René Magritte Promenades d’Euclid 1955

Plenty scary thought.
• Whoever Leads In AI Will Rule The World – Putin (RT)
Vladimir Putin spoke with students about science in an open lesson on September 1, the start of the school year in Russia. He told them that “the future belongs to artificial intelligence,” and whoever masters it first will rule the world. “Artificial intelligence is the future, not only for Russia, but for all humankind. It comes with colossal opportunities, but also threats that are difficult to predict. Whoever becomes the leader in this sphere will become the ruler of the world,” Russian President Vladimir Putin said. However, the president said he would not like to see anyone “monopolize” the field.
“If we become leaders in this area, we will share this know-how with entire world, the same way we share our nuclear technologies today,” he told students from across Russia via satellite link-up, speaking from the Yaroslavl region. During the 45-minute open lesson (the standard academic hour in Russia), Putin also discussed space, medicine, and the capabilities of the human brain, pointing out the importance of cognitive science. “The movement of the eyes can be used to operate various systems, and also there are possibilities to analyze human behavior in extreme situations, including in space,” Putin said, adding that he believes these studies provide unlimited opportunities. The open lesson was attended by students and teachers from 16,000 schools, Rossiyskaya Gazeta reports. The total audience exceeded one million.

“..never since the mid-1960s, when records began, has core CPI (less food, energy and shelter) declined over a six-month period..”
• Deflation Is Already Here – Albert Edwards (ZH)
At the start of the year, we were surprised when SocGen’s Albert “Ice Age” Edwards, the biggest perma-deflationist on Wall Street, flipped his outlook on the US economy, and said he now expected a fast spike in inflation driven by wage growth, which in turn would prompt an even more accelerated tightening cycle by the Fed. We did not see it, and said so, pointing out that the bulk of US job growth in recent years has been among industries that have little to no wage power. More than half a year later, and several months after a puzzled Edwards asked “Where Is The Wage Inflation?”, the SocGen strategist has finally thrown in the towel, and in a note released this morning, admits he was wrong, or as he puts it “I was too optimistic”, to wit:
“At this point in the US economic cycle a tight labour market would normally be producing a notable upturn in wage and CPI inflation. This would usually prompt the Fed into a tightening cycle that would typically end in a surprise recession. This is exactly what I expected to occur at the start of this year and I thought it would be that recession that would tip the US into outright deflation ? but I was wrong. I was too optimistic!” And while there has been a modest improvement in average hourly earnings according to the BLS, if not according to the BEA’s wage data, which according to the just released Personal Income data showed another drop in both private and government worker wages…
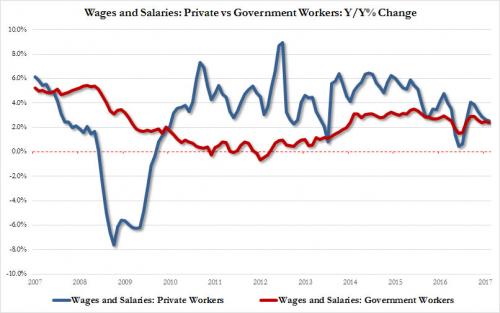
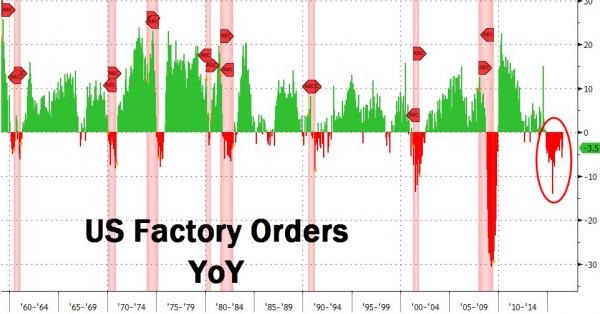
… broader inflation trends continue to disappoint. Furthermore, when digging through the recent CPI data, Edwards noticed something unexpected: as he writes, although wages have accelerated due to the tight labor market, the last six months has seen consistent downside surprises. And then this: “this has come hand-in-hand with an unprecedented slump in underlying US CPI inflation into outright deflation – in stark contrast to the eurozone where core CPI inflation has decisively risen.” Putting the finding in context, the “wrong, too optimistic” Edwards writes that never since the mid-1960s, when records began, has core CPI (less food, energy and shelter) declined over a six-month period, as demonstrated by the red line in the chart below. Or, as he summarizes, “Deflation did not need another US recession to emerge. It is already here.”
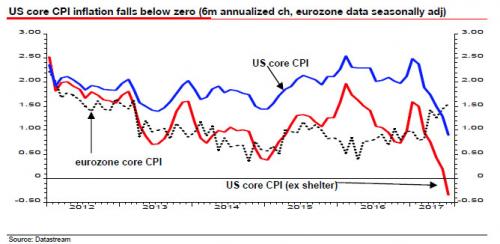
the SocGen strategist has some advice to the Fed: “If I were a Fed Governor I would be pretty shocked/concerned/bemused at inflation developments this year. However confident the Fed is of a self-sustaining-recovery, there is growing evidence of a slide into outright deflation even ahead of the next recession which will likely unambiguously take us deep into deflationary territory.” Imminent deflationary prints notwithstanding, Edwards still thinks rates should be normalised. Why? “Well, because the longer the current credit excesses are allowed to continue, the deeper the next recession and deflationary bust will ultimately be.”

“What a complete, utter, disastrous failure of public policy, not just for Greece but for the world.”
• Fiscal Austerity After The Great Recession Was A Catastrophic Mistake (Coppola)
In a new paper presented at Jackson Hole last week, the economists Alan Auerbach and Yuriy Gorodnichenko showed that, contrary to popular belief, fiscal expansion after a major financial shock such as that in 2008 did not cause debt/GDP ratios to rise. In fact, the researchers found that debt could become more sustainable, not less, after fiscal stimulus: For a sample of developed countries, we find that government spending shocks do not lead to persistent increases in debt-to-GDP ratios or costs of borrowing, especially during periods of economic weakness. Indeed, fiscal stimulus in a weak economy can improve fiscal sustainability along the metrics we study. Fiscal stimulus works. What a pity we did not allow ourselves to do it, much. But what about Greece? Surely fiscal austerity was necessary there?
Well, maybe. “The experience of Greece and other countries in Southern Europe is a grave warning about the political risks and limits of fiscal policy,” say the researchers. “Bridges to nowhere, “pet” projects and other wasteful spending can outweigh any benefits of countercyclical fiscal policy.” But they nevertheless find that fiscal expansion works even when debt/GDP levels are high. “The penalty for a high debt-to-GDP ratio does not appear to be high at the debt levels experienced historically for developed countries,” they say. So when Greece’s debt was a mere 100% of GDP, fiscal expansion could have been a good strategy. Now, of course, Greece’s debt/GDP ratio is off the chart, because of the aforementioned catastrophic failure of public policy. The researchers warn that their results are uncertain at very high debt/GDP levels. So fiscal expansion might now be too late for Greece. What a tragedy.
“We have been giving catastrophically bad advice to countries with high debt to GDP ratios”, said Jason Furman, the former chair of Barack Obama’s Council of Economic Advisers who is now at Harvard. Too right. And Greece has paid the price. But it is not just Greece that has paid. If Auerbach and Gorodnichenko are right, then the policy path since 2010 has been wrong for many more countries. They have truncated their recoveries and hurt their populations by embarking on premature fiscal consolidation, while cudgeling central banks into somehow conjuring up a recovery that monetary policy is incapable of producing at the lower bound. As a result, there has been a prolonged and wholly unnecessary global slowdown, which will leave lasting scars, particularly on the young. What a complete, utter, disastrous failure of public policy, not just for Greece but for the world.

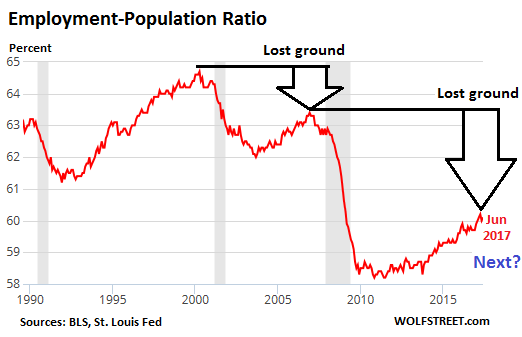
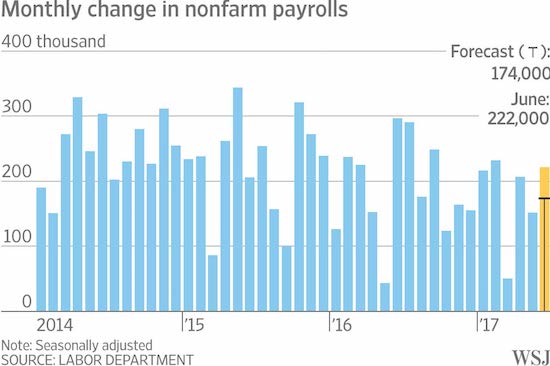
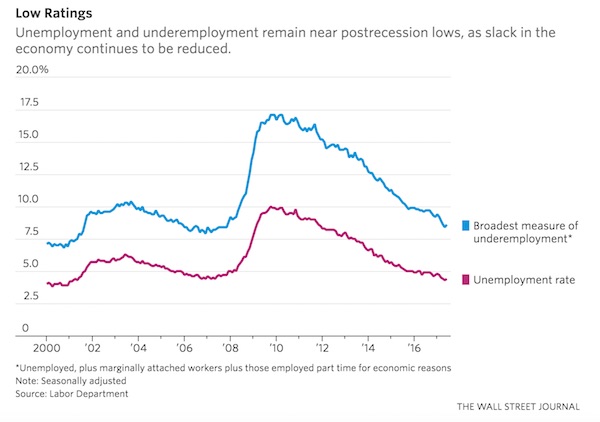
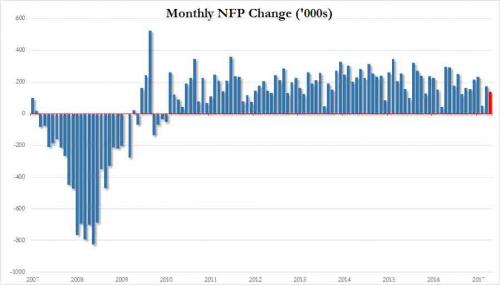
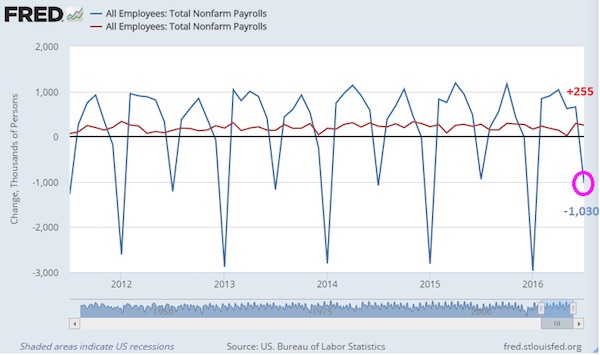
Pre-Harvey ugly.
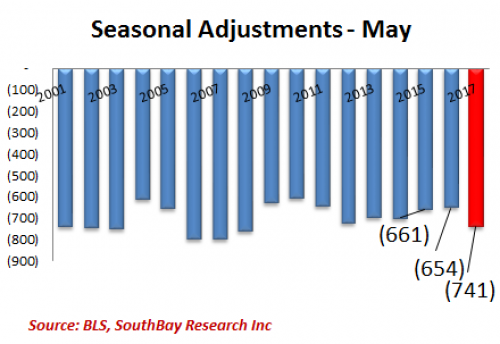
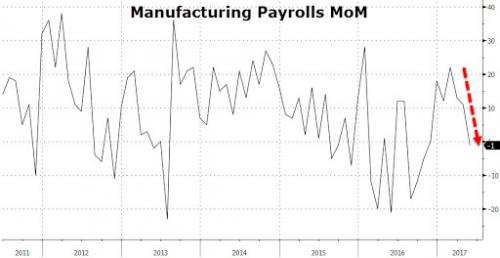
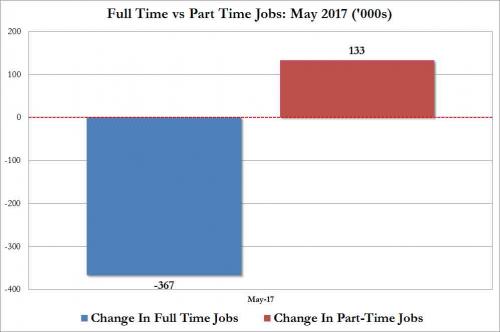
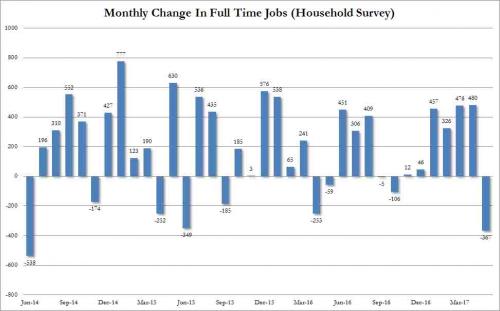
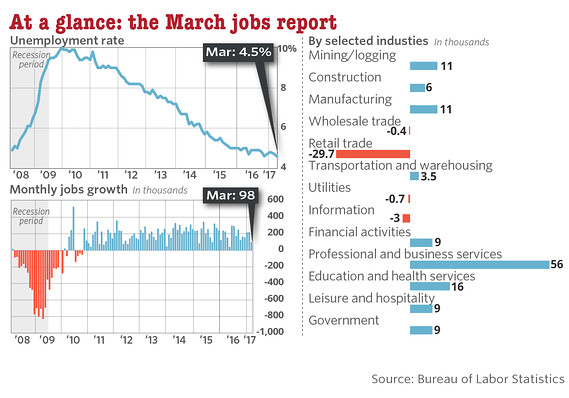
• Ugly Jobs Report: August Payrolls Miss (ZH)
[..] moments ago the BLS reported that in August just 156K jobs were created, a big miss to the 180K expected, and following a sharp downward revision to June and July, which were revised to 210K and 189K, respectively, a 41K drop combined. But don’t worry, the worse, the better as the more disappointing the economic data, the less likely the Fed will hike in September, December, or ever for that matter. And keep in mind, today’s data did not include the Harvey devastation, which will assure no rate hikes from the Fed for months, if not decades to come. Not helping matters – for the economy, if not the stock market which now once again loves bad data – was the Household Survey, according to which the number of employed Americans declined by 74,000 to 153,439K. On an annual basis, the increase in the employment level dropped to 1.2%, the lowest since March.
The unemployment rate also disappointed, rising from 4.3% to 4.4%, while the avg hourly earnings missed, increasing by 2.5% Y/Y in August, below the 2.6% estimate and the same as July. The sequential increase in earnings was just 0.1%, also below the 0.2% expected, and far below the 0.3% in July. Furthermore, since average weekly hours declined also, from 34.5 to 34.4, average weekly earnings declined outright from $909.42 to $907.82 in August. Furthermore, average weekly earnings rose just 2.2% Y/Y, the lowest rate of increase since January.
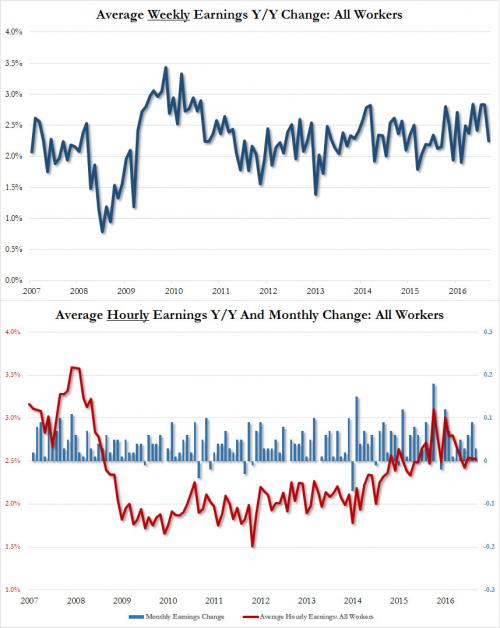
While the labor force participation rate remained unchanged at 62.9%, the number of Americans not in the labor force increased once again, growing by 128K in August to 94.785 million.
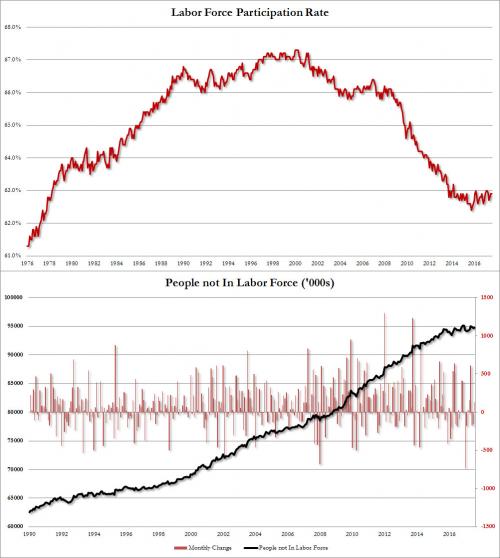

Mitch wants investigations. And not the ones going on right now.
• Deciphering The Swamp’s Unemployment Deception (Feierstein)
I strongly see the need for a full and open inquiry into Hillary’s illegal server, Clinton’s leaking of top secret documents, the pay-to-play Clinton Foundation, the entire ‘Fake news’ Russian collusion affair and James Comey’s ‘Fake FBI investigation’ with a predetermined outcome. I am not taking a partisan position here. However, I am guessing many people will reason: ‘The Republicans are bashing the Democrats over these inquiries; this guy Feierstein wants an inquiry, so he must be a Republican.’ I don’t blame people for making these assumptions. Our whole country has become infected with this kind of twisted logic. Our entire political debate has caught the virus. Yet, it makes no sense. No sense at all. Here are two facts and one conclusion:
Fact One : Hillary had an illegal server in the basement of her home that contained ‘Top-Secret Emails.’ Fact Two : Senators Grassley and Graham’s statement regarding FBI’s James Comey’s exoneration of Clinton read: “Conclusion first, fact-gathering second—that’s no way to run an investigation. The FBI should be held to a higher standard than that, especially in a matter of such great public interest and controversy.” Conclusion : These allegations are serious enough to deserve an open investigation, period. Partisan bickering and political spin is simply a diversion from the action that American people deserve — and the truth that the American people require.
I say all this because I’m about to call attention to another government department: the Bureau of Labor Statistics. Now, I know that Democrats are currently bashing President Trump over everything he does. I know that Trump is bashing back. But, people, the issue at stake is the creation of jobs in America and the way those things are being recorded and reported. The issues I’m about to address were present under George W. Bush and Barack Obama. They haven’t changed under Donald Trump. The depression which struck this country in the wake of financial crisis 1.0 might have peaked under a Democrat, but it was born in a Republican era. If you yourself are so partisan that you want to make fine distinctions about these things, you should go ahead and make them. Me: I see two peas in a pod.
Good. Preamble over. Here’s the issue: “The number of jobs created in America declined by 74,000 to 153,439 in August. A horrible number, far below expectations. The jobless rate rose to 4.4 and hourly earnings missed increasing only 2.5% year-over-year. Average hours worked also declined, seeing as weekly wages followed suit.” Yet, central bank manipulated stocks are surging, on the terrible economic news, in anticipation of more global central bank easing. News and economic data are irrelevant in our “rigged” system as market participants eagerly line up like heroin addicts awaiting another federal reserve fix.

As if anyone still believes in that dream.
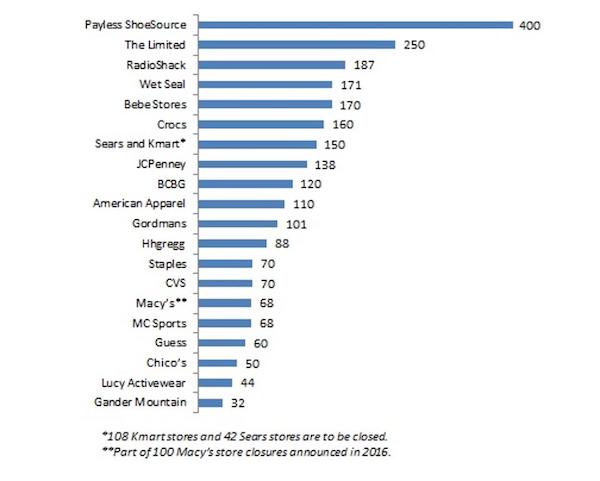
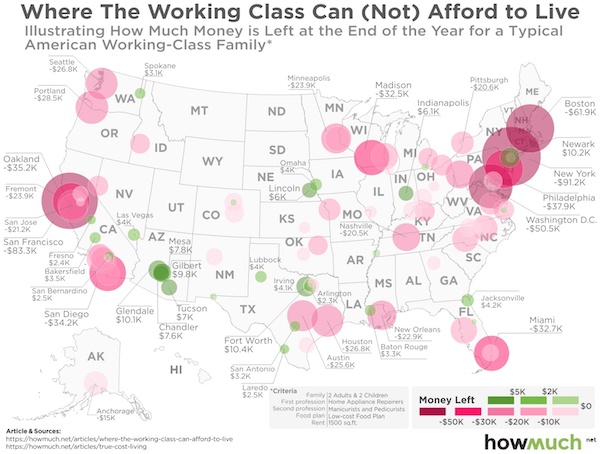
• The Working Class Can’t Afford the American Dream (HowMuch)
The national conversation in the U.S. is focused squarely on improving the lives of people in the working class. The debate revolves around exactly how to do that. Politicians and pundits have all sorts of ideas, from efforts to save jobs, create tax cuts, subsidize housing, and provide universal healthcare. Thing is, people don’t even agree on how to define the working class, much less how their living conditions stack up across the country. We created a data visualization to illustrate this complex situation. Each bubble represents a city. The color corresponds to the amount of money a typical working-class family would have left over at the end of the year after paying for their living costs, like housing, food and transportation.
The darker the shade of red, the worse off you are. The darker the shade of green, the better off you are. The size of the bubble also fits on a sliding scale—large and dark red means the city is totally unaffordable. Bigger dark green bubbles likewise indicate a city where the working class can get by. The data come from our new True Cost of Living Tool. It’s kind of a big deal because it lets you drill down to a specific city and search through layers of relevant information to understand exactly how much money it takes to live in any given area. We stitched together a variety of different reputable sources, like the Bureau of Labor Statistics for income levels, the National Bureau of Economic Research for tax data, and the U.S. Department of Agriculture for the cost of food. Basically, you can check our work.

Banks say central banks must be ready to give money to … banks.
• Central Banks Must Be Ready With Cash To Calm Brexit Nerves – Bank Lobby (R.)
Central banks should be ready to inject cash into the financial markets to keep them stable after Britain leaves the European Union in 2019, a draft report from a bank industry lobby said. The Association for Financial Markets in Europe (AFME), in a draft report seen by Reuters, said that regulators, central banks and national governments should continue to support financial market stability between Britain’s departure from the EU and start of new trading terms. “This may require particular attention during the uncertain period around Brexit, and in particular during the transition, and may involve more regular market communications and targeted support in case of market need, for example, access to liquidity schemes,” the report said. This and other steps would be needed to minimise disruption, it said. AFME’s report also provides a blueprint for a transition phase after Britain’s EU exit in March 2019.
This would include a “bridging phase” to avoid “short-term disruption” until new trading terms are ratified and an “adaptation phase” for moving to the new terms. The report did not specify a time frame for the transition but said it should be limited. “It is crucial that clarity is provided as soon as possible on a transitional period, and ideally before the end of this year,” AFME said. AFME wants existing market arrangements maintained throughout the transitional period, reflecting worries among bankers that they might have to comply first with a transition period and then the new trading terms. “This means that existing legislation, regulation, permissions and authorisations should continue to be effective during the transitional period,” it said. Company bosses also want Britain to negotiate a staggered departure from the EU by the end of this year or they will have to push ahead with plans that assume they will lose all access to the single market after March 2019.

Rickards sticks to his guns.
• How to Crack the Code on Gold – Rickards (DR)
“Don’t underestimate the extent to which gold is being impacted by hedge funds, leverage players, and others that are in the mix for the current high in gold. They don’t really care if it is gold, soybeans, etc. but it is simply another commodity. They receive a nice profit with tight profits, tight stops.” “The bigger picture to look as here is that gold hit an interim low last December and has been grinding higher ever since. Now gold is up over $200 an ounce and is one of the best performing assets in 2017. There’s a pattern of higher highs and shows a very positive occurrence.” [..] “This all relates to currency wars. I think of gold by weight.”
“When most people look at the cost of gold they relate it to the dollar. That gives the dollar a privilege to say that it is the way to count everything. It is also possible to count gold in euro, yen or even bitcoin. I think of gold as money. These are all just cross rates. When I see a higher dollar price for gold, I think of the dollar as being weaker. Likewise, if I see a lower price for gold it just shows that gold is constant and the dollar got stronger.” “There are three things going on right now in gold. There’s a fear trade, there’s technicals with supply shortages and ultimately a weaker dollar. If you want to know where the dollar price for gold is going, ask yourself where the dollar is headed. As the dollar gets weaker due to Federal Reserve Chair Yellen’s plan to tighten rates into weakness. We’re getting disinflation, not inflation and the desire from the Fed is a weaker dollar.”
[..] “I expect to see gold hit $5,000 and eventually to $10,000 an ounce. Maybe not tomorrow or a couple of years but that is the fundamental price of gold as money.” [..] “Bitcoin is a very small market cap compared to gold. I don’t think it has much impact on gold and looks like a bubble right now.” “As someone who has been around Wall Street a long time I’ve seen a lot of different tricks of the trade and frauds that come and go. I am seeing all of the various schemes in bitcoin right now. There’s good forensic evidence that there are people doing wash sales right now and the suckers don’t know they are getting sucked in. Gold is still the ultimate safe haven.”

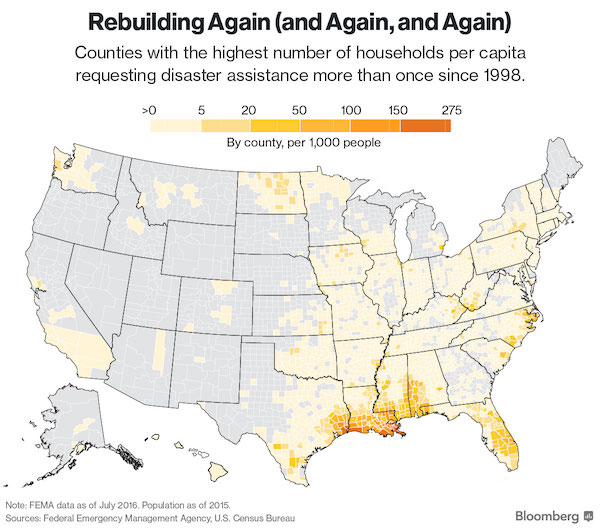
That’s just emergency funding. Washington will need to find ways to help the uninsured.
• Trump Seeks $7.85 Billion For Harvey Relief, Warns On Debt Ceiling (R.)
U.S. President Donald Trump has asked Congress for an initial $7.85 billion for Hurricane Harvey recovery efforts, the White House budget director said on Friday, adding that failure to raise the budget ceiling may hinder disaster relief spending. In a letter to U.S. House of Representatives Speaker Paul Ryan, White House budget director Mick Mulvaney said the request included $7.4 billion for the Federal Emergency Management Agency’s Disaster Relief Fund and $450 million for the Small Business Administration’s disaster loan program. “This request is a down-payment on the president’s commitment to help affected states recover from the storm, and future requests will address longer-term rebuilding needs,” Mulvaney said. Trump had been expected to request $5.95 billion for the recovery effort after Harvey flooded areas of Houston and other parts of Texas.
The White House has said that it would make multiple requests for aid from Congress to fund the Harvey recovery effort. White House homeland security adviser Tom Bossert told reporters on Thursday aid funding requests would come in stages as more became known about the impact of the storm. Texas Governor Greg Abbott has said that his state may need more than $125 billion. Bossert said the Trump administration wanted Congress to pass the disaster relief measure on its own and not add it to other measures, such as the effort to raise the debt ceiling. The U.S. government has a statutory limit on how much money it can borrow to cover the budget deficit that results from Washington spending more than it collects in taxes. Only Congress can raise that limit. Mulvaney urged Congress to act “expeditiously to ensure that the debt ceiling does not affect these critical response and recovery efforts.”

Ethylene, polypropylene. It’s silly, but we ‘need’ them.
• Harvey: “Unprecedented” Disruptions To Supplies Of “Essential” Chemicals (ZH)
The unprecedented destruction wrought by Hurricane Harvey will impact the US economy in ways may not be immediately apparent. Until recently, coverage of the storm’s impact has focused on property damage and the impact on the energy industry. But in a story published Friday, Bloomberg explains the devastating impact the storm has had on Texas’s chemicals industry, which is already causing supply-chain headaches for American manufacturers who’re struggling to source the chemicals required to produce plastics and other components used in everything from milk jugs to car parts. Indeed, if Texas’s chemicals plants are closed for an extended period, production at a potentially huge number of American manufacturers to grind to a halt.
More than 60% of the US’s production capacity for ethylene – one of the most important chemical building blocks for American manufacturers – has been taken offline by the storm, a development that could ripple across the US manufacturing industry. “Texas alone produces nearly three quarters of the country’s supply of one of the most basic chemical building blocks. Ethylene is the foundation for making plastics essential to U.S. consumer and industrial goods, feeding into car parts used by Detroit and diapers sold by Wal-Mart. With Harvey’s floods shutting down almost all the state’s plants, 61% of U.S. ethylene capacity has been closed, according to PetroChemWire.” Ethylene, the gas given off by fruit as it ripens, occurs naturally, but it’s also a crucial product of the $3.5 trillion global chemical industry, with factories pumping out 146 million tons last year.
Processing plants turn the chemical into polyethylene, the world’s most common plastic, which is used in garbage bags and food packaging. When transformed into ethylene glycol, it’s the antifreeze that keeps engines and airplane wings from freezing in winter. It’s used to make polyester for both textiles and water bottles. Ethylene is an ingredient in vinyl products such as PVC pipes, life-saving medical devices and sneaker soles. It helps combat global warming with polystyrene foam insulation and lighter, fuel-saving plastic auto parts. It’s used to make the synthetic rubber found in tires. It’s even an ingredient in house paints and chewing gum. Ethylene and its derivatives account for about 40% of global chemical sales, according to Hassan Ahmed, an analyst at Alembic Global Advisors. And the Gulf Coast is a crucial player in the global market: US production accounts for one of every five tons on the market. International ethylene plants were running nearly full out to meet rising demand before Harvey.

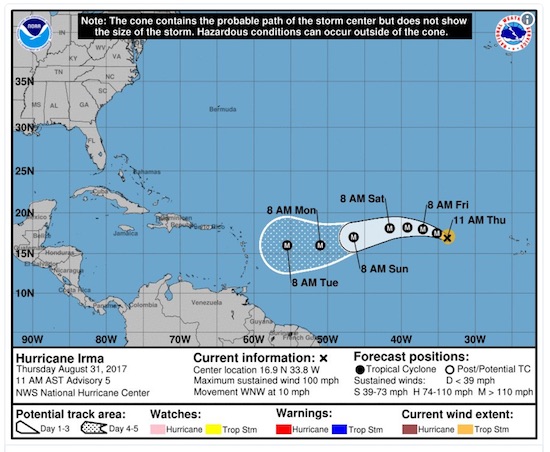
‘T is the season. The lesser Antilles could get hit bigtime.
• Irma Intensifies Over The Atlantic (R.)
As Harvey diminishes a new storm has emerged. Irma, the fourth hurricane of the 2017 Atlantic hurricane season, has strengthened over the eastern Atlantic to become a Category 3 storm, the U.S. National Hurricane Center said in its latest advisory Thursday. Irma is forecast to intensify Thursday night and is projected to be a very dangerous hurricane for the next few days, the Miami-based center said. Irma is located about 1,845 miles east of the Leeward Islands and has maximum sustained winds of 115 mph, the NHC said. NHC forecast models were showing it heading for the U.S. territory of Puerto Rico, the Dominican Republic, and neighboring Haiti with possible landfall by the middle of next week.
While currently a Category 3 storm, Irma’s winds could strengthen to become a Category 4 storm in five days’ time, the Miami Herald reported. Irma will not reach the eastern Caribbean Lesser Antilles islands until the middle of next week, and it is too soon to determine whether or not the storm will pose a threat to the U.S., according to The Weather Channel. Still, the potential for a U.S. landfall should prompt all who may be affected in those areas to closely monitor the storm in the coming days, The Weather Channel said. “Irma is forecast to become a major hurricane by tonight and is expected to be an extremely dangerous hurricane for the next several days,” the NHC said Thursday, while adding there is no current risk to land from the storm.