al-Jadaan said in April that the government didn’t withdraw from its central bank reserves during the first quarter. He said the decline could be attributed to local contractors paying overseas vendors after the government settled its arrears.

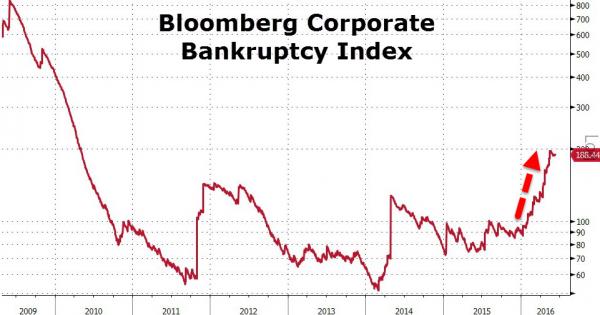
It’s not (just) the shale companies, it’s their lenders who are in danger.
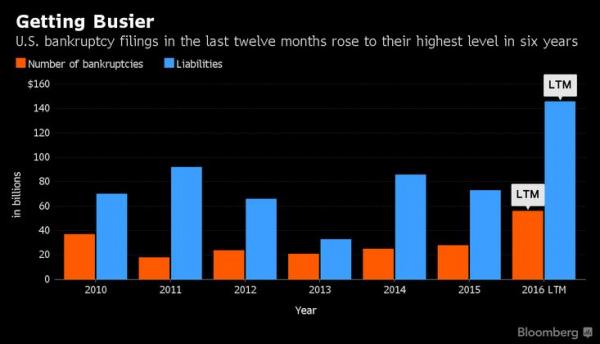
• The Great US Energy Debt Wall (SRSRocco)
While the U.S. oil and gas industry struggles to stay alive as it produces energy at low prices, there’s another huge problem just waiting around the corner. Yes, it’s true… the worst is yet to come for an industry that was supposed to make the United States, energy independent. So, grab your popcorn and watch as the U.S. oil and gas industry gets ready to hit the GREAT ENERGY DEBT WALL. So, what is this “Debt Wall?” It’s the ever-increasing amount of debt that the U.S. oil and gas industry will need to pay back each year. Unfortunately, many misguided Americans thought these energy companies were making money hand over fist when the price of oil was above $100 from 2011 to the middle of 2014. They weren’t. Instead, they racked up a great deal of debt as they spent more money drilling for oil than the cash they received from operations.
As they continued to borrow more money than they made, the oil and gas companies pushed back the day of reckoning as far as they could. However, that day is approaching… and fast. According to the data by Bloomberg, the amount of bonds below investment grade the U.S. energy companies need to pay back each year will surge to approximately $70 billion in 2017, up from $30 billion in 2016. That’s just the beginning…. it gets even worse each passing year. As we can see, the outstanding debt (in bonds) will jump to $110 billion in 2018, $155 billion in 2019, and then skyrocket to $230 billion in 2020. This is extremely bad news because it takes oil profits to pay down debt. Right now, very few oil and gas companies are making decent profits or free cash flow. Those that are, have been cutting their capital expenditures substantially in order to turn negative free cash flow into positive.
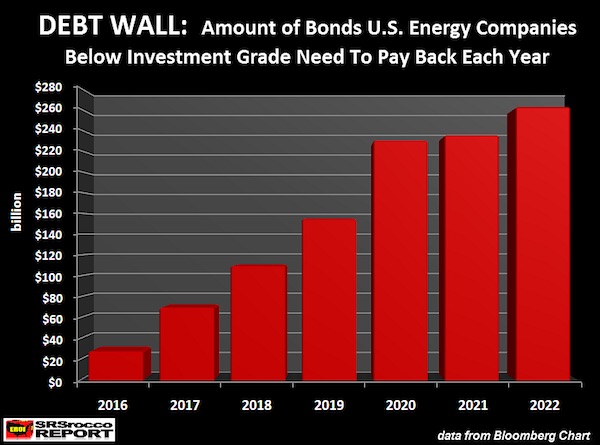
Unfortunately, it still won’t be enough… not by a long-shot. If we use some simple math, we can plainly see the U.S. oil industry will never be able to pay back the majority of its debt: Shale Oil Production, Cost & Profit Estimates For 2018 • REVENUE = 5 million barrels per day shale oil production x 365 days x $50 a barrel = $91 billion. • EST. PROFIT = 5 million barrels per day shale oil production x 365 days x $10 a barrel = $18 billion. If these shale oil companies do actually produce 5 million barrels of oil per day in 2018, and were able to make a $10 profit (not likely), that would net them $18 billion. However, according to the Bloomberg data, these companies would need to pay back $110 billion in debt (bonds) in 2018. If they would use all their free cash flow profits to pay back this debt, they would still owe $92 billion.

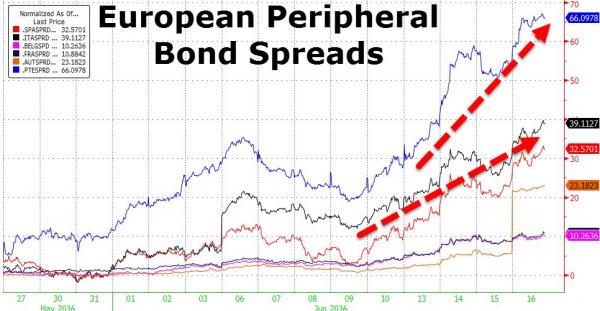
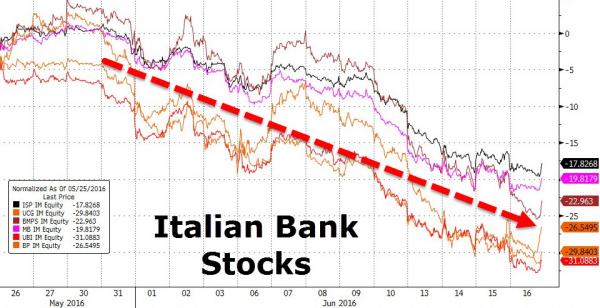
BILD says Greeks have mentioned defaulting on July payments.
• Greece, Italy Tensions Hit Euro, Asian Stocks, Lift Yen, Gold (R.)
Concerns about a Greek bailout, early Italian elections and comments by the ECB chief about the need for continued stimulus all kept the euro under pressure on Tuesday. European geopolitical fears sapped risk appetite, weighing on Asian stocks and lifting safe havens including the yen and gold, though trading was thin with several markets closed for holidays. The euro slid 0.3% to $1.1129 in its fourth session of declines. James Woods at Rivkin Securities in Sydney attributed most of the currency’s decline on Tuesday to a German press report saying Athens may opt out of its next bailout payment if creditors cannot strike a debt relief deal. “The bailout payments are necessary to meet existing debt repayments due in July, so if Greece were to forgo this bailout payment the probability of a default would spike, reopening the discussion around a Grexit from the Euro zone,” Woods said.
However, he cautioned against reading “too much into it” without more details or confirmation, adding it was unlikely Greece would forego the bailout payment at this stage. Euro zone finance ministers failed to agree with the International Monetary Fund on Greek debt relief or to release new loans to Athens last week, but did come close enough to aim to do both at their June meeting. Comments by former Italian Prime Minister Matteo Renzi on Sunday in favour of holding an election at the same time as Germany’s in September also pulled the euro lower. So did a statement by ECB President Mario Draghi reiterating the need for “substantial” stimulus given subdued inflation.

If he includes Greece, it becomes harder for Germany to plunder it. And they’re not done with that.
• Draghi Rules Out Including Greece in ECB QE For Now (K.)
ECB chief Mario Draghi took the wind out of the government’s sails on Monday, telling the European Parliament that the ECB will not consider including Greece in its QE program before the conclusion of its bailout review and its debt is made sustainable. “First, let’s have an agreement, a full agreement, and let’s find measures that will make the debt sustainable through time,” Draghi told European lawmakers in Brussels, adding that he regretted that “a clear definition of the debt measures was not reached in the last Eurogroup.” Draghi also said that after creditors agree on what sort of debt relief measures Greece will get, the Governing Council of the ECB will carry out its own “fully independent” analysis to see if the debt would also be sustainable in adverse scenarios.
His comments came as Prime Minister Alexis Tsipras said that Greece was hoping that there will be an initiative in June for “a definitive settlement of the crisis through a clear solution of reducing the debt.” “Let there be a solution and let it come when it comes,” he said after his meeting in Athens with Estonian Prime Minister Juri Ratas, adding that the sooner the matter is solved the better. The tough road ahead for Greece was reflected in remarks yesterday by Finance Minister Euclid Tsakalotos, who said the country’s inclusion in QE is indeed “a difficult issue.” “The ECB, like our Lord, works in mysterious ways,” he told reporters. Draghi’s remarks were seen as another another blow, if not the killer, to the government’s narrative regarding the time frame it had laid out for the country to get on the road to economic recovery.
More specifically, Prime Minister Alexis Tsipras’s roadmap stipulated that after the second review of the country’s third bailout is wrapped up, creditors and the IMF would agree on how to make the country’s debt sustainable, and this would in turn allow Greece join the QE program, which would pave the way for the country’s return to international markets. But with the review all but concluded, and no definitive statements from the creditors on what sort of debt relief measures it can expect – or when – the best the government can hope for now is that the sequence of events outlined in the Tsipras roadmap will take place in the fall at the earliest, and definitely after the German national elections in September. The way things stand now, the most the government can expect from the June 15 Eurogroup is the release of the bailout tranche of more than €7 billion, but not the reassurance it wants in order to join the QE program.

That’s exactly why these deals keep on being blocked. The EU doesn’t want a Greek recovery. Cart, horse.
• Greece Warns Recovery Threatened If Debt Deal Is Blocked At Next Talks (G.)
Greece on Monday issued a panic warning that its recovery would be thrown into doubt if Brussels blocked a debt deal at the next meeting of euro area finance ministers. Fearing that Germany will insist on delays to an agreement until at least after elections in September, Athens’ finance minister hinted that the beleaguered nation could be plunged deeper into recession after seeing its economy contract by more than 25% since the start of its financial crisis. With £7.5bn in debt repayments due in July and lenders meeting on 15 June to try and reach an agreement after failing last month, Euclid Tsakalotos made an urgent appeal for clarity on Monday. “It is incumbent on all sides to find a solution,” he told foreign correspondents. “There is very little point in entering a [bailout] programme if the goal is not to leave the programme. And leaving the programme should be the responsibility not just of the debt country but the creditor country as well.”
Athens, Tsakalotos continued, had kept its side of the bargain, legislating highly unpopular reforms to produce savings of 2% of GDP, while the EU and IMF had not kept theirs. “We can’t accept a deal which is not what was on the table,” he said. “What was on the table was if Greece carried outs its reform package then creditors would ensure that there would be a clear runway through clarity for debt.” Instead, the IMF had refused to endorse the proposed solution – saying it fell far short of what was necessary to engender debt sustainability – with the result that Athens had been forced to reject it, Tsakalotos added. The Fund and Berlin – the biggest contributor of Greece’s three rescue programs – have long been in disagreement over how to reduce Greek debt.
Tsakalotos was addressing a hastily arranged press conference. Held in the dining room of the Athens’ mansion that houses the prime minister’s office, it appeared to highlight the mood of nervousness pervading the Greek government. With a debt mountain hovering around €314bn – or 180% of GDP – the Syriza-dominated coalition of Alexis Tsipras has long argued that debt relief is essential to foreign investment and economic recovery. [..] ..time, said Tsakalotos on Monday, was running out. “Our ask is … that everyone keeps their side of the bargain. The position [of creditors] is going to be very difficult to defend. What can they say? That the Greek government did everything but we will send it to the rocks.”

Which will affect Greek banks, which will affect the state, etc etc. There never was another option.
• Deposits And Loans At Greek Banks Continue Slide (K.)
Deposits in Greek banks declined by more than €2.4 billion in the first four months of the year, while credit contraction has continued in 2017 for an eighth consecutive year. Still, April was the second month of credit expansion. The sum of Greek deposits reached almost €118.9 billion at the end of last month, down from about €121.4 billion at end-December 2016, due to the uncertainty that has prevailed over the Greek economy this year. Bank of Greece data show a fresh €313.3 million drop in deposits from end-March to end-April – a result of the €665.3 million decline in the cash flow of corporations, from nearly €20.5 billion in March to almost €19.8 billion last month. In fact the picture of corporate deposits in April looks technically better than it would had it not been for the €620 million share capital increase by Fraport Greece and Sklavenitis’s €400 million bond.
The level of savings has practically reverted to what it was in 2001, when Greece was still using the drachma, and forecasts speak of a stable picture with few fluctuations expected in the rest of 2017. Senior bank officials say the next few months will be difficult despite the projections for more revenues from tourism: The tax obligations starting from July, with income tax and later Single Property Tax (ENFIA) deadlines, are expected to eat further into the savings of households and corporations’ cash flow. Meanwhile the difference between loans issued and old loans paid back has remained in negative territory in 2017, reaching a rate of -0.9% in the first four months. However, April showed a positive flow amounting to €659 million after an expansion of €307 million in March.

Yeah, they’re going to risk bankrupting German and French carmakers, right?
• EU Moves To Crack Down On Carmakers In Wake Of VW Emissions Scandal (G.)
The European Union has moved towards cracking down on carmakers who cheat emissions tests by giving the EU executive more powers to monitor testing and impose fines. The European council overcame initial objections from Germany and agreed to try to reform the system for approving vehicles in Europe in the wake of the Volkswagen emissions scandal. The draft now goes for negotiations with the European commission and the European parliament, where the car industry holds a strong influence. “Above all, the objective is building trust and credibility again in the European type-approval system,” said Chris Cardona, the economy minister of Malta, which holds the EU’s six-month rotating presidency.
The VW emissions scandal erupted in September 2015, with the carmaker admitting it had installed software defeat devices in 11m diesel cars worldwide, meaning the vehicles only cut their nitrogen oxide pollution during certification tests. The draft EU rules call for reducing the power of national authorities and empowering the European commission to test and inspect vehicles, to ensure compliance with emissions standards, and to respond to any irregularities. “This will increase the independence and quality of the EU type-approval system,” the council said in a statement. “The commission could also impose fines for infringements on manufacturers and importers of up to €30,000 [£26,000] per noncompliant vehicle.” Under the draft rules, every EU country will be required to check emissions in one in every 50,000 new vehicles based on real driving conditions.

The EU comes prepared.
• Painstaking Detail Of Brexit Process Revealed In EU Documents (G.)
Just 10 days before the general election, the EU published two documents that will affect every person living in Britain for years to come. Despite being dropped into the maelstrom of an election caused by Brexit, there was hardly a murmur. The documents were the most detailed positions yet from the EU’s chief negotiator, Michel Barnier, on the upcoming divorce talks with the UK. In two policy papers, the bloc has elaborated its stance on the Brexit bill and citizens’ rights. [..] The muted reaction can be explained partly by the fact that the texts were published with zero fanfare, when the country was still reeling from the terrorist atrocity in Manchester. Furthermore, the EU documents contain no surprises. The equivalent of dotting the Is and crossing the Ts, they are a reminder the EU has had 11 months to get ready for Brexit.
That is almost one year to assemble squadrons of specialists to pore over EU treaties and legal tomes to map the way ahead. The 10-page paper on the bill does not put a price on the divorce, but sets out in painstaking detail all EU bodies with a vested interest in the spoils – 40 agencies, eight joint projects on new technologies and a panoply of funds agreed by all countries, from aid for refugees in Turkey to supporting peace in Colombia. No detail is too small. Britain is even on the hook for funding teachers at the elite European schools that educate EU civil servants’ children. On citizens’ rights, the EU spells out in greater detail the protections it wants to secure for nearly 5 million people on the wrong side of Brexit – 3.5 million EU nationals in the UK and 1.2 million Britons on the continent.

Fear is all they have left. Blunt lies about Corbyn.
• May Battles Against Complacency as UK Election Lead Slips Away (BBG)
Theresa May began the U.K. election campaign warning that pollsters giving her a 20-point lead could be wrong. With her lead now slashed, she’s hoping they really are. A series of missteps by May and her advisers, along with a populist Labour campaign, have put the prime minister on the defensive. Activists no longer laugh when she raises the prospect of a Corbyn victory at her rallies and some have questioned the wisdom of building a campaign around her own personal brand, urging people to vote for “Theresa May and her team.” Investors have awoken to the fact that May’s promise of “strong and stable” government — never mind a landslide to match Tony Blair’s in 1997 — could be in jeopardy with the pound dipping after a specific poll showed May’s Conservative Party leading the Labour Party by just five points.
“The Tories are right to be worried if the momentum looks to be with Labour, but they can still turn it around,” Andrew Hawkins, chairman of pollsters ComRes, said in a telephone interview. With a nation still in shock over the Manchester bombing and June 8 elections round the corner, May got back to the campaign trail and reverted to her tested lines on Brexit: That Labour leader Jeremy Corbyn cannot be trusted to navigate Britain through two years of talks. “It’s important as people come closer to that vote – that’s only next week – that they focus on the choice that’s there before them,” the prime minister told activists at a rally in Twickenham, southwest London, on Monday. “If I lose just six seats my government loses its majority, that could mean in 10 days time a government in chaos with Jeremy Corbyn in Number 10.”
But gone was the confidence when she stunned Britain by calling a snap election on April 18. On the day of the announcement, an ICM/Guardian poll gave May’s Tories a lead over Labour of 21 points and surveys in the following weekend’s newspapers suggested leads of 24 and 25 points. Now, she is vulnerable to attack. Interviewer Jeremy Paxman quizzed May about her U-turns, in an interview on Sky News on Monday: “You have backed down over social care, and over national insurance. If I was in Brussels, I would think you are a blowhard who collapses at the first sign of gunfire.” Her rival on the other hand has grown more relaxed, holding his own against the same interviewer who has a reputation for being a rottweiler in his style of questioning. In one instance, Corbyn won a big round of applause when asked about whether he’d want to abolish monarchy: “Do you know what? I had a very nice chat with the Queen.”

US room to move gets smaller fast.
• Russia Expects China To Help Resolve Syrian Crisis (DS)
Moscow hopes for China’s help in solving the Syrian crisis and restoring the country, Russian Deputy Foreign Minister Igor Morgulov said Monday. “Our cooperation with China on Syria at various international venues is unprecedented. We blocked six attempts to pass anti-Syrian resolutions in the U.N. Security Council,” Morgulov said at “Russia and China: Taking on a New Quality of Bilateral Relations” international conference. The Russian deputy foreign minister added that Russia values Beijing’s position on the Syrian crisis, and hopes that, “the Chinese partners will continue their efforts to promote a political settlement.”
“Together we call for a peaceful and political-diplomatic solution to conflicts, without double standards, unilateral action or attempts at ousting regimes. Our approaches coincide, among other things, on the uncompromising fight against terrorism,” Morgulov said. Russia and China have repeatedly vetoed U.N. Security Council resolutions imposing sanctions against the Assad regime. Moscow has long-standing links to the Assad regime and is its key ally, while China has an established policy of non-intervention in other countries’ affairs.

French interests in Russia are substantial. Macron going after RT and Sputnik is a weird way to not offend Merkel.
• Putin, Macron Have ‘Open, Frank Exchange Of Opinions’ (RT)
Russian President Vladimir Putin and his French counterpart, Emmanuel Macron, had “difficult” but “frank” talks during their first meeting in Versailles. The two leaders vowed to improve relations and jointly address international problems. The first meeting of the Russian and French leaders lasted almost three hours, with Macron saying that “Franco-Russian friendship” was at the heart of the talks. The French president admitted, however, that he has “some disagreements” with his Russian counterpart, but said that the two leaders discussed them openly in a “frank exchange of views.” Putin also said that the two leaders have some differences, but said that they view many issues in a similar way, and that French-Russian relations could be “qualitatively” improved. “We sought … common ground [in dealing] with key issues of the international agenda. And I believe that we see it. We are able to … at least try to start resolving the key contemporary problems together,” Putin said.
The Russian leader went on to say that his talks with Macron helped the pair to find common points in dealing with major international problems, and the that two sides would try to further bring together their views on these issues. Putin also invited his French counterpart to Russia, saying: “I hope that he will be able to spend several weeks in Moscow.” French President Macron said that serious international problems cannot be resolved without Moscow, as he stressed the importance of the role Russia plays in the modern world. “No major problem in the world can be solved without Russia,” he told the press conference. Macron then said that France is interested in intensifying cooperation with Russia, particularly in resolving the Syrian crisis. The French leader went on to say that this issue demands “an inclusive political solution.”

Pretty brilliant. Much more at the link.
• Let’s All Agree To Lock In This Russophobia For At Least 3.5 More Years (Saker)
There I was again, flying first class on my shareholders’ dime from New York to San Francisco, when I was deeply saddened to read about the death of Zbigniew Brzezinski, National Security Adviser to Jimmy Carter. For a moment I thought: “Surely I can find some anti-Putin articles to read rather than this one?” Those always make me so happy! But then I remembered that Zbig was a man after my own heart, because he was one of the West’s greatest Russophobes. Even the New York Times talked of his “rigid hatred of the Soviet Union”. Zbig ended the détente led by Nixon as Carter, not Reagan, restarted good, old-fashioned, American Russophobia: Selling the Soviets computers with bugs for industrial sabotage, the propaganda effort of the 1980 Olympic Boycott, the US grain embargo to try and starve the Russian people, the arming of the Taliban’s forerunners to destabilize a left-wing government in Afghanistan and thus unleashing Islamic terrorism on the world, etc.
Just as American Democrats know for an undeniable fact that Jimmy Carter is our nation’s greatest living man of peace, I contend that Zbig’s anti-Russian stance makes him nearly as great a humanitarian, and certainly a model Democrat in 2017. And Zbig knew, as I and all good Democrats know, that the greatest fight of our generation is the fight against Vladimir Putin. Poverty, starvation, refugees, terrorism, climate change – everyone in America is realizing that if we can just get rid of Putin, everything else will surely fall into line. Surely! So I was pretty sad to read of Zbig’s passing, but that’s when it hit me: Just because he’s gone, it doesn’t mean we have to give up hating Russia! We’ve been hating Russia since November – more than 6 months now – and, frankly…it feels awesome! I don’t how long it takes to make a habit permanent, so let’s all agree to lock in this Russophobia for at least 3.5 more years, possibly 7.5!
It would be a fitting testament to a man whose prophetic Russophobia was misunderstood as “anti-communism”. Say it loud: It’s time for progressive Americans to unite behind hating Russians! Again! Let’s party like it’s 1979! Now, I’m as politically-correct a CEO as was ever made -my allegiance to Hillary proves that – but I can tell that some people think that I should equivocate by writing “hating the Russian government” instead of the “Russians”. Well, it’s bold, but being bold is why we CEOs deserve the big bucks and you deserve our crumbs. Not our table crumbs – those are too good for you – I mean the crumbs that fall around our fine, Italian shoes. Here’s the problem with the Russians: Putin’s approval rating is over 85%. It is a testament to the master of evil that he has duped nearly all 144 million Russian citizens. They said that 50 million Elvis fans can’t be wrong, but 124 million Putin fans clearly are. I don’t know anything about Russian domestic politics, but I don’t have to – that’s my right as an American.

Hillary posing as the resistance says it all. They don’t even have a narrative left.
• The So-Called Resistance (Jim Kunstler)
[..] what would a real resistance look like? First, it would oppose the aforementioned asset-stripping that the US economy has become, the transfer of capital in all its forms — monetary, political, cultural, social — from the dis-employed former middle classes to the tiny, select beneficiaries of financial manipulation. Note that the things being manipulated — markets, currencies, securities, and interest rates — are increasingly phantom entities that appear to maintain their value only because the high priests of financial authority say that they do. The shelf-life of that flim-flam approaches its endgame as it self-evidently immiserates the masses and their sheer faith in its recondite promises dwindles away to nothing.
A genuine resistance would begin to deconstruct this clerisy and its institutions, namely Too Big To Fail banks and the Federal Reserve. The best opportunity to accomplish that would have been the early months of Mr. Obama’s turn in the White House, the dark time of the previous financial crash when the damage was fresh and obvious. But the former president blew that under the influence of high priests Robert Rubin and Larry Summers. And the lower order clerics were allowed run their hoodoo machine flat out in the following eight years. Just look at the long chart of the Standard & Poors index. Tragically, this ever-upward arc is now taken to be the normal state of things, and when it fails the implosion will be orders of magnitude more violent than the last time.
One would think that a genuine resistance would also oppose the growing consolidation of power in the now-colossal spying apparatus of the nation — the often averred to “seventeen intel agencies” that show signs of being actively at war against other parts of the government and against citizens themselves. Hence, the non-stop murmur of allegation about “Russian interference in the election,” going back to the summer of 2016 without either any real evidence, or any clarification of what is actually alleged to have happened. Another tragic turn is that this fifth column of rogue intel agencies has recruited the major organs of the news to incessantly repeat its allegations until the public accepts the story as established fact rather than just the manufactured story it so far appears to be. Well, the lives of persons and societies founder on versions of the “reality” they fabricate for their own purposes. A genuine resistance would show foremost some fidelity to a reality beyond the spin-factories of self-delusion.

Election coming up, perhaps?
• Germany Steps Up Attack On Trump For ‘Weakening’ The West (G.)
Germany has unleashed a volley of criticism against Donald Trump, slamming his “short-sighted” policies that have “weakened the west” and hurt European interests. The sharp words from foreign minister Sigmar Gabriel came after the US president concluded his first official tour abroad taking in Saudi Arabia, Israel, Brussels and then Italy for a G7 summit. Angela Merkel warned on Sunday that the US and Britain may no longer be completely reliable partners. Germany’s exasperation was laid bare after the G7 summit, which wrapped up on Saturday with Trump refusing to affirm US support for the 2015 Paris climate accord. Days earlier, in Saudi Arabia, Trump presided over the single largest US arms deal in American history, worth $110bn over the next decade and including ships, tanks and anti-missile systems.
Gabriel said on Monday that “anyone who accelerates climate change by weakening environmental protection, who sells more weapons in conflict zones and who does not want to politically resolve religious conflicts is putting peace in Europe at risk”. “The short-sighted policies of the American government stand against the interests of the European Union,” he said, judging that “the west has become smaller, at least it has become weaker”. “We Europeans must fight for more climate protection, fewer weapons and against religious [fanaticism], otherwise the Middle East and Africa will be further destabilised,” Gabriel said. [..] The relationship between Merkel and Trump contrasts with the warm ties between herself and Barack Obama. The previous US president last week travelled to Berlin to attend a key Protestant conference. Obama’s participation in a forum with Merkel last Thursday came hours before her meeting with Trump in Brussels at the Nato summit.

Right, election coming up. Which trumps human rights and international law.
• Greece, Germany Agree To Slow Refugee Family Reunification (F24)
Greece and Germany have agreed to slow the reunification of refugee families divided between the two nations during their scramble to safety, according to a leaked letter published Monday. “Family reunification transfer to Germany will slow down as agreed,” Greek Migration Minister Yiannis Mouzalas wrote to German Interior Minister Thomas de Maiziere in a May 4 letter obtained by leftist daily Efimerida ton Syntakton. The Greek migration ministry declined to comment, but earlier this month Mouzalas said the slowdown was due to “technical difficulties.” In the letter, Mouzalas reportedly acknowledges that the move – enacted because of the sheer volume of asylum requests – will affect “more than two thousand people” while some “will have to wait for years” to reach Germany even though their requests have been approved.
Asylum seekers – mostly Syrian refugees in Greece’s case – are entitled to join family members elsewhere in the European Union within six months from the date their request is approved. In his letter, Mouzalas said Berlin and Athens had to agree on a “common line” to address “increasingly desperate and critical comments” so that Athens is not blamed for the delays. He then suggests a joint response: “We understand that asylum seekers are eager to meet with their family, but given that both Greece and Germany have very large asylum seeking populations, delays are inevitable.” Ulla Jelpke, a deputy of German far-left Party Die Linke, earlier this month said Berlin had capped the number of refugees eligible for reunification at 70 people per month. Accordingly, Efimerida ton Syntakton said there were just 70 transfers in April compared to 540 in March and 370 in February.