Marjory Collins “Crowds at Pennsylvania Station, New York” Aug 1942



The economy allgedly grows at 7%, and official inflation is 1.4%?
• China Inflation Eases To Five-Year Low (BBC)
Inflation in China eased to a five-year low in November, suggesting continued weakness in the Asian economic giant. The inflation rate fell to 1.4% in November from 1.6% in October, which is the lowest since November 2009. The reading was also below market expectations of a 1.6% rise. Producer prices, which have been entrenched in deflation, also fell more than forecast, down 2.7% from a year ago – marking a 33rd consecutive monthly decline. Economists had predicted a fall of 2.4% after drop of 2.2% in the previous month as a cooling property market led to slowing demand for industrial goods. The figures are the latest in a string of government data that showed a deeper-than-expected slowdown in the Chinese economy.
Dariusz Kowalczyk, an economist at Credit Agricole, said the data partly reflected low commodity and food prices but also confirmed softness in domestic demand. “It will likely convince policymakers to ease their policy stance further and we continue to expect a RRR (bank reserve requirement ratio) cut in the near term, most likely this month,” he told Reuters. Last month, the country’s central bank unexpectedly cut interest rates for the first time in more than two years to spur activity. In reaction to the data, Chinese shares continued their downward trend after the Shanghai Composite fell more than 5% on Tuesday.

“On both prior occasions of such a maniacal surge in speculative accounts, the Shanghai Composite made a significant top and fell dramatically in the ensuing months.”
• Popping The Chinese Stock Market Mania (Zero Hedge)
If you are wondering what triggered the PBOC to pull the punchbowl of leveraged collateral away from the ‘wealth-creating’ stock market exuberance in China… wonder no more. The last 2 weeks saw the biggest surge in new Chinese brokerage accounts ever, with this week alone the highest since October 2010 and January 2008 with a stunning 228,000 new accounts opened. On both prior occasions of such a maniacal surge in speculative accounts, the Shanghai Composite made a significant top and fell dramatically in the ensuing months.
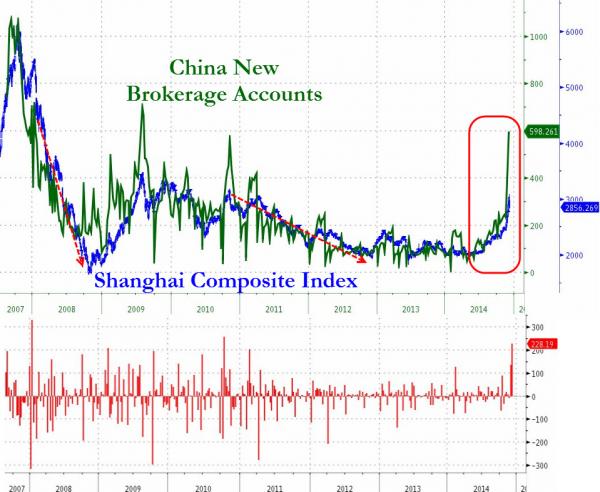
How oddly dis-similar the PBOC is to the Fed!! Instead of encouraging open leveraged speculation, the central bank of China appears more risk averse, recognizing the potential medium-term disastrous consequences from such boom-bust moves (and likely has no cheer-leading CNBC channel to take care of).

Oh boy: “Some might already be regretting taking those risks [..] Especially those who might have pledged their property to get in on the rally and offset the slide in house prices.”
• Easy Credit Feeds Risky Margin Trades In Chinese Stocks (Reuters)
“High leverage, low thresholds!” the website says. “(China’s) A shares are heating up; if you don’t allocate capital now, then when?” Many, it appears, are choosing now, gorging on cheap credit to ride a wild stock market rally. The website, Jinfuzi.com, will let investors borrow up to 10 times their principal with only 2,000 yuan ($323) down in order to buy stocks and futures. The peer-to-peer lender has an easy sell; Chinese benchmark indexes have posted record-smashing trading volumes in recent weeks, with average share values up over 30% in just 12 trading days. Ordinary investors, who conduct 60-80% of China’s stock trades, charged into the market after a surprise interest rate cut by Beijing on Nov. 21, and brokerages and shadow bankers have rushed in to help them trade on margin – essentially borrowed money.
“Margin trading has clearly played a big role in the recent rally, and government is worried,” wrote Oliver Barron of NSBO in a research note on Tuesday, estimating that gross margin trading purchases accounted for 164 billion yuan ($26.5 billion) on Monday, the equivalent of 17% of total turnover on Chinese bourses. There has been a steady relaxation of restrictions on margin trading in the last two years, and while in good times it allows investors to make a lot of money with only a small amount of their own cash, it also carries big risks when the market falls.
Some might already be regretting taking those risks after the Shanghai Composite Index lost over 5% on Tuesday, its largest single-day drop in five years. Especially those who might have pledged their property to get in on the rally and offset the slide in house prices. “We provide our customers with service to borrow money with their property as collateral,” said Mr. Yu, president of Qianteng Asset Management Company in Hangzhou. “We have plenty of funds on hand, which makes it easy for our customers to get money ASAP once they sign the contract.”

“In China, the Heisenberg uncertainty principle of physics holds sway, whereby the mere observation of economic numbers changes their behavior.”
• Why Beijing’s Troubles Could Get a Lot Worse (Barron’s)
Few foreigners know China as intimately as Anne Stevenson-Yang does. She has spent the bulk of her professional life there since first arriving in 1985, working as a journalist, magazine publisher, and software executive, with stints in between heading up the U.S. Information Technology office and the China operations of the U.S.-China Business Council. She’s now research director of J Capital, an outfit that works for foreign investors in China doing fundamental research on local companies and tracking macroeconomic developments.
Barron’s: Investors seem far more concerned about Europe’s sinking into economic despond than slowing growth in China. Are they whistling past the graveyard?
Stevenson-Yang: I think so. China, for all its talk about economic reform, is in big trouble. The old model of relying on export growth and heavy investment to power the economy isn’t working anymore. Sure, the nation has been hugely successful over recent decades in providing its people with literacy, a decent life, basic health care, shelter, and safe cities. But starting in 2008, China sought to counter global recession with huge amounts of ill-advised investment in redundant industrial capacity and vanity infrastructure projects—you know, airports with no commercial flights, highways to nowhere, and stadiums with no teams. The country is now submerged by the tsunami of bad debt that begets further unhealthy credit growth to service this debt. The recent lowering of benchmark deposit rates by the People’s Bank of China won’t accomplish much because it won’t offer more income to households. It also gave China’s biggest banks the discretion to raise their deposit rates back up to old levels, which would give them a competitive advantage
Barron’s: How bad can the situation be when the Chinese economy grew by 7.3% in the latest quarter?
Stevenson-Yang: People are crazy if they believe any government statistics, which, of course, are largely fabricated. In China, the Heisenberg uncertainty principle of physics holds sway, whereby the mere observation of economic numbers changes their behavior. For a time we started to look at numbers like electric-power production and freight traffic to get a line on actual economic growth because no one believed the gross- domestic-product figures. It didn’t take long for Beijing to figure this out and start doctoring those numbers, too. I put much stock in estimates by various economists, including some at the Conference Board, that actual Chinese GDP is probably a third lower than is officially reported. And as for the recent International Monetary Fund report calling China the world’s biggest economy on a purchasing-power-parity basis, how silly was that? China is a cheap place to live if one is willing to eat rice, cabbage, and pork, but it’s expensive as all get out once you factor in the cost of decent housing, a car, and health care.
I’d be shocked if China is currently growing at a rate above, say, 4%, and any growth at all is coming from financial services, which ultimately depend on sustained growth in the rest of the economy. Think about it: Property sales are in decline, steel production is falling, commercial long-and short-haul vehicle sales are continuing to implode, and much of the growth in GDP is coming from huge rises in inventories across the economy. We track the 400 Chinese consumer companies listed on the Shanghai and Shenzhen stock markets, and in the third quarter, their gross revenues fell 4% from a year ago. This is hardly a vibrant economy.

Demand is way down.
• OPEC Says 2015 Demand for Its Crude Will Be Weakest in 12 Years (Bloomberg)
OPEC cut the forecast for how much crude oil it will need to provide in 2015 to the lowest in 12 years amid surging U.S. shale supplies and reduced estimates for global consumption. The Organization of Petroleum Exporting Countries lowered its projection for 2015 by about 300,000 barrels a day, to 28.9 million a day. That’s about 1.15 million a day less than the group’s 12 members pumped last month, and the 30-million barrel target they reaffirmed at a meeting in Vienna on Nov. 27. The impact of this year’s 40% price collapse on supply and demand remains unclear, OPEC said. “The downward revision reflects the upward adjustment of non-OPEC supply as well as the downward revision in global demand,” the group’s Vienna-based research department said in its monthly oil market report.
Brent crude futures collapsed to a five-year low of $65.29 a barrel in London yesterday amid speculation that OPEC’s decision to maintain output levels despite swelling North American supplies will intensify the glut in global oil markets. Demand for OPEC’s crude will slump to 28.92 million barrels a day next year, according to the report. That’s below the 28.93 million required in 2009, and the lowest since the 27.05 million a day level needed in 2003, the group’s data show. Output from the 12 members declined by 390,000 barrels a day in November to 30.05 million a day amid lower production in Libya, according to data from analysts and media organizations referred to in the report as ‘‘secondary sources.” Libyan output dropped last month by 248,300 barrels a day to 638,000 a day. Pumping at the Sharara oil field, the country’s biggest-producing asset, and the neighboring El Feel site, was halted after Sharara was seized by gunmen, according to the International Energy Agency.

But OPEC will fight for market share, or rather its separate mebers will.
• Don’t Look For Oil Glut To End Any Time Soon (CNBC)
The global oil glut is expected to get much bigger before it’s over, keeping pressure on oil prices well into next year. Companies like ConocoPhillips and Chevron are reducing spending on new projects, but the impact of already planned increases in U.S. production into the first half of the year is likely to keep the world well supplied before the flow of new supply starts to slow in the second half of the year. Besides shale production, U.S. Gulf of Mexico production is also expected to increase with new projects coming on line. Within a year, the projects will take U.S. Gulf production from 1.3 million barrels to roughly 1.6 million barrels a day. “It’s not like the supply reaction is instantaneous. It takes time to wind these things down,” said John Kilduff of Again Capital. “I wouldn’t expect a decrease in the rate of (production) growth until next year at the earliest.”
The U.S. Energy Information Administration on Tuesday cut its forecast for daily U.S. production by another 100,000 barrels, to 9.3 million. That follows a reduction in its forecast of 100,000 barrels per day last month. The U.S. produced 9.08 million barrels a day in the week of Nov. 28 and has been producing over 9 million barrels a day for the past month. The government’s forecast for 2015 is now below some private analysts’ assumptions that oil production can continue to grow at a higher rate of anywhere from 500,000 to more than 1 million barrels per day next year, depending on oil prices. The EIA on Monday issued a new report on U.S. oil production showing the increase in production in the three main shale plays—Bakken, Permian and Eagle Ford—is growing by more than 100,000 barrels a day in December over November, and is expected to increase at about the same rate in January.

Discord is all that’s left at OPEC. Nobody can risk the initial losses of an output cut. And nobody trusts the others.
• Oil Resumes Drop as Iran Sees $40 If There’s OPEC Discord (Bloomberg)
Brent resumed its decline as an Iranian official predicted a further slump in prices if solidarity among OPEC members falters. West Texas Intermediate in New York also erased yesterday’s gains. Futures slid as much as 1.6% in London after snapping a five-day losing streak. Crude could fall to as low as $40 a barrel amid a price war or if divisions emerge in OPEC, said an official at Iran’s oil ministry. The 12-member group, which supplies 40% of the world’s oil, may need to call an extraordinary meeting in the first quarter if the drop continues, according to Energy Aspects Ltd. Brent has collapsed 40% this year as OPEC agreed at a Nov. 27 gathering not to cut output to force a slowdown in U.S. production, which has risen to the highest level in three decades. Saudi Arabia and Iraq this month widened discounts on crude exports to their customers in Asia, bolstering speculation that group members are fighting for market share.
“With OPEC looking like a dysfunctional family, no pullback in U.S. production and a lack of geopolitical concerns, it’s all adding up to lower prices,” Michael McCarthy, a chief strategist at CMC Markets in Sydney, said by phone today. Brent for January settlement decreased as much as $1.06 to $65.78 a barrel on the London-based ICE Futures Europe exchange and was at $66.25 at 3:12 p.m. Singapore time. The contract climbed 65 cents to $66.84 yesterday. The European benchmark crude traded at a premium of $3.12 to WTI. WTI for January delivery fell as much as $1, or 1.6%, to $62.82 a barrel in electronic trading on the New York Mercantile Exchange. It increased 77 cents to $63.82 yesterday. The volume of all futures traded was about 2% below the 100-day average.
Oil’s collapse has left the market below equilibrium, according to Mohammad Sadegh Memarian, the head of petroleum market analysis at the oil ministry in Tehran. Iran, hobbled by economic sanctions over its nuclear program, wants to raise production to 4.8 million barrels a day once the curbs are removed, he said at a conference in Dubai yesterday. OPEC pumped 30.56 million barrels a day in November, exceeding its collective target of 30 million for a sixth straight month, a Bloomberg survey of companies, producers and analysts showed. Financially strapped members such as Iran, Iraq and Venezuela may press for discussions before the group’s next scheduled meeting on June 5, predicted Amrita Sen, the chief oil market analyst at Energy Aspects.

And more’s to come.
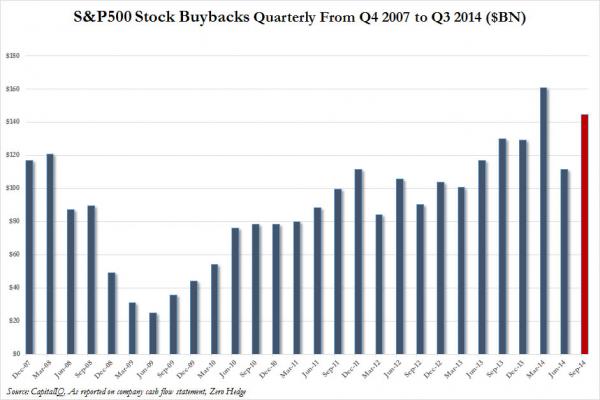
• “Yes, it Was a Brutal Week for the Oil & Gas Loan Sector” (WolfStreet)
Yesterday, I discussed how the plunging price of oil is wreaking havoc on leveraged loans in the energy sector. These loans are issued by junk-rated corporations already burdened by a large amount of debt. Banks that originate these loans can retain them on their balance sheets or sell them in various creative ways, including by repackaging them into synthetic structured securities, called Collateralized Loan Obligations. Earlier today, I discussed how the current generation of leveraged loans in general compares to the leveraged loans issued at the cusp of the Financial Crisis. Spoiler alert: by almost every metric, they’re bigger and crappier now than they were in 2007.
So here’s a chart of S&P Capital IQ’s energy-sector leveraged-loan index for the latest week, and it was such a doozie that it caused leveraged-loan focused LCD News, a unit of S&P Capital IQ, to tweet: “Yes, it Was a Brutal Week for the Oil & Gas Loan Sector.” The average bid price of first-lien oil & gas Index loans fell to 90.35 cents on the dollar for the week, from 94.90 at the November 28 close and down from 96.77 at the end of October, S&P Capital IQ’s LeveragedLoan.com reported. And yields soared: the spread to maturity implied by the average bid jumped from Libor plus 500 basis points in August to Libor plus 600 basis points at the end of November, to Libor plus 731 basis points at the end of the latest week. The US dollar Libor rate is about 0.1%, so yields jumped from 5.1% in August to 7.4% in the latest week. An exponential increase:
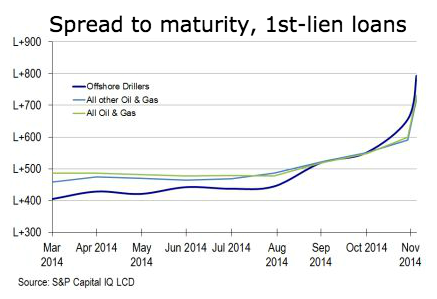
Note how offshore drillers (blue line) got hammered the most, though they had the lowest yields of the bunch for most of the year. Their spreads nearly doubled from 400 basis points over Libor in March to nearly 800 basis points over Libor last week. That’s a move from about 4% in March to nearly 8% now, and a big part of it within a single month. It’s really brutal out there. In the oil and gas sector, revenues are already plunging. Earnings will get hit. Earnings estimates are crashing at a rate not seen since crisis year 2009. Liquidity is drying up. And stocks got eviscerated. It’s tough out there.

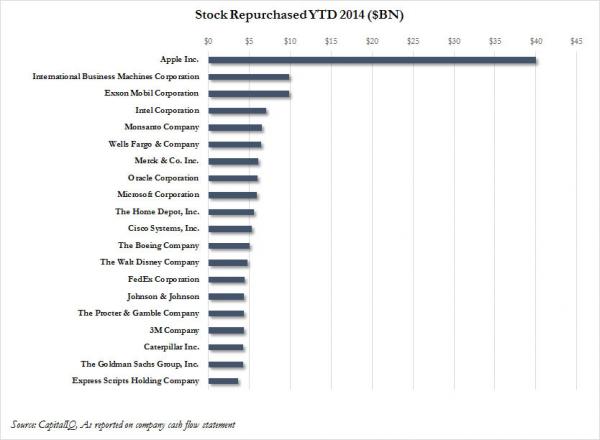
And that’s just for the four biggest ones.
• US Shale Contractors To See Net Income Cut By 25% In 2015 (Bloomberg)
Oilfield contractors hired to drill wells and fracture rock to raise crude and natural gas to the surface will have to lower prices by as much as 20% to help keep their cash-strapped customers working. Ultimately, that could carve out more than $3 billion from the 2015 earnings outlined by analysts for the world’s four biggest oil-service companies – Schlumberger, Halliburton, Baker Hughes and Weatherford International. The potential losses loom just as the service providers were looking ahead to higher rates after a glut in pressure-pumping gear dragged prices down in past years. Now, crude oil prices that have fallen more than 40% since June are squeezing them once again. As they look for ways to cut costs, oil producers will be pushing for discounts wherever they can find them.
“They’re already going to confront significant cash-flow pressures with the decline in oil prices,” Bill Herbert, an analyst at Simmons in Houston, said in a phone interview. “They’re going to need all the help they can get.” The price cuts may begin to take shape as early as this month, Herbert said. Hydraulic fracturing, in which high-pressure streams of water, sand and chemicals are used to crack rock underground to allow oil and gas to flow, may see the biggest chunk of pricing discounts because it’s the largest part of the cost of drilling a new well. Earnings estimates for service companies that have been cut since last week will continue to be revised lower as analysts don’t usually reduce their forecasts in one go when the outlook for an industry worsens, James Wicklund, an analyst at Credit Suisse in Dallas, said by phone. “We’ve just gotten started.”
Lower prices and lost business will probably reduce about $14.5 billion of net income estimated for the big four service companies in 2015 by as much as 25%, or about $3.6 billion, Wicklund said. Jeff Tillery, an analyst at Tudor Pickering Holt & Co. predicts roughly the same. After two years of declining service prices, providers were finally able to stop the slide this year and start pushing rates back up to help compensate for their own rising costs for fracking materials such as sand. Dave Lesar, chief executive officer of Halliburton, the top provider of fracking work, declared less than two months ago that better days were ahead. “This quarter things are clearly accelerating out of that turn and we do not see momentum slowing any time soon,” Lesar told analysts and investors Oct. 20 on a conference call.

The Fed has helped blow the bubble.
• This Time Is The Same: The Fed Ignores The Shale Bubble (David Stockman)
We are now far advanced into the third central bank generated bubble of the last two decades, but our monetary politburo has taken no notice whatsoever of its self-evident leading wave. Namely, the massive malinvestments and debt mania in the shale patch. Call them monetary bourbons. It is no exaggeration to say that inhabitants of the Eccles Building deserve every single word of Talleyrand’s famous epithet: “They learned nothing and forgot nothing.” To wit, during the last cycle they claimed to be fostering the Great Moderation and permanent full employment prosperity. It didn’t work. When the housing and credit bubble blew-up, it washed out all the phony gains from the Greenspan/Bernanke printing spree. By the time the liquidation was finished in early 2010, there were 2 million fewer payroll jobs than there had been at the turn of the century.
Never mind. The Fed simply doubled-down. Instead of expanding its balance sheet by 50%, as happened during the eight years between 2000 and 2008, it went into monetary warp drive, ballooning its made-from-thin-air liabilities by 5X in only six years. Yet even after Friday’s ballyhooed jobs report there were three million fewer full-time breadwinner jobs in November 2014 than there were in the early 2000s. That’s right. Two cycles of lunatic monetary expansion and what they have to show for it is two short-lived bursts of part-time job creation that vanish when the underlying financial bubble bursts. So, yes, our monetary central planners forget nothing. It doesn’t matter what the actual results have been.
Like the original Bourbons, the small posse of unelected academics and policy apparatchiks which control the nation’s all-powerful central bank most surely believe they have a divine right to run the printing presses as they see fit—even if it accomplishes nothing for the 99% of Americans who don’t have family offices or tickets to the hedge fund casino. Still, you would think that the purported “labor economist” who is now chair person of the joint would be at least troubled by the chart below. Even liberals like Yellen usually do acknowledge that that the chief virtue of the state is that it purportedly generates “public goods” that contribute to societal welfare—-not that it is a fount of productivity and new wealth generation. For that you need private enterprise and business driven efficiency.

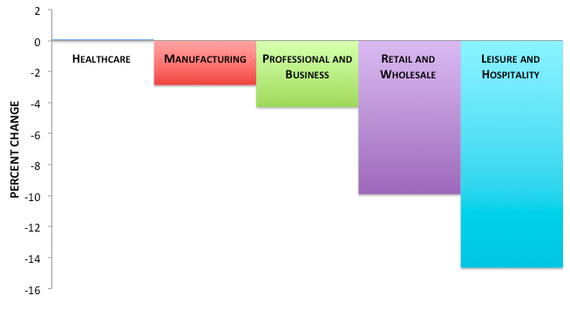
20% is a big number.
• Thanksgiving Weekend Box Office Plunges 20% vs 2013 To 16-Year Low (Alhambra)
The recession-like “stimulus” of recent vintage doesn’t seem to have affected the movie business. The Thanksgiving weekend is typically devoid of tremendous or blockbuster new titles for obvious reasons. However, just like people failed to show up at the mall they also skipped the theater. As I have noted before, this is not because movies are mostly narrowly-tailored junk, as they are, but that 2014 has seen a conspicuous drop in theater revenue despite offering largely the same junk as last year. The weekend following Thanksgiving 2014 was 20% below 2013. But we also have an almost direct comparison of “blockbuster” activity as the second installment of the Hunger Games is nearly 25% behind the first in the same number of days. Having taken in about $257 million (which is still quite good) in 17 days, the first version grabbed $335 million in the same timeframe.
Revenue over the summer was already 15% below 2013 despite having about the same number of “can’t miss” titles. Every single one underperformed every expectation. The “mystery” persists as the only plausible explanation offered is that people are staying home and watching Netflix or Amazon Prime. I think that is a big part of it, but, just as online shopping takes the bite out of holiday spending in-store, that isn’t enough for me to explain the size of these declines. Both movie revenue and bricks and mortar shopping are so far far below all expectations, as especially online spending has failed tremendously to fill the gap this year.

Where else could it have gone?
• Greece Lurches Back Into Crisis Mode (Bloomberg)
Greek stocks fell more than at any point during Europe’s debt crisis today after Prime Minister Antonis Samaras gambled his political future on bringing forward a parliamentary vote on a new head of state. Greek stocks tumbled the most since 1987 and three-year yields surged in response to the prime minister’s move. Unless he can persuade 25 opposition lawmakers to support his choice, Samaras will be forced to call a parliamentary election that anti-austerity party Syriza would be favorite to win. “Investors have taken a second look at Syriza and understood that at this point in time it’s more radical than the traditional left in Greece,” said Nicholas Veron, a fellow at the Bruegel research institute in Brussels. “If Syriza takes over it won’t be a smooth ride.”
Less than a month before Samaras had hoped to lead Greece out of the bailout program that has ravaged the country for the past four years, the resistance to his policies is fueling doubts about whether he can stay the course. While Syriza has pledged to stick with the euro, its plans to roll-back Samaras’s budget cuts evoke memories of the financial chaos that threatened to bust apart the currency union in 2012. Greece’s benchmark stock index dropped 13% and the bond market signaled investors are concerned about short-term disruptions, as the yield on 3-year debt jumped 176 basis points to 8.23%, surpassing 10-year rates. “It’s possibly a good decision, but in the end it’s in the hands of the decision makers in parliament and the population,” German Finance Minister Wolfgang Schaeuble told reporters in Brussels.
Greece’s reform program is “not yet over the hill,” he added. Samaras nominated Stavros Dimas, a 73-year-old former European Union commissioner, for the largely ceremonial post of president. Voting will begin next week, on Dec. 17, with two further rounds possible. Under Greece’s constitution, a supermajority of at least 180 lawmakers in the 300-seat chamber is needed to elect a successor to the incumbent, President Karolos Papoulias. The government has the support of just 155 lawmakers. Failure to install a candidate after three attempts would force Samaras to dissolve parliament.

Tha Japan elections are a big story this week.
• Japan Threatened With Credit Rating Downgrade (CNBC)
Japan’s “A-plus” credit rating is under threat, after Fitch Ratings placed the country’s debt on negative watch on Tuesday. The ratings agency said it could cut Japan’s rating in the first half of next year, following the government’s decision to delay a consumption tax hike to April 2017 from October 2015. “The delay implies it will be almost impossible to achieve the government’s previously-stated objective of reducing the primary budget deficit to 3.3% of GDP by the fiscal year April 2015-March 2016,” said Fitch in a report on Tuesday. Fitch estimates the proportion of Japan’s debt to the size of its gross domestic product would reach 241% by the end of this year, up from 184% at end-2008. The 57 percentage point rise in the ratio would be the second-highest over the period in the A or double-A category after Ireland, the agency noted.

If you can say a bank belongs to its shareholders, it’s teh latter who pay for the criminal activities of the traders and managers. And nowhere in there does the Justice department see a taks?
• Citigroup Sets Aside $2.7 Billion For Legal Costs (BBC)
Michael Corbat, the chief executive of US bank Citigroup, has said the firm is setting aside $2.7bn (£1.7bn) for legal costs in the fourth-quarter. Costs have risen due to US investigations into Citigroup’s behaviour in currency markets, setting the Libor rate, as well as an anti-money-laundering probe. In October, the bank was forced to restate its third-quarter results. It wrote off $600m due to the “rapidly evolving regulatory inquiries”. Mr Corbat made the remarks during a presentation at an investor conference, in which he also said that bank would write down $800m in expenses related to real estate and employee headcount. He said he expects the bank to remain “marginally profitable” during the period. Shares in Citigroup fell 2.5% after his remarks.

Lovely. And that’s without counting China.
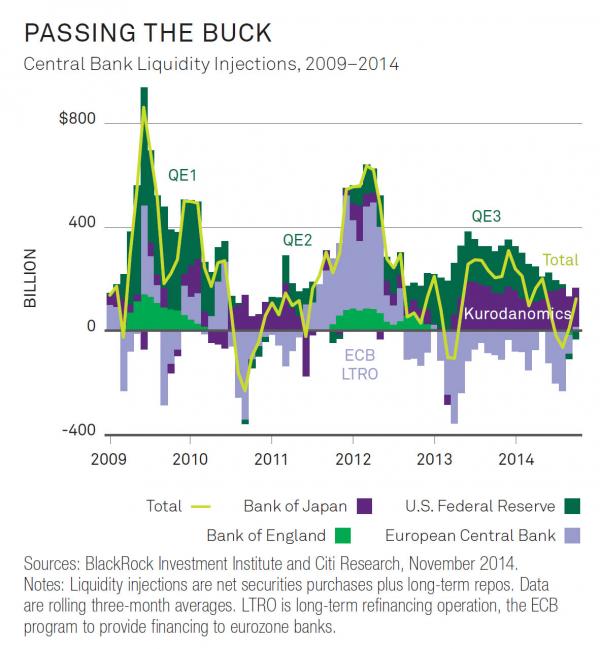
• This Is What 6 Years Of Central Bank Liquidity Injections Look Like (Zero Hedge)
Curious how over the past 6 years we got to a point where the market is now so irreparably broken, even the BIS couldn’t take it anymore and threw up all over the the world’s central bankers? Then look no further than the following chart summarizing 6 years of global central bank liquidity injections that have made it imperative to use quotation marks every time one writes the word “market”

They’re still TBTF, so what does it matter?
• Big US Banks Face Capital Requirement of 4.5% on Top of Global Minimum (BBG)
Big U.S. banks face capital surcharges of as much as 4.5% as the Federal Reserve readies new capital rules that single out firms reliant on short-term market funding as posing the greatest systemic risk. The Fed today proposed two methods to calculate what capital surcharges eight big U.S. firms will face on top of those already levied on the world’s largest banks by international regulators. While the central bank stopped short of listing the surcharges for each firm, it said they probably will range from 1% to 4.5% based on 2013 data – exceeding the maximum of 2.5% set under global rules. The aggregate amount the eight banks need to meet the surcharges from current levels is $21 billion, Federal Reserve officials said.
While stiffer rules can lower returns for shareholders of companies that hold onto profits to build capital, the Fed said “almost all” of the firms already meet the new requirements, and all are on their way to meeting them by the end of a phase-in period that runs from 2016 to 2019. The new U.S. regulations will focus in part on how much the banks borrow from institutional investors in short-term contracts, a form of funding deemed as riskier during a crisis. “Reliance on short-term wholesale funding is among the more important determinants of the potential impact of the distress or failure of a systemically important financial firm on the broader financial system,” Fed Governor Daniel Tarullo said. “Unfortunately, the surcharge formula developed by the Basel Committee does not directly take into account reliance on short-term wholesale funding.”
In the wave of rules meant to prevent a repeat of the 2008 financial crisis, the Fed has made global agreements tougher when applying them to U.S. lenders. The eight U.S. firms covered by today’s proposal are JPMorgan, Citigroup, Bank of America, Goldman Sachs, Morgan Stanley, Wells Fargo, Bank of New York Mellon and State Street. “The U.S. once again chooses to go its own way and exceed international minimums,” Karen Shaw Petrou, managing partner of Washington-based research firm Federal Financial Analytics Inc., said before today’s announcement. “If they squeeze the big banks too much, they’ll force some out of some businesses.”

America will pay a dear price for these crimes.
• Stop Believing The Lies: America Tortured More Than ‘Some Folks’ (Guardian)
The torture defenders from the CIA and the Bush administration probably won’t even make a serious attempt to say they didn’t torture anyone – just that it was effective, that there were “serious mistakes”, but that “countless lives have been saved and our Homeland is more secure” – with a capital H. This highlights the mistake of the Senate committee, in a way. Instead of focusing on the illegal nature of the torture, Senator Dianne Feinstein’s investigators worked to document torture’s ineffectiveness. The debate, now, is whether torture worked. It clearly didn’t. But the debate should be: Why the hell aren’t these torturous liars in jail?
Worse still, the CIA has still largely succeeded in stripping the landmark report of anything that could lead to accountability. The agents who were not only protected from discipline for their actions but were promoted now have their names completely redacted. So, too, are the names of the dozens of countries that helped the CIA carry out its torture regime. That includes many of the world’s worst dictators – the very men America now claims to hate, including Egypt’s Hosni Mubarak, Syria’s Bashar al-Assad, and Libya’s Muammar Gaddafi.
But make no mistake: there’s still an extraordinary amount to take away from this report. If there is one tragic story, out of the many, that is emblematic of the CIA program, as its supporters defend it in the days, it’s that of Gul Ruhman. It may be two stories – it’s hard to know, so much has been redacted and the atrocities are so countless – but at least one Gul Ruhman we know was tortured at the notorious CIA black site known as the Salt Pit, chained to the floor and frozen to death. The CIA’s inspector general referred this person’s case to CIA leadership for discipline, but was overruled. Four months after the incident, the officer who gave the order that led to Rahman’s death was recommended for a $2,500 “cash reward” for his “consistently superior work”.
Footnote 32 explains why a dead prisoner ended up in CIA custody in the first place: “Gul Ruhman, another case of mistaken identity.”

“Ignorance is not just strength – it is the most awesome force in the universe. Consider this: knowledge is always limited and specific, but ignorance is infinite and completely general ..”
• Defeat is Victory (Dmitry Orlov)
America is the world’s indispensable nation, world’s (second) greatest economic power (but rising fast), and American leadership is respected throughout the world. When President Obama said so in a recent speech he gave in China, the audience did not at all laugh out loud right in his face, roll their eyes, make faces or move their heads side to side slowly while frowning.
How can you avoid recognizing the importance of such things, and the fact that they spell DEFEAT? Easy! Ignorance to the rescue! Ignorance is not just strength – it is the most awesome force in the universe. Consider this: knowledge is always limited and specific, but ignorance is infinite and completely general; knowledge is hard to convey, and travels no faster than the speed of light, but ignorance is instantaneous at all points in the known and unknown universe, including alternate universes and dimensions of whose existence we are entirely ignorant. In short, there is a limit to how much you can know, but there is no limit at all to how much you don’t know but think you do!
Here is something that you probably think you know. The American empire is an “empire of chaos.” Yes, it sort of fails somehow to achieve peace, prosperity, democracy, stability, avert humanitarian crises, or stop lots of horrible crimes. But it does achieve chaos. What’s more, it achieves a wunnerful new type of chaos just invented, called “controlled chaos.” It’s much better than the old kind; sort of like “clean coal” – which you can rub all over yourself, go ahead, try it! Yes, there are naysayers out there that say things like “You reap what you sow, and if you sow chaos, you shall reap chaos.” I guess they just don’t like chaos. To each his own. Whatever.

They have to do research to figure that out?!
• Rising Inequality ‘Significantly’ Curbs Growth (CNBC)
The chasm between the richest and poorest is at a 30-year high in developed countries, dragging down world economic growth, according to a new international report. Worsening income inequality is estimated by the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) to have knocked nearly 9 percentage points off growth in the U.K. between 1990 and 2010, and between 6 and 7 percentage points off growth in the U.S. “This long-term trend increase in income inequality has curbed economic growth significantly,” said the OECD, which is made up of 34 major economies, in a report out Tuesday.
Looking ahead, the organization forecast that over a 25 year period, inequality would reduce growth by an average of 0.35% points per year in OECD countries. “The biggest factor for the impact of inequality on growth is the gap between lower income households and the rest of the population,” said the OECD. “These findings imply that policy must not (just) be about tackling poverty, it also needs to be about addressing lower incomes more generally.” Worst hit between 1990 and 2010 were Mexico and New Zealand, where the OECD estimated that rising inequality had knocked more than 10 percentage points off growth. “On the other hand, greater equality prior to the crisis helped increase GDP per capita in Spain, France and Ireland,” said the OECD.

We should never let this through. Once signed, it’ll be very hard to get rid off, and it benefits the wrong people.
• TTIP Divides A Continent As EU Negotiators Cross The Atlantic (Guardian)
Rarely has a trade agreement invited such hyperbole and paranoia. The Transatlantic Trade and Investment Partnership (TTIP) – or proposed free trade pact between the US and the European Union – has triggered apocalyptic prophecies: the death of French culture; an invasion of transatlantic toxic chickens into Germany; and Britain’s cherished NHS will become a stripped-down Medicare clone. From the point of view of free-trade cheerleaders, EU carmakers will more than double their sales, Europe will be seized by a jobs and growth bonanza and city halls from Chicago to Seattle will beg European firms to build their roads and schools. The world’s biggest trading nations will have no choice but to play by the west’s rules in the new world created by TTIP. Such are some of the claims made for TTIP which is now stoking a propaganda war on a scale never seen before in the arcane world of tariffs and non-tariff trade negotiations.
“It’s the most contested acronym in Europe,” said Cecilia Malmström of Sweden, the EU trade commissioner about to take charge of the European side of the negotiations. She stepped into the fray on Sunday, her first trip to Washington since taking up her post in November. TTIP dominates her intray. Eighteen months after the launch and seven rounds of talks, everything remains up in the air. The Americans are worried. Those in Brussels running the negotiations sound crestfallen. The opposition in Europe to a transatlantic free trade area believes it has the momentum, buoyed by scare stories regularly amplified by the European media. A petition against the trade pact surpassed the 1m mark this week. It will be handed to Jean-Claude Juncker, the European commission chief, in Brussels on Tuesday, as a present on his 60th birthday. “There is mistrust,” Matthew Barzun, the US ambassador in London, told the Guardian. A key EU official put it another way: “[TTIP is] more sensitive politically in Europe than in the US.”

“The risk to the world “is always there” while the outbreak continues ..”
• Ebola Virus Still ‘Running Ahead Of Us’, Says WHO (BBC)
The Ebola virus that has killed thousands in West Africa is still “running ahead” of efforts to contain it, the head of the World Health Organization has said. Director general Margaret Chan said the situation had improved in some parts of the worst-affected countries, but she warned against complacency. The risk to the world “is always there” while the outbreak continues, she said. She said the WHO and the international community failed to act quickly enough. The death toll in Guinea, Liberia and Sierra Leone stands at 6,331. More than 17,800 people have been infected, according to the WHO. “In Liberia we are beginning to see some good progress, especially in Lofa county [close to where the outbreak first started] and the capital,” said Dr Chan.
Cases in Guinea and Sierra Leone were “less severe” than a couple of months ago, but she said “we are still seeing large numbers of cases”. Dr Chan said: “It’s not as bad as it was in September. But going forward we are now hunting the virus, chasing after the virus. Hopefully we can bring [the number of cases] down to zero.” The official figures do not show the entire picture of the outbreak. In August, the WHO said the numbers were “vastly under-estimated”, due to people not reporting illnesses and deaths from Ebola. Dr Chan said the quality of data had improved since then, but there was still further work to be done.
She said a key part of bringing the outbreak under control was ensuring communities understood Ebola. She said teams going into some areas were still being attacked by frightened communities. “When they see people in space suits coming into their village to take away their loved ones, they were very fearful. They hide their sick relatives at home, they hide dead bodies. “[This is] extremely dangerous in terms of spreading disease. So we must bring the community on our side to fight the Ebola outbreak. Community participation is a critical success factor for Ebola control. “In all the outbreaks that WHO were able to manage successfully – that was a success element and this [is] not happening in this current situation.”