DPC El Paso, Texas 1903

Three things: First, in the jargon, “the backlash against globalization” has now become equal to the anti-trade movement. Which is nonsense: preferring another approach to trade is not the same as being against it altogether.
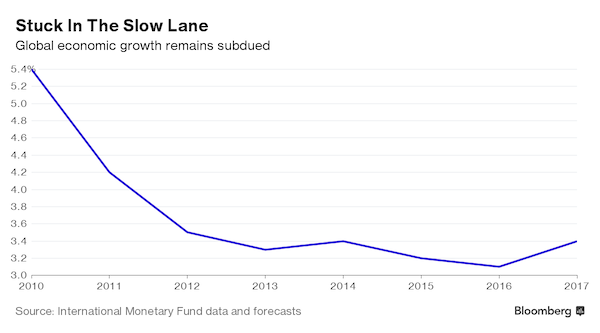
And second, look at that first graph! See that upward line at the end? Well, it’s an IMF growth ‘forecast’. Which are always so wrong, and always revised downward, that you must wonder if the term ‘forecast’ is even appropriate.
Third: “Existential Threat To World Order” ?! Isn’t that perhaps what the IMF and the rest of the elites themselves are?
• Existential Threat To World Order Confronts Elite At IMF Meeting (BBG)
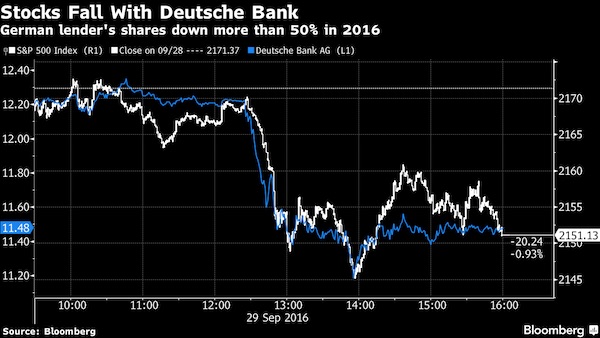
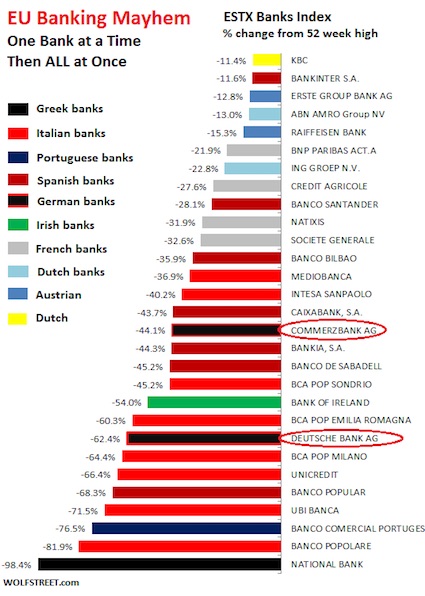
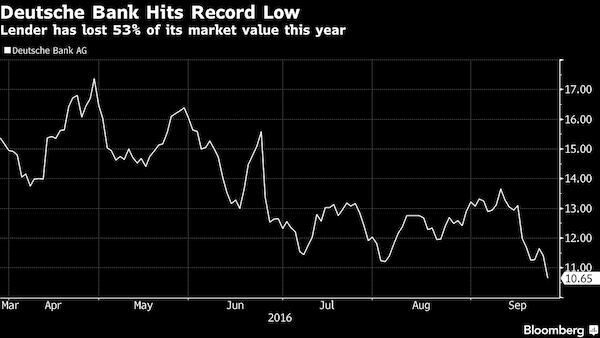
Policy-making elites converge on Washington this week for meetings that epitomize a faith in globalization that’s at odds with the growing backlash against the inequities it creates. From Brexit to Donald Trump’s championing of “America First,” pressures are mounting to roll back the economic integration that has been a hallmark of gatherings of the IMF and World Bank for more than 70 years. Fed by stagnant wages and diminishing job security, the populist uprising threatens to depress a world economy that IMF Managing Director Christine Lagarde says is already “weak and fragile.” The calls for less integration and more trade barriers also pose risks for elevated financial markets that remain susceptible to sudden swings in investor sentiment, as underscored by recent jitters over Deutsche Bank’s financial health.
“The backlash against globalization is manifesting itself in increased nationalistic sentiment, against the outside world and in favor of increasing isolation,” said Louis Kuijs at Oxford Economics, a former IMF official. “If we lose consensus on what kind of a world we want to have, the world will probably be worse off.” In its latest World Economic Outlook released Tuesday, the fund highlighted the threats from the anti-trade movement to an already subdued global expansion. After growth of 3.2% in 2015, the world economy’s expansion will slow to 3.1% this year before rebounding to 3.4% in 2017, according to the report, keeping those estimates unchanged from July projections. The forecasts for U.S. growth were cut to 1.6% this year and 2.2% in 2017. “We’d like to see an end to the creeping protectionism in the world and more progress on moving ahead with free-trade agreements and other trade-creating measures,” Maurice Obstfeld, director of the IMF’s research department, said.
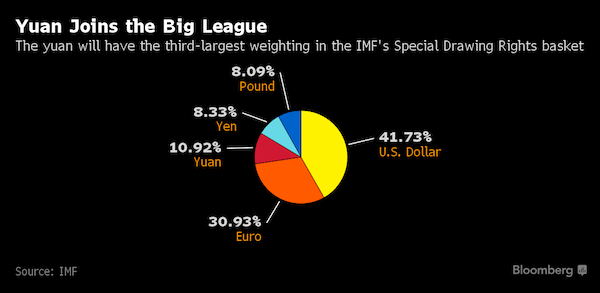
[..] Perhaps the biggest beneficiary of free trade over the past generation, China, still restricts access to many of its key industries, with economists worried about increasingly mercantilist policies. It’s also seeking a larger role in the existing global framework, with entry of the yuan into the IMF’s basket of reserve currencies on Oct. 1 the most recent example. An all-out trade war would be a disaster for China’s economy, with Trump’s threatened tariff potentially wiping off almost 5% of its GDP, according to a calculation by Daiwa Capital Markets. John Williamson, whose Washington Consensus of open trade and deregulation was effectively the governing ethos for the IMF and World Bank for decades, said the 2008-09 financial meltdown had undercut support for economic integration. “There was agreement on globalization before the crisis and that’s one thing that’s been lost since the financial crisis,” said Williamson.
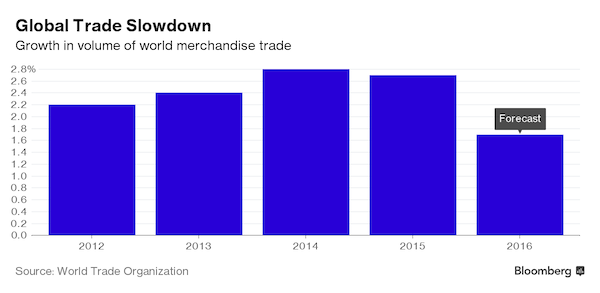

Deteriorating quality of debt. Not good.
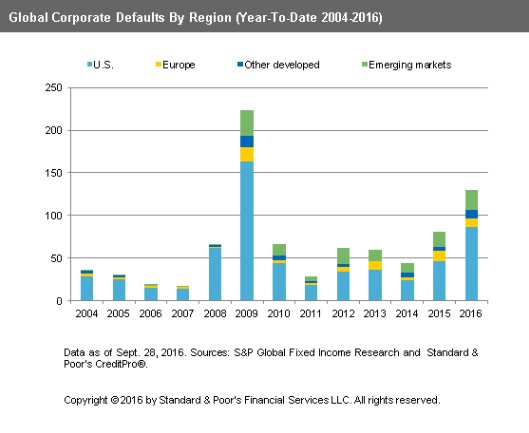
• US High-Yield Default Rates Hit 6-Year High (S&P)
The U.S. speculative-grade default rate has hit a six-year high of 4.79%, while the global default rate has crept to 4.04%, also a six-year high, according to S&P Global Fixed Income Research. Of course, the long-troubled energy sector plays a major role here. Excluding energy and natural gas companies, the U.S. default rate drops to 2.44%. Looking ahead, S&P says the number of ‘Weakest Links’ – issuers rated B- or lower, with either a negative outlook or implication – grew to 249 as of Sept. 20, the second-highest total since 2009.

“You cannot save your faltering economy by killing your financial system..”
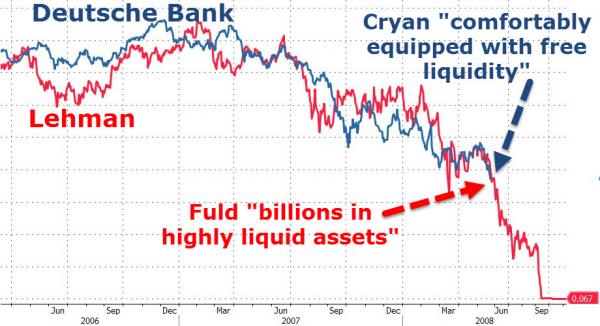
• Gundlach Says Deutsche Bank Shows Harm of Negative Rates (BBG)
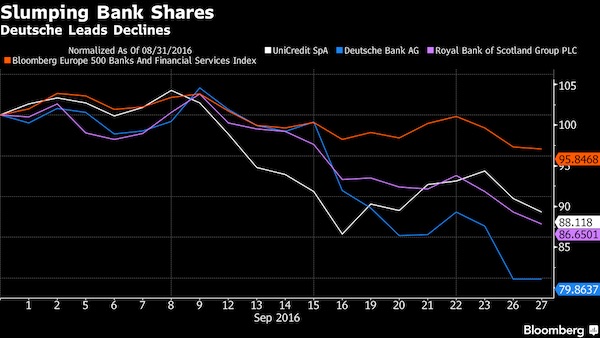
Famed bond investor Jeffrey Gundlach said Deutsche Bank’s slumping share price highlights the impact of the negative-interest-rate policy in Europe on the region’s lenders and may help prompt central bankers to reconsider their approach. “You cannot save your faltering economy by killing your financial system and one of the clear poster children for this is Deutsche Bank’s stock price,” Gundlach, 56, said at Grant’s Fall 2016 Investment Conference on Tuesday in New York. “If you keep these negative interest rate policies for a sufficient future period of time you are going to bankrupt these banks.” Europe’s banks have seen their value shrink by about $280 billion this year, with Deutsche Bank losing almost half its market value.
Germany’s largest lender extended losses after the U.S. Department of Justice last month requested $14 billion to settle a probe into residential mortgage-backed securities, sparking concerns that it will have to raise capital. While the Frankfurt-based bank would ultimately be rescued by the German government if needed, other banks in the region wouldn’t be able to count on such support, Gundlach said. “Deutsche Bank will be supported by Germany if push comes to shove,” he said. “But what about Credit Suisse, which has shown a similar decline in stock price? Who’s there to bail them out?”

More Gundlach. “I can bring back inflation by 5:00 pm by giving everyone $1 billion. The lines at BMW lots would be a sight to see..”
• Jeff Gundlach Thinks A ‘Pivot’ Is Coming To Economic Policy (BI)
Jeff Gundlach, Wall Street’s bond god, thinks the world of monetary and fiscal policy is about to pivot. “How in the world could we be talking about rates never going up when in fact rates have bottomed?” he asked the crowd of investors at the Grant’s Interest Rates Observer conference in New York City on Tuesday. He explained that it was on July 6th when he decided that the narrative that benchmark interest rates around the world would stay lower for longer was “getting quite old.” He cited several reasons: inflation is picking up, the dollar did not strengthen after the Federal Reserve raised rates the last time. Also there’s this: “In the investment world when you hear ‘never’,” ( as in rates are ‘never going up’), “it’s probably about to happen,” said Gundlach, who is CEO of DoubleLine Funds.
Now, an uptick in inflation and the dollar’s tolerance for higher rates are factors that don’t necessarily require urgency. And generally without urgency there is no change in policy. They are also factors he discussed in his last presentation, ‘Turning Points,’ back in September. But there is one thing that has changed since then. That thing is Deutsche Bank. “You cannot save your faltering economy by killing the financial system,” said Gundlach. That is, in effect, what low rates do. Over the last few weeks the world has watched as Deutsche Bank has struggled to convince investors and the public that it is in a sound fiscal position. Two weeks ago the US threatened the bank with a massive $14 billion fine for transgressions that led up to the financial crisis, and the bank’s stock really started to plummet.
In euros, Deutsche Bank’s stock price has hovered near the single digits. “There’s something about big banks being in the single digits that makes people nervous,” Gundlach said. He believes that Germany will bail out Deutsche Bank, despite the fact that the government has said that it intends to do no such thing. The problem isn’t Deutsche Bank in his mind, though — it’s other banks in a similar position that don’t have countries like Germany to bail them out. He mentioned Credit Suisse, arguing that Switzerland can’t handle a banking catastrophe its size.
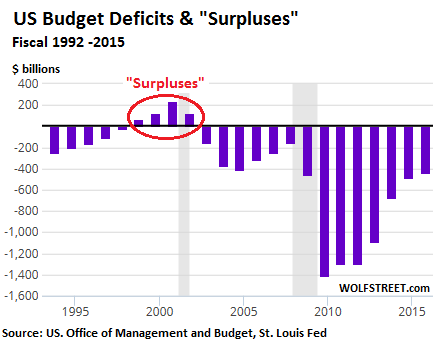
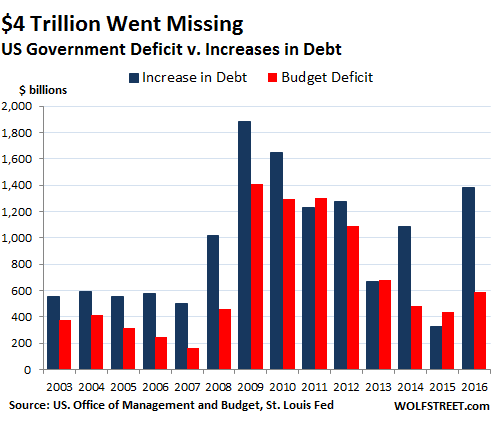
So what will the new world order be if rates must go up to save international banks? “I can bring back inflation by 5:00 pm by giving everyone $1 billion. The lines at BMW lots would be a sight to see,” he joked. What he’s saying is that now is the time to pivot to fiscal stimulus. Both presidential candidates Donald Trump and Hillary Clinton have talked about spending hundreds of billions on infrastructure and other investments. Meanwhile, US debt to GDP has been stable since 2011, and no one is really talking about the deficit anymore. Here’s a key chart he showed to the crowd. It was also in his last presentation:
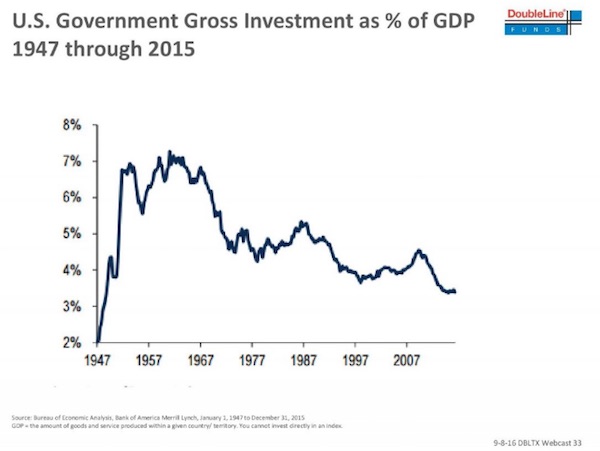

Sounds doable.
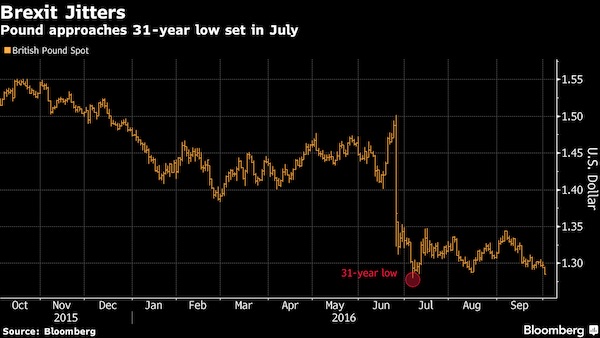
• Pound Sinks To 1985 Low, Is Likely ‘Going To Go Down The Tubes’ (CNBC)
Sterling’s tumble isn’t finished, Koon How Heng, a senior foreign-exchange strategist at Credit Suisse, told CNBC, as the currency dropped below July’s post-Brexit referendum low. “We still have a very negative view on the sterling,” Heng said. Sterling was fetching as little as $1.2683 in Asia trading hours on Wednesday, under the $1.2796 low it hit on July 6 in the wake of Brexit. Wednesday’s levels were down from levels over $1.30 last week and well off the high of $1.5018 the currency touched before the June 23 poll. The pair is currently at their lowest level since March 1985, when the pound neared parity with the U.S. dollar amid an acrimonious miners’ strike in the U.K. “Officially, our forecast for sterling dollar is at 1.25,” Heng told CNBC’s “Street Signs” just hours before the currency took its latest leg lower. “We would think it’s going to head lower. It’s probably going to go down the tubes.”

It’ll take more to prick that bubble.
• Manhattan Apartment Sales Plunge 20% (BBG)
There are a lot more apartments available for purchase these days in Manhattan. And fewer people are buying. Sales of previously owned condominiums and co-ops fell 20% in the third quarter from a year earlier as potential buyers grew cautious amid more choices, according to a report Tuesday from appraiser Miller Samuel and brokerage Douglas Elliman Real Estate. There were 5,290 resale apartments on the market at the end of September, 53% more than the number available in late 2013, the lowest point for listings. The swelling inventory is providing an opportunity to New Yorkers shut out of a market in which construction has been dominated by ultra-luxury condos aimed at the wealthiest buyers.
Resales, particularly those priced at less than $1 million, were in chronically short supply in recent years, and those that made it to the market sparked bidding wars. Now, more owners are listing apartments to profit from climbing values, and they’re finding lots of company. “Rapidly rising prices over the years have pulled more sellers into the market hoping to cash out,” Jonathan Miller, president of Miller Samuel, said in an interview. “But buyers are more wary. There isn’t the same intensity of activity to burn through the new supply.”

Funny, Don Quijones makes the same comparison I did last week between Monte dei Paschi and Goldman’s very lucrative and very shady derivatives deals enabling former Greek governments to hide debt. Italy has indicted MPS, Nomura and Deutsche Bank over MDP. Goldman was never charged over Greece.
• Rescue of Italy’s Monte dei Paschi Gets ‘Dark’ & ‘Complicated’ (DQ)
Shares of Monte dei Paschi di Siena, the world’s oldest bank and by now the world’s most famous penny stock, trade at €0.18. Things have gotten so bad that Italy’s financial markets regulator Consob extended the deadline and widened the scope of its ban on short selling of the bank’s shares. The restrictions were initially introduced on July 7 just after the bank’s shares had crashed 20% in one day. Since then they have shed a further 45%. Doubts continue to mount over the chances of success for the bank’s latest rescue program, its third since the Global Financial Crisis began. “The situation has got more complicated,” reported Il Corriere della Sera, one of Italy’s most influential newspapers. It’s also apparently quite “dark” — as in sinister.
“For weeks, MPS has been in the center of dark, worrying maneuvers,” said Azione Mps, an association of the bank’s retail shareholders. If the worst comes to the worst, the institution they’re invested in will either be bailed-in, resulting in a complete loss of their already basically worthless investment, and/or bailed-out by either Italy’s government or the ECB, in the process massively diluting the value of their already basically worthless shares. Nonetheless, “dark” is an interesting turn of phrase, especially given that the Italian bank’s latest desperate bid to save its derriere without outright state intervention is being led by America’s most corrupt financial institution (according to Forbes), JP Morgan Chase.
Also, in recent days MPS’ head offices, fittingly housed within a restored ancient fortress, have been transformed into a gargantuan crime scene after a Milan court ordered MPS, Nomura and Deutsche Bank to stand trial for a string of alleged financial crimes, including crimes that the Bank of Italy, under Mario Draghi’s tutelage, apparently knew about yet sat on its hands. The court also indicted 13 former and current managers from the three banks over the case, with prosecutors alleging they had used complex derivatives trades to conceal losses at MPS, in much the same way that Goldman Sachs helped the Greek government to conceal its mountain of excess debt with complex derivatives.

Rock and a hard place or two.
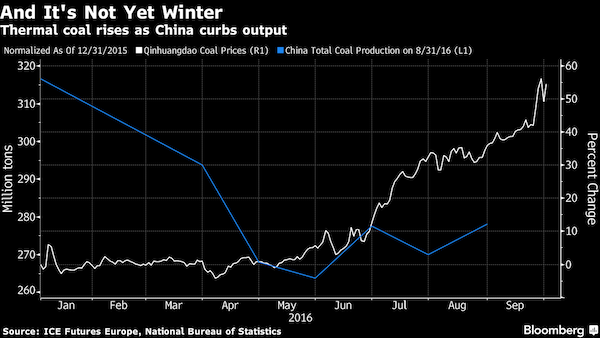
• China’s Efforts To Shrink Bloated Coal Industry May Have Worked Too Well (BBG)
China’s efforts to shrink its bloated coal industry may have worked too well, too fast. Prices have surged more than 50% this year after the government ordered miners to cut output to ease a glut and help lift the industry out of crisis. Now, as winter looms and fuel demand peaks, the consumer and producer of about half the world’s coal is having to relax some of those controls, or face even higher fuel costs, according to analysts at Citigroup and ICIS China, as well as China Coal Transport and Distribution Association. “The extent of the production cuts earlier this year has been too severe,” David Fang, a director with the CCTD, said. “Now the government is trying to fix the problem by relaxing some controls on output, but there is only limited time now before the winter arrives.”
The government earlier this year unveiled efforts to revitalize the coal industry and throw a lifeline to miners, many of them government-controlled, who struggled to repay debts as prices of the fuel used in power stations fell to the lowest in about a decade amid excess supply. President Xi Jinping’s administration ordered miners to lower output to the equivalent of 276 days of production, from the standard 330 days. And as part of the country’s broader “supply side structural reform,” regulators went after the industry’s massive overcapacity, cutting about 150 million tons of unneeded capacity as of August, out of a target of 500 million tons by 2020. The reforms may be a victim of their own success. Output fell more than 10% in the first eight months of this year, pushing up domestic prices and helping imports, including coking coal used to make steel, rise to the highest since December 2014.

Veteran Intelligence Professionals for Sanity.
• Obama Warned to Defuse Tensions with Russia (CN)
A group of ex-U.S. intelligence officials is warning President Obama to defuse growing tensions with Russia over Syria by reining in the demonization of President Putin and asserting White House civilian control over the Pentagon.
ALERT MEMORANDUM FOR: The President
FROM: Veteran Intelligence Professionals for Sanity
SUBJECT: PREVENTING STILL WORSE IN SYRIAWe write to alert you, as we did President George W. Bush, six weeks before the attack on Iraq, that the consequences of limiting your circle of advisers to a small, relatively inexperienced coterie with a dubious record for wisdom can prove disastrous.* Our concern this time regards Syria. We are hoping that your President’s Daily Brief tomorrow will give appropriate attention to Saturday’s warning by Russia’s Foreign Ministry spokesperson Maria Zakharova: “If the US launches a direct aggression against Damascus and the Syrian Army, it would cause a terrible, tectonic shift not only in the country, but in the entire region.”
Speaking on Russian TV, she warned of those whose “logic is ‘why do we need diplomacy’… when there is power… and methods of resolving a problem by power. We already know this logic; there is nothing new about it. It usually ends with one thing – full-scale war.” We are also hoping that this is not the first you have heard of this – no doubt officially approved – statement. If on Sundays you rely on the “mainstream” press, you may well have missed it. In the Washington Post, an abridged report of Zakharova’s remarks (nothing about “full-scale war”) was buried in the last paragraph of an 11-paragraph article titled “Hospital in Aleppo is hit again by bombs.” Sunday’s New York Times totally ignored the Foreign Ministry spokesperson’s statements.
In our view, it would be a huge mistake to allow your national security advisers to follow the example of the Post and Times in minimizing the importance of Zakharova’s remarks. Events over the past several weeks have led Russian officials to distrust Secretary of State John Kerry. Indeed, Foreign Minister Sergey Lavrov, who parses his words carefully, has publicly expressed that distrust. Some Russian officials suspect that Kerry has been playing a double game; others believe that, however much he may strive for progress through diplomacy, he cannot deliver on his commitments because the Pentagon undercuts him every time. We believe that this lack of trust is a challenge that must be overcome and that, at this point, only you can accomplish this.

Maybe the clean-up will work. But we add more faster.
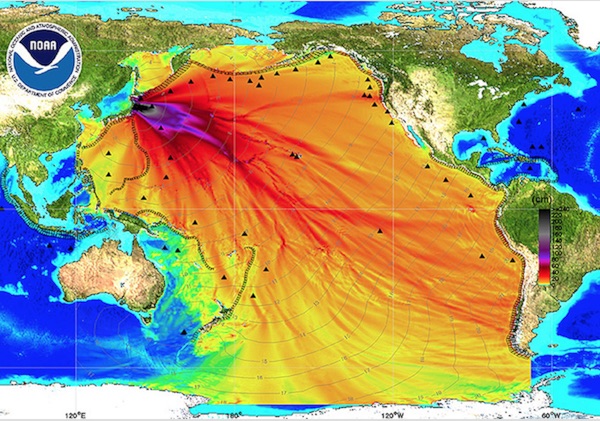
• ‘Great Pacific Garbage Patch’ Far Bigger Than Imagined (G.)
The vast patch of garbage floating in the Pacific Ocean is far worse than previously thought, with an aerial survey finding a much larger mass of fishing nets, plastic containers and other discarded items than imagined. A reconnaissance flight taken in a modified C-130 Hercules aircraft found a vast clump of mainly plastic waste at the northern edge of what is known as the “great Pacific garbage patch”, located between Hawaii and California. The density of rubbish was several times higher than the Ocean Cleanup, a foundation part-funded by the Dutch government to rid the oceans of plastics, expected to find even at the heart of the patch, where most of the waste is concentrated. “Normally when you do an aerial survey of dolphins or whales, you make a sighting and record it,” said Boyan Slat, the founder of the Ocean Cleanup.
“That was the plan for this survey. But then we opened the door and we saw the debris everywhere. Every half second you see something. So we had to take snapshots – it was impossible to record everything. It was bizarre to see that much garbage in what should be pristine ocean.” The heart of the garbage patch is thought to be around 1m sq km (386,000 sq miles), with the periphery spanning a further 3.5m sq km. [..] Following a further aerial survey through the heart of the patch on Sunday, the Ocean Cleanup aims to tackle the problem through a gigantic V-shaped boom, which would use sea currents to funnel floating rubbish into a cone. A prototype of the vulcanized rubber barrier will be tested next year, with a full-sized 100km (62-mile) barrier deployed by 2020 if trials go well.

1000 on one crappy boat.
• At Least 28 Migrants Found Dead Off Libya (AFP)
Twenty-eight Europe-bound migrants were found dead on a day of frantic rescues off Libya on Tuesday, including at least 22 in an overloaded wooden boat, an AFP photographer and the Italian coastguard said. The photographer, who was able to go aboard the vessel, said it appeared that many of the dead had suffocated. He said there were about 1,000 people on three levels. He counted 22 bodies and said there were more dead in the hold. The Italian coastguard – which is coordinating rescue efforts in international waters north of Libya – said 28 bodies had been recovered over the course of 33 operations on Tuesday, while 4,655 migrants had been rescued.
The photographer was travelling on the Astral, a ship chartered by Spanish NGO ProActiva Open Arms, which rescues migrants at sea. Late on Tuesday, the Italian navy took over helping survivors and retrieving bodies, the photographer said. It was yet another day of drama at sea after more than 6,000 migrants, most of them Africans in packed rubber dinghies, were rescued off Libya on Monday. Nine bodies were found in those operations, including a pregnant woman.