Pablo Picasso The old fisherman 1895

Debt is the answer. They want you to think they don’t know that.
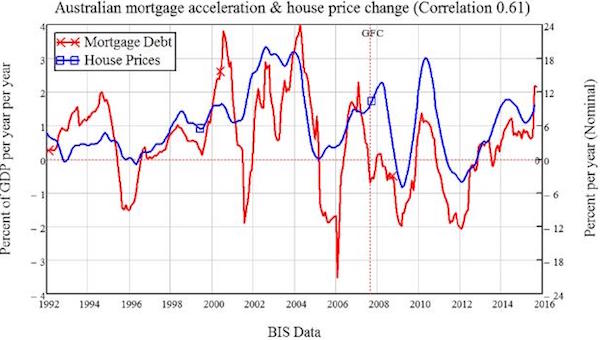
• Muted Inflation A Trillion-Dollar Puzzle – BIS (R.)
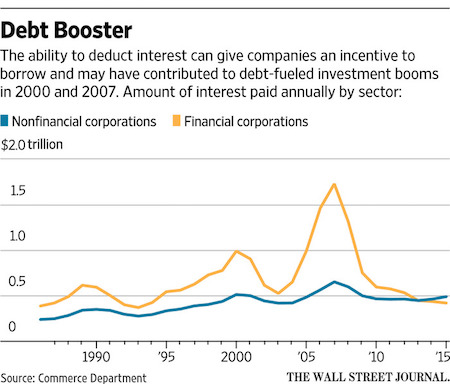
The conundrum of stubbornly low inflation despite a pick-up in global growth and continued monetary stimulus is a “trillion dollar” question, the umbrella body for the world’s leading central banks said on Sunday. The Bank for International Settlements (BIS) said in its latest quarterly report that cheap borrowing rates and the rare simultaneous expansion of advanced and developing economies are driving financial markets higher, with signs of “exuberance” starting to re-emerge. U.S. corporate debt is much higher than before the financial crisis and a drop in the premiums investors demand for riskier lending has boosted sales of so-called covenant-lite bonds offering high yields. The BIS said this raises a question over the potential for another crisis if there is a significant rise in interest rates.
The body has called for a gradual return to higher rates, though central banks are being tentative because of persisting low inflation. “It feels like ‘Waiting for Godot’,” said Claudio Borio, the head of the monetary and economic department of the BIS, referring to a play in which the main characters wait for someone who never arrives. But the BIS says no one has yet worked out why inflation has remained so subdued while economies have approached or surpassed estimates of full employment and central banks have provided unprecedented stimulus. “This is the trillion-dollar question that will define the global economy’s path in the years ahead and determine, in all probability, the future of current policy frameworks,” Borio said. “Worryingly, no one really knows the answer.”

The BIS is surprised by lack of inflation, or does it pretend that? And it’s also surprised by swaps and forwards? Really?
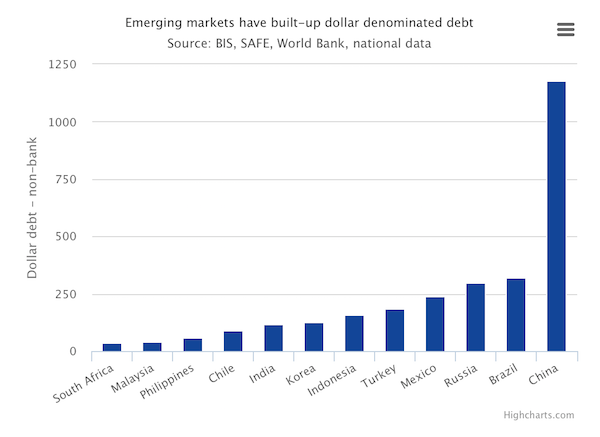
• Global Debt Underreported By $14 Trillion – BIS (ZH)
In its latest annual summary published at the end of June, the IIF found that total nominal global debt had risen to a new all time high of $217 trillion, or 327% of global GDP…
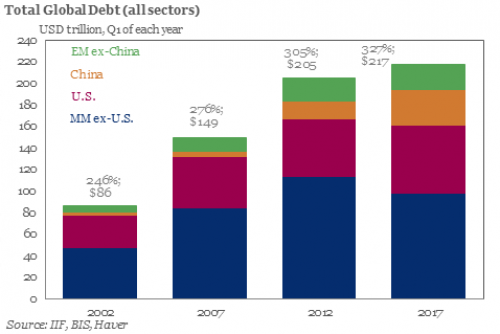
… largely as a result of an unprecedented increase in emerging market leverage.
While the continued growth in debt in zero interest rate world is hardly surprising, what was notable is that debt within the developed world appeared to have peaked, if not declined modestly in the latest 5 year period. However, it now appears that contrary to previous speculation of potential deleveraging among EM nations, not only was this conclusion incorrect, but that developed nations had been stealthily piling on just as much debt, only largely hidden from the public eye, in the form of swaps and forwards.
According to a just released analysts by the Bank of International Settlements, “FX swaps and forwards: missing global debt?” non-banks institutions outside the United States owe large sums of dollars off-balance sheet through instruments such as FX swaps and forwards. The BIS then calculates what balance sheets would look like if borrowing through such derivative instruments was recorded on-balance sheet, as functionally equivalent repo debt, and calculates that the total “is of a size similar to, and probably exceeding, the $10.7 trillion of on-balance sheet dollar debt”, potentially as much as $13-14 trillion.
[..] “Every day, trillions of dollars are borrowed and lent in various currencies. Many deals take place in the cash market, through loans and securities. But foreign exchange (FX) derivatives, mainly FX swaps, currency swaps and the closely related forwards, also create debt-like obligations. For the US dollar alone, contracts worth tens of trillions of dollars stand open and trillions change hands daily. And yet one cannot find these amounts on balance sheets. This debt is, in effect, missing.”

Who says they’re ignoring it? They’re frantically looking to control it.
• World’s Central Banks Can’t Ignore the Bitcoin Boom – BIS (BBG)
The world’s central banks can’t sit back and ignore the growth in cryptocurrencies as it could pose a risk to the stability of the financial system, according to the Bank for International Settlements. It said central banks will need to figure out whether to issue a digital currency and what its attributes should be, though the decision is most pressing in countries like Sweden where cash use is dwindling. Institutions need to take into account of not only privacy issues and efficiency gains in payment systems, but also economic, financial and monetary policy repercussions, the BIS said in its Quarterly Review. The analysis comes at the end of a rough week for digital currencies, with JPMorgan CEO Jamie Dimon calling bitcoin a “fraud” and China moving to crack down on domestic trading of cryptocurrencies.
But with bitcoin and others gaining in popularity as payment systems go mobile and investors pour in money, central banks are beginning to delve into them and their underlying blockchain technology, which promises to speed up clearing and settlements. At the Bank of England, Mark Carney has cited cryptocurrencies as part of a potential “revolution” in finance. To better understand the system, the Dutch central bank has created its own cryptocurrency, albeit for internal use only. U.S. officials are exploring the matter too, though in March Federal Reserve Governor Jerome Powell said there were “significant policy issues” that needed further study, including vulnerability to cyber-attack, privacy and counterfeiting.
According to the BIS, one option for central banks might be a currency available to the public, with only the central bank able to issue units that would be directly convertible with cash and reserves. There might be a greater risk of bank runs, however, and commercial lenders might face a shortage of deposits. Another question to be resolved would be the question of privacy.

“It’s going to be like the dot-com bust, but on a much more epic scale.”
• Dogecoin Creator On Cryptocurrencies: “Very Bubble. Much Scam. So Avoid.” (NYT)
Jackson Palmer no longer thinks it’s funny to imitate Doge, the internet meme about a Shiba Inu dog whose awe-struck expressions and garbled syntax (e.g. “Wow. So pizza. Much delicious.”) made him a viral sensation several years ago. But if he did, he might channel Doge to offer a few cautionary words for investors who are falling for cryptocurrency start-ups, Silicon Valley’s latest moneymaking craze: Very bubble. Much scam. So avoid. Mr. Palmer, the creator of Dogecoin, was an early fan of cryptocurrency, a form of encrypted digital money that is traded from person to person. He saw investors talking about Bitcoin, the oldest and best-known cryptocurrency, and wanted to find a way to poke fun at the hype surrounding the emerging technology. So in 2013, he built his own cryptocurrency, a satirical mash-up that combined Bitcoin with the Doge meme he’d seen on social media.
Mr. Palmer hoped to use Dogecoin to show the absurdity of wagering huge sums of money on unstable ventures. But investors didn’t get the joke and bought Dogecoin anyway, bringing its market value as high as $400 million. Along the way, the currency became a magnet for greed and attracted a group of scammers and hackers who defrauded investors, hyped fake products, and left many of the currency’s original backers empty-handed. Today, Mr. Palmer, 30, is one of the loudest voices warning that a similar fate might soon befall the entire cryptocurrency industry. “What’s happening to crypto now is what happened to Dogecoin,” Mr. Palmer told me in a recent interview. “I’m worried that this time, it’s on a much grander scale.”
[..] Mr. Palmer, a laid-back Australian who works as a product manager in the Bay Area and describes himself as “socialist leaning,” was disturbed by the commercialization of his joke currency. He had never collected Dogecoin for himself, and had resisted efforts to cash in on the currency’s success, even turning down a $500,000 investment offer from an Australian venture capital firm. [..] Mr. Palmer worries that the coming reckoning in the cryptocurrency market — and it is coming, he says confidently — will deter people from using the technology for more legitimate projects. “The bigger this bubble goes, the bigger negative connotation it’s going to have,” he said. “It’s going to be like the dot-com bust, but on a much more epic scale.”

Peters is the CIO at One River Asset Management. “Once private markets perfect cryptocurrency technology, governments will commandeer it, killing today’s pioneers. Then with every cryptodollar, yen, euro and renminbi registered on their servers, they’ll have complete dominion over money, laundering, taxation.”
• The Future Of Cryptocurrency Is Not As It Seems (Eric Peters)
“Any other thoughts on the matter?” he asked. We’d spent quite some time discussing Bitcoin, Ethereum, and copycat cryptocurrencies popping up faster than North Korean nukes. I mostly listened, he knew far more about the subject; blockchain, distributed ledgers, mining, halving, hash rates. Unlike the S&P 500 realized volatility’s collapse to 8%, these new creations are realizing at 90%. Which makes them attractive to day-traders, adrenaline junkies, who launched 100 crypto hedge funds just last month. It’s the millennial’s wild west. Like all generations, they’ve discovered a new frontier, with few rules, seedy saloons, gunfights, corpses. As our earthly unknowns disappear, we find new ones in the ether. Which is where money belongs; it’s not real, it’s an abstraction, an age-old illusion.
As a golden myth captured mankind’s imagination, we built our societies upon a rare yellow metal. For 2,500 years we fought, killed, conquered. Until governments tired of the arbitrary spending constraints imposed upon them by a scarce element. So they invented today’s fiction, a printed promise, fiat currency. Seigniorage is the difference between that currency’s market value and its cost of production – that spread is a source of vast wealth and power. And in all human history, not a single government has willingly forfeited such a thing. Nor will one ever. Only after a hyperinflationary depression, confronted with revolution, do governments sometimes relinquish their power to print (Zimbabwe most recently).
Consequently, the future of cryptocurrency is not as it seems. Once private markets perfect cryptocurrency technology, governments will commandeer it, killing today’s pioneers. Then with every cryptodollar, yen, euro and renminbi registered on their servers, they’ll have complete dominion over money, laundering, taxation. They’ll track every transaction. Imposing negative interest rates in an instant. There will be no hiding, no mattresses. And in a deflationary panic, they’ll instantaneously add an extra zero to every account, their own especially.

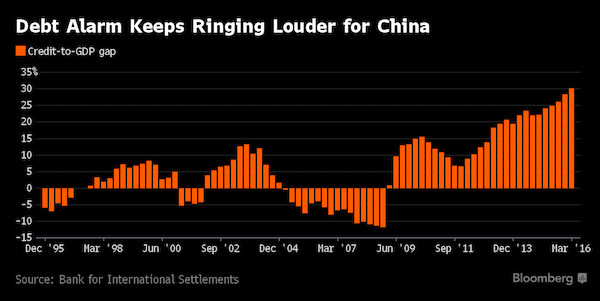
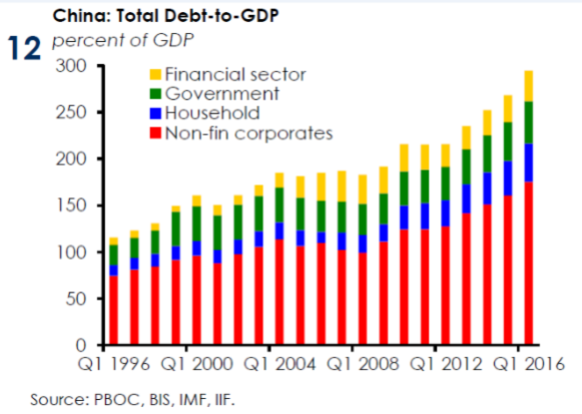
“..we’re on a $40 trillion credit system on $2 trillion of equity on maybe $1 trillion of liquid reserves.”
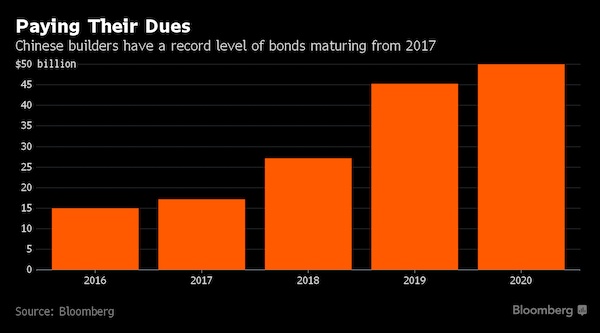
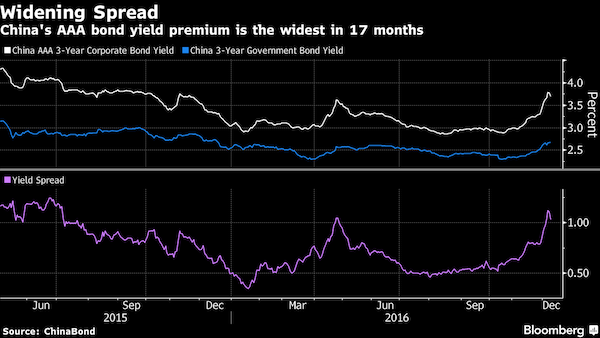
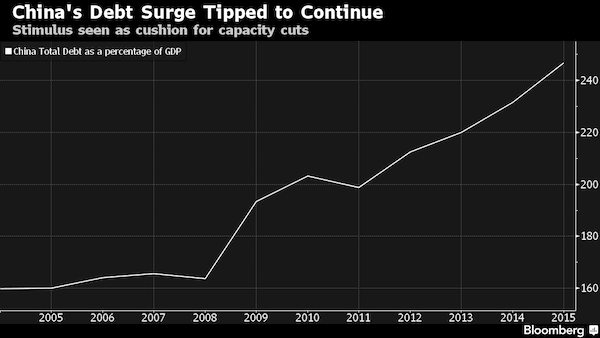
• China’s $40 Trillion Banking System: “Largest Imbalances I’ve Ever Seen” (ZH)
KB: We’re in the such late stages of a game that is the largest global imbalance I’ve ever seen in my life. When you look at on balance sheet and off balance sheets, you look at on balance sheet in the banks, you look in the shadow banks. The number of total credit in the system, China is right at $40 trillion. Think about the number I just said. $40 trillion. And that’s using an exchange rate of call it 6.7 to the dollar, right? So it’s grown 1,000% in a decade. And we’re on a $40 trillion credit system on $2 trillion of equity on maybe $1 trillion of liquid reserves.
RP: Where do you get the equity and liquid reserves from?
KB: Well, it’s the amount of equity in the banks of China. It’s right at about $2 trillion. So that’s kind of a stated number. The reserves is my own calculation, right? The Chinese magically have leveled their reserves out around $3 trillion, which happens to be the minimum level of IMF reserve adequacy as defined by the IMF rule.
RP: So what have they been doing now? So, they were under pressure, and then everything kind of eased off, I guess, as the dollar started weakening a bit.
KB: Yeah. Actually, they’ve done three things. Well, so four things have caused this, quote, easing off that you refer to. Three have been driven by SAFE and the PBOC, one that’s been driven by our illustrious Trump. So the first three are, number one, they essentially halted all cross-border M&A. So if you look at the parabola of M&A coming out of China from 2012 to 2016, it reached dizzying heights in 2016. In 2017, it’s like 15% of the 2016 number and no new deals being announced. Now, they’ll always be some outbound M&A that’s driven by really policy at the Communist Party level, right?
They’ll always buy copper mines in Uganda. They’ll always invest in ports in Greece. They’ll always do things that are from a strategic perspective and a policy perspective. The things that the Communist Party needs to procure resources for its people over the long-term. But when you look at the rampant M&A of money leaving China, they just put a halt to it in November of 2016. And the second thing they did was they made it impossible for multinational corporations to get their profits and or working capital out of China. And that’s something that has been a problem for a lot of the multinationals that do business in China.”

Perma bear.
• Stockman: Trump’s Now ‘Blowing Kisses to Janet Yellen’
Stockman: Trump’s ‘Done Nothing in Nine Months’ and Is Now ‘Blowing Kisses to Janet Yellen’ (Fox Business, September 15, 2017)

EU, UN, US, nobody stands up for democracy. Revealing.
• Spain’s Prosecutor Warns Over Catalonia Referendum As Leaflets Seized (R.)
Spanish authorities on Sunday pursued efforts to block an independence vote in Catalonia, seizing campaign materials as the chief prosecutor said jailing the region’s top politician could not be ruled out. The government in the northeastern region is intent on holding a referendum on October 1 that will ask voters whether they support secession from Spain, a ballot Madrid has declared illegal. In a raid on a warehouse in the province of Barcelona on Sunday, police confiscated around 1.3 million leaflets and other campaign materials promoting the vote issued by the Catalan government. The haul was the largest in a series of similar raids, the Interior Ministry said in a statement.
Spanish prosecutors, who have ordered police to investigate any efforts to promote the plebiscite, said last week that officials engaged in any preparations for it could be charged with civil disobedience, abuse of office and misuse of public funds. More than 700 Catalan mayors gathered in Barcelona on Saturday to affirm their support for it. Asked if arresting regional government head Carles Puigdemont was an option if preparations continued, Spain’s chief public prosecutor said in an interview: ”We could consider it because the principal objective is to stop the referendum going ahead. “I won’t rule out completely the option of seeking jail terms… It could happen under certain circumstances,” Jose Manuel Maza was quoted as also telling Sunday’s edition of newspaper El Mundo.

Promising.
• After Single Payer Failed, Vermont Embarks On Big Health Care Experiment (WP)
Doug Greenwood lifted his shirt to let his doctor probe his belly, scarred from past surgeries, for tender spots. Searing abdominal pain had landed Greenwood in the emergency room a few weeks earlier, and he’d come for a follow-up visit to Cold Hollow Family Practice, a big red barnlike building perched on the edge of town. After the appointment was over and his blood was drawn, Greenwood stayed for an entirely different exam: of his life. Anne-Marie Lajoie, a nurse care coordinator, began to map out Greenwood’s financial resources, responsibilities, transportation options, food resources and social supports on a sheet of paper. A different picture began to emerge of the 58-year-old male patient recovering from diverticulitis: Greenwood had moved back home, without a car or steady work, to care for his mother, who suffered from dementia. He slept in a fishing shanty in the yard, with a baby monitor to keep tabs on his mother.
This more expansive checkup is part of a pioneering effort in this New England state to keep people healthy while simplifying the typical jumble of private and public insurers that pays for health care. The underlying premise is simple: Reward doctors and hospitals financially when patients are healthy, not just when they come in sick. It’s an idea that has been percolating through the health-care system in recent years, supported by the Affordable Care Act and changes to how Medicare pays for certain kinds of care, such as hip and knee replacements. But Vermont is setting an ambitious goal of taking its alternative payment model statewide and applying it to 70% of insured state residents by 2022 which — if it works — could eventually lead to fundamental changes in how Americans pay for health care.
“You make your margin off of keeping people healthier, instead of doing more operations. This drastically changes you, from wanting to do more of a certain kind of surgery to wanting to prevent them,” said Stephen Leffler, chief population health and quality officer of the University of Vermont Health Network. Making lump sum payments, instead of paying for each X-ray or checkup, changes the financial incentives for doctors. For example, spurring the state’s largest hospital system to invest in housing. Or creating more roles like Lajoie’s, focused on diagnosing problems with housing, transportation, food and other services that affect people’s well-being.

The Troika is in Athens to turn on the thumbscrews.
• Greek Government Told To Begin Online Auctions Or Face A Bank Bail-In (K.)
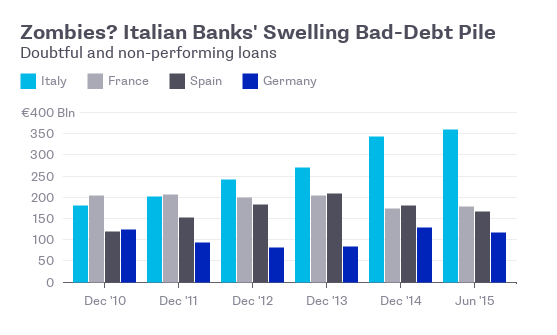
The possibility that banks will need for a fresh recapitalization grows with every day the delay in the implementation of online property transactions drags on. This might lead to a deposit haircut, along with generating a major crisis in relations between the government and the country’s creditors. Creditor representatives are accusing the government of delay tactics, for party political purposes, in starting electronic auctions. This puts the sustainability of the credit system at risk as it denies them a crucial tool in efforts to tackle the problem of nonperforming loans (NPLs).
The creditors have explicitly warned Athens about the prospect of a new recapitalization and the risk of a bail-in for banks and their depositors unless the auctions proceed quickly, as their representatives told notaries and banks in Greece during the presentations of the auctions’ online platform, according to the president of the Notaries’ Association, Giorgos Rouskas. The creditors reacted strongly when told that the first online auctions would not take place before early 2018 even though during the second bailout review Athens had committed to start the auctions on September 1. The government claimed the system is in place but the law provides for a period of two months between the submission of an auction request and its realization.
Seeing that the government is again trying to renege on its commitments, the creditors put fresh pressure on Athens, which backed down and said the system may open in the coming days for banks, so that the first online auctions can take place by end-November. In an interview with Kathimerini, Rouskas stressed that “the online platform is ready and all technical tests have been completed.” The onus is therefore on the banks now, which Rouskas explains have to register the repeat auctions or any new ones in the system, being the party initiating the auctions. They will then get a date based on the new system. “We have prepared the platform. It is now up to the lender, be that a bank or a private individual, to issue a request for an online auction scheduling, which notaries are forced to follow. This has not happened yet, but I believe we are very close to its implementation,” said Rouskas.

Why Greece will not recover. Money supply way down, money velocity way way down.
• In Greece, Full-Time Work Is Not The Norm It Once Was (K.)
Official data by the Hellenic Statistical Authority point to an increase in employment by about 250,000 jobs in the last three years (from the second quarter of 2014 to this year’s Q2), but that is only part of the truth. The figures also reveal a constant decline in average salaries, an ongoing increase in the percentage of employed workers who earn less than 500 euros a month – at least one in four gets less than that amount – soaring temporary work (either due to project-specific hirings, subsidies being paid for a restricted period, or time contracts), and a rise in the rate of part-time employment.
Senior and top officials are no longer offered such handsome pay packages, the primary sector is being abandoned and any new enterprises that are being set up are mostly in the field of restaurants, hotels and retail stores. Greeks can only find jobs such as waiters, cleaners, maids or sales assistants, which as a rule are of a seasonal character and fetch a low salary. The 40-hour working week concerns ever fewer workers nowadays, and without the subsidies handed out by the Manpower Organization (OAED) and the increase in tourism flows the unemployment rate probably wouldn’t have declined at all.

The season is far from over.
• Hurricane Maria Heading For Caribbean (AFP)
Maria became a hurricane Sunday as it headed toward the storm-staggered eastern Caribbean with 75 mile (120 kilometer) per hour winds, the US National Hurricane Center said. Storm warnings and watches went up in many of the Caribbean islands still reeling from the destructive passage of Hurricane Irma earlier this month. As of 2100 GMT, Maria was a Category One hurricane, the lowest on the five point Saffir-Simpson scale, located 140 miles (225 kilometers) northeast of Barbados, the NHC said, bearing west-northwest at 15 miles (24 kilometers) an hour. “On the forecast track, the center of Maria will move across the Leeward Islands Monday night and then over the extreme northeastern Caribbean Sea on Tuesday,” it said.
Hurricane warnings were triggered for St Kitts, Nevis and Montserrat, while lesser ‘watches’ were issued for the US and British Virgin Islands where at least nine people were killed during Irma. A warning is typically issued 36 hours before the first occurrence of tropical storm-force winds while watches are issued 48 hours in advance. Tropical storm warnings were, meanwhile, issued for Martinique, Antigua and Barbuda, Saba and St Eustatius and St Lucia. Barbuda was decimated by Hurricane Irma September 5-6 when it made its first landfall in the Caribbean as a top intensity Category Five storm. The NHC said Maria could produce a “dangerous storm surge accompanied by large and destructive waves” that will raise water levels by four to six feet (1.2 to 1.8 meters) when it passes through the Leeward Islands.