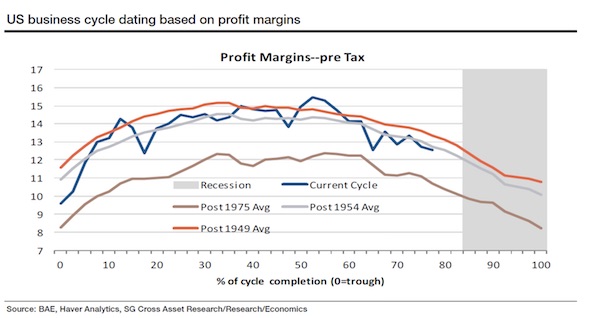
Henri Cartier-Bresson Trafalgar Square on the Day of the Coronation of George VI 1937
The Jackson Hole gathering of central bankers and other economics big shots is on again. They all still like themselves very much. Apart from a pesky inflation problem that none of them can get a grip on, they publicly maintain that they’re doing great, and they’re saving the planet (doing God’s work is already taken).
But the inflation problem lies in the fact that they don’t know what inflation is, and they’re just as knowledgeable when it comes to all other issues. They get sent tons of numbers and stats, and then compare these to their economic models. They don’t understand economics, and they’re not interested in trying to understand it. All they want is for the numbers to fit the models, and if they don’t, get different numbers.
Meanwhile they continue to make the most outrageous claims. Bank of England Governor Mark Carney said in early July that “We have fixed the issues that caused the last crisis.” What do you say to that? Do you take him on a tour of Britain? Or do you just let him rot?
Fed head Janet Yellen a few days earlier had proclaimed that “[US] Banks are ‘very much stronger’, and another financial crisis is not likely ‘in our lifetime’. “ While we wish her a long and healthy life for many years to come, we must realize that we have to pick one: it has to be either a long life, or no crisis in her lifetime.
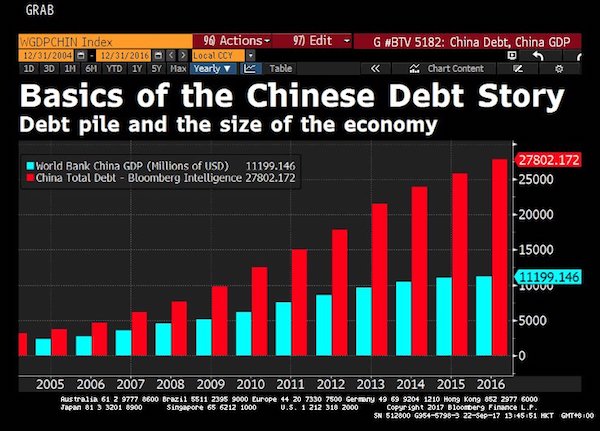
Just a few days ago, ECB President Mario Draghi somehow managed to squeeze through his windpipe that “QE has made economies more resilient”. Even though everybody -well, everybody who’s not in Jackson Hole- knows that QE has blown huge bubbles in lots of asset classes and caused severe damage to savings and pensions, problems that will reverberate through economies for a long time and rip entire societies apart.
But they really seem to believe what they say, all of them. Which is perhaps the biggest problem of all. That is, either they know better and lie straight-faced or they are blind to what they’re doing. Which might be caused by the fact that they are completely blind to what goes on in their countries and societies, and focus exclusively on banking systems. But that’s not where financial crises reside, or at least not only there.
How do we know? Easy. Try this on for size.
78% of Americans Live Paycheck To Paycheck
No matter how much you earn, getting by is still a struggle for most people these days. 78% of full-time workers said they live paycheck to paycheck, up from 75% last year, according to a recent report from CareerBuilder. Overall, 71% of all U.S. workers said they’re now in debt, up from 68% a year ago, CareerBuilder said. While 46% said their debt is manageable, 56% said they were in over their heads. About 56% also save $100 or less each month, according to CareerBuilder.
Haven’t seen anything as ironic in a long time as having a company called CareerBuilder report on this. But more importantly, when almost 4 out of 5 people live paycheck to paycheck, that is a financial crisis right there. Just perhaps not according to the models popular in Jackson Hole. What do they know about that kind of life, anyway? So why would they care to model it?
Yellen’s Fed proudly report almost full employment -even if they felt forced to abandon their own models of it. But what does full employment constitute, what does it mean, when all those jobs don’t allow for people to live without fear of the next repair bill, the next hospital visit, their children’s education?
What does it mean when banks are profitable again and pay out huge bonuses while at the same time millions work two jobs and still can’t make ends meet? How is that not a -financial- crisis? In the economists’ models, all those jobs must lead to scarcity in the labor market, and thus rising wages. And then inflation, by which they mean rising prices. But the models fail, time and time again.
Moreover, talking about inflation without consumer spending, i.e. velocity of money, is empty rhetoric. 78% of Americans will not be able to raise their spending levels, they’re already maxed out at the end of each week, and 71% have debts on top of that. So where will the inflation, rising wages, etc., come from? When nobody has money to spend? Nobody can put that Humpty Dumpty together again.
An actual -as opposed to theoretical- recovery of wages and inflation will certainly not come from QE for banks, that much should be clear after a decade. And that is exactly where the problem is. That is why so many people work such shitty jobs. The banks may be more resilient (and that comes with a big question mark), but it has come at the cost of the economies. And no, banks are not the same as economies. Moreover, ‘saving’ the banks through asset purchases and ultra low rates has made ‘real economies’ much more prone to the next downturn.
The asset purchases serve to keep zombie firms -including banks- alive, which will come back to haunt economies -and central banks- when things start falling. The ultra low rates have driven individuals and institutions into ‘investments’ for which there has been no price discovery for a decade or more. Homes, stocks, you name it. Everyone and their pet hamster overborrowed and overpaid thanks to Bernanke, Yellen and Draghi, and their ‘policies’.
QE for banks didn’t just not work as advertized, it has dug a mile deep hole in real economies. No economy can properly function unless most people can afford to spend money. It’s lifeblood. QE for banks is not, if anything it’s the opposite.
Another -joined at the hip- example of what’s really happening in -and to- America, long term and deep down, and which will not be a discussion topic in Jackson Hole, is the following from the Atlantic on marriage in America. And I can hear the disagreements coming already, but bear with me.
Both the above 78% paycheck to paycheck number and the Atlantic piece on marriage make me think back of Joe Bageant. Because that is the world he came from and returned to, and described in Deer Hunting with Jesus: Dispatches from America’s Class War. The Appalachians. I don’t believe for a moment that Joe, if he were still with us, would have been one bit surprised about Trump. And reading this stuff, neither should you.
This is not something that is new, or that can be easily turned around anymore. This is the proverbial oceanliner which requires a huge distance to change course. Victor Tan Chen’s piece is a worthwhile read; here are a few bits:
America, Home of the Transactional Marriage
Over the last several decades, the proportion of Americans who get married has greatly diminished—a development known as well to those who lament marriage’s decline as those who take issue with it as an institution. But a development that’s much newer is that the demographic now leading the shift away from tradition is Americans without college degrees—who just a few decades ago were much more likely to be married by the age of 30 than college graduates were.
Today, though, just over half of women in their early 40s with a high-school degree or less education are married, compared to three-quarters of women with a bachelor’s degree; in the 1970s, there was barely a difference. [..] Fewer than one in 10 mothers with a bachelor’s degree are unmarried at the time of their child’s birth, compared to six out of 10 mothers with a high-school degree.
The share of such births has risen dramatically in recent decades among less educated mothers, even as it has barely budged for those who finished college. (There are noticeable differences between races, but among those with less education, out-of-wedlock births have become much more common among white and nonwhite people alike.)
And then you make education so expensive it’s out of reach for a growing number of people… Insult and injury.
Plummeting rates of marriage and rising rates of out-of-wedlock births among the less educated have been linked to growing levels of income inequality. [..] Why are those with less education—the working class—entering into, and staying in, traditional family arrangements in smaller and smaller numbers? Some tend to stress that the cultural values of the less educated have changed, and there is some truth to that.
But what’s at the core of those changes is a larger shift: The disappearance of good jobs for people with less education has made it harder for them to start, and sustain, relationships. What’s more, the U.S.’s relatively meager safety net makes the cost of being unemployed even steeper than it is in other industrialized countries—which prompts many Americans to view the decision to stay married with a jobless partner in more transactional, economic terms.
And this isn’t only because of the financial ramifications of losing a job, but, in a country that puts such a premium on individual achievement, the emotional and psychological consequences as well. Even when it comes to private matters of love and lifestyle, the broader social structure—the state of the economy, the availability of good jobs, and so on—matters a great deal.
This is the erosion of social cohesion. And there is nothing there to fill that void.
Earlier this year, the economists David Autor, David Dorn, and Gordon Hanson analyzed labor markets during the 1990s and 2000s—a period when America’s manufacturing sector was losing jobs, as companies steadily moved production overseas or automated it with computers and robots. Because the manufacturing sector has historically paid high wages to people with little education, the disappearance of these sorts of jobs has been devastating to working-class families, especially the men among them, who still outnumber women on assembly lines.
Autor, Dorn, and Hanson found that in places where the number of factory jobs shrank, women were less likely to get married. They also tended to have fewer children, though the share of children born to unmarried parents, and living in poverty, grew. What was producing these trends, the researchers argue, was the rising number of men who could no longer provide in the ways they once did, making them less attractive as partners.
The perks of globalization. Opioids, anyone?
[..] In doing research for a book about workers’ experiences of being unemployed for long periods, I saw how people who once had good jobs became, over time, “unmarriageable.” I talked to many people without jobs, men in particular, who said that dating, much less marrying or moving in with someone, was no longer a viable option: Who would take a chance on them if they couldn’t provide anything?
It’s not only Joe Bageant. These are also the people Bruce Springsteen talked about when he was still the Boss.
[..] The theory that a lack of job opportunities makes marriageable men harder to find was first posed by the sociologist William Julius Wilson in regard to a specific population: poor, city-dwelling African Americans. [..] In later decades of the last century, rates of crime, joblessness, poverty, and single parenthood soared in cities across the country.
[..] In a 1987 book, Wilson put forward a compelling alternative explanation: Low-income black men were not marrying because they could no longer find good jobs. Manufacturers had fled cities, taking with them the jobs that workers with less in the way of education—disproportionately, in this case, African Americans—had relied on to support their families. The result was predictable. When work disappeared, people coped as best they could, but many families and communities frayed.
By now it’s all Springsteen, Darkness on the Edge of Town. That album is some 40 years old. That’s -at least- how long this has been going on. And why it’ll be so hard to correct.
Decades later, the same storyline is playing out across the country, in both white and nonwhite communities, the research of Autor, Dorn, and Hanson (as well as others) suggests. The factory jobs that retreated from American cities, moving to suburbs and then the even lower-cost South, have now left the country altogether or been automated away.
[..] “The kinds of jobs a man could hold for a career have diminished,” the sociologists wrote, “and more of the remaining jobs have a temporary ‘stopgap’ character—casual, short-term, and not part of a career strategy.” The result: As many men’s jobs have disappeared or worsened in quality, women see those men as a riskier investment.
This next bit is painful: life ain’t gonna get any better, so we might as well have kids.
At the same time, they are not necessarily postponing when they have kids. As the sociologists Kathryn Edin and Maria Kefalas have found in interviews with low-income mothers, many see having children as an essential part of life, and one that they aren’t willing to put off until they’re older, when the probability of complications in pregnancy can increase.
For mothers-to-be from more financially stable backgrounds, the calculation is different: They often wait longer to have children, since their career prospects and earnings are likely to improve during the period when they might otherwise have been raising a child. For less-educated women, such an improvement is much rarer.
Tan Chen follows up with a comparison of European and American safety nets, and suggests that “It’s not a matter of destiny, but policy”, but I don’t find that too relevant to why I found his piece so touching.
It describes a dying society. America is slowly dying, and not all that slowly for that matter. The Fed is comfortably holed up in Jackson Hole after having handed out trillions to bankers and lured millions of Americans into buying -or increasingly renting- properties that have become grossly overpriced due to its ZIRP policies, and congratulating itself on achieving “full employment”.
Why that ever became part of its mandate, g-d knows. I know, ML King et al. But. Thing is, when full employment means 78% of people have such a hard time making ends meet that they can’t afford to keep each other in a job by spending their money in stores etc., you’re effectively looking at a dying economy. Maybe we should not call it ‘full’, but ’empty employment’ instead.
Yeah, I know, trickle down. But instead of wealth miraculously trickling down, it’s debt that miraculously trickles up. How many Americans have mortgages or rents to pay every month that gobble up 40-50% or more from their incomes? That’d be a useful stat. Model that, Janet!
The article on marriage makes clear that by now this is no longer about money. The 40+ year crisis has ‘transcended’ all that. If and when money becomes too scarce, it starts to erode quality of life, first in individuals and then also in societies. It erodes the fabric of society. And you don’t simply replace that once it’s gone, not even if there were a real economic recovery.
But there will be no such recovery. As bad as things are for Americans today, they will get a whole lot worse. That is an inevitable consequence of the market distortion that QE has wrought: a gigantic financial crisis is coming. And the crowd gathered at Jackson Hole will be calling the shots once more, and bail out banks, not people. What’s that definition of insanity again?