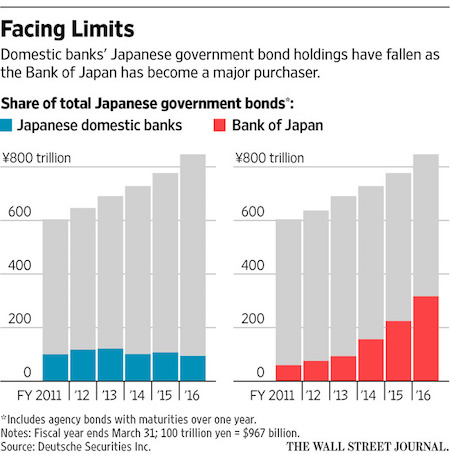
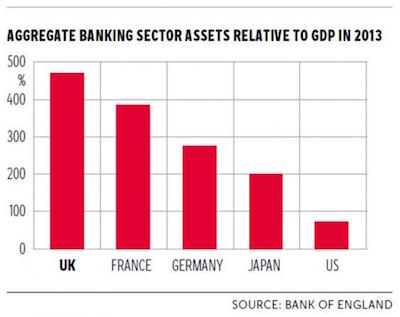
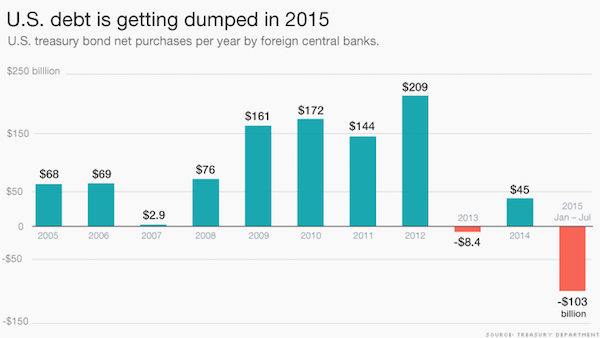
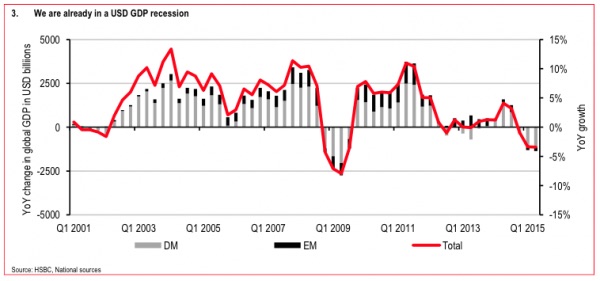
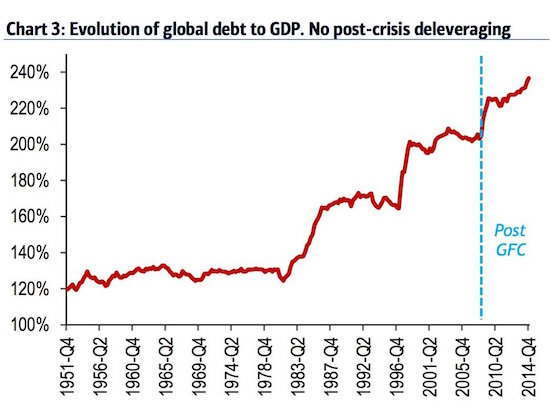
NPC “Poli’s Theater, Washington, DC. Now playing: Edith Taliaferro in “Keep to the Right” Jul 1920



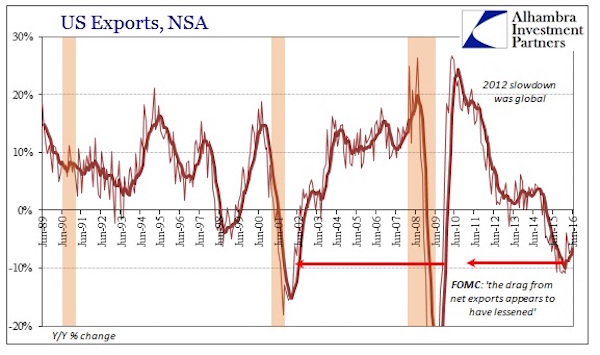
Hilarious. Flood the markets even more, bring down the price further, and then find you can’t make any money with your exports. And stop talking about OPEC ‘strategy’ already. Start thinking about US strategy.
• US Opening Door to More Oil Exports Seen Foiling OPEC Strategy (Bloomberg)
The Obama administration’s move to allow exports of ultralight crude without government approval may encourage shale drilling and thwart Saudi Arabia’s strategy to curb U.S. output, further weakening oil markets, according to Citigroup Inc. A type of crude known as condensate can be exported if it is run through a distillation tower, which separates the hydrocarbons that make up the oil, according to U.S. government guidelines published yesterday. That may boost supplies ready to be sold overseas to as much as 1 million barrels a day by the end of 2015, Citigroup analysts led by Ed Morse in New York said in an e-mailed report. Saudi Arabia led the Organization of Petroleum Exporting Countries to maintain its production quota at a meeting last month even as a shale boom boosted U.S. output to the highest in more than three decades. That prompted speculation OPEC was willing to let prices fall to force some companies with higher drilling costs to stop pumping.
“U.S. producers are under the gun to reduce capital expenditures given lower prices,” Citigroup said in the report. “Now an export route provides a new lease on life that can further weaken crude oil markets and throw a monkey wrench into recent Saudi plans to cripple U.S. production.” Current U.S. export capacity is at about 200,000 barrels a day, which could be expanded to 500,000 a day by the middle of 2015, according to the bank. While the guidelines on the website of the Commerce Department’s Bureau of Industry and Security are the first public explanation of steps companies can take to avoid violating export laws, they don’t mean an end to the ban on most crude exports, which Congress adopted in 1975 in response to the Arab oil embargo. “While government officials have gone out of their way to indicate there is no change in policy, in practice this long-awaited move can open up the floodgates to substantial increases in exports by end-2015,” Citigroup said.
The U.S. produces about 3.81 million barrels a day of light and ultralight crude, according to the bank. West Texas Intermediate in New York dropped as much as 1.4% today to $53.38 a barrel, down 46% this year. Brent, the global marker crude, slid 1.8% to $56.87 in London, bringing losses in 2014 to 48%. Both benchmark grades are headed for the biggest annual slump since 2008. Oil producers have been testing the prohibition on crude exports as U.S. output surged amid technological advances that have opened up shale rock formations to development in Texas, North Dakota and elsewhere. The government earlier this year signaled a new way to export oil by approving permits for Pioneer and Enterprise to sell processed condensate. The guidelines seek to clarify how the Commerce Department will implement export rules and follow a “review of technological and policy issues,” Eric Hirschhorn, the under secretary for industry and security, said in a statement.
Read more …

“This time though it’s not about a flight to safety. Investors are flocking to the dollar because they like it. The U.S. economy has outperformed and American assets are in vogue.”
• The Market Chart Of The Year: Nope, It’s Not Oil (CNBC)
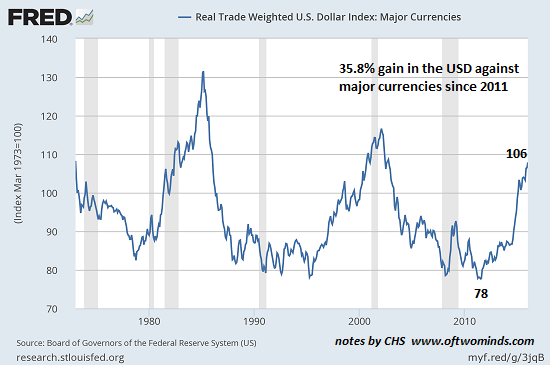
There are many strong contenders to be the chart of the year. Some point to oil prices, which shockingly plunged 50% in a matter of months. Others would look to the S&P 500, which exploded higher for a third year in row and has closed at a record high 53 times (so far), more than 20% of 2014’s trading days. They’re each compelling stories, but neither is as impactful nor as important as the breakout of the U.S. dollar. Presenting the chart of 2014: the broad trade-weighted dollar. The trade-weighted dollar tracks the U.S. greenback’s value against a basket of other currencies, representing both developing and emerging markets. It’s a broader measure than the regularly cited dollar index and the best indication of how a strong dollar hurts American companies that do business overseas.
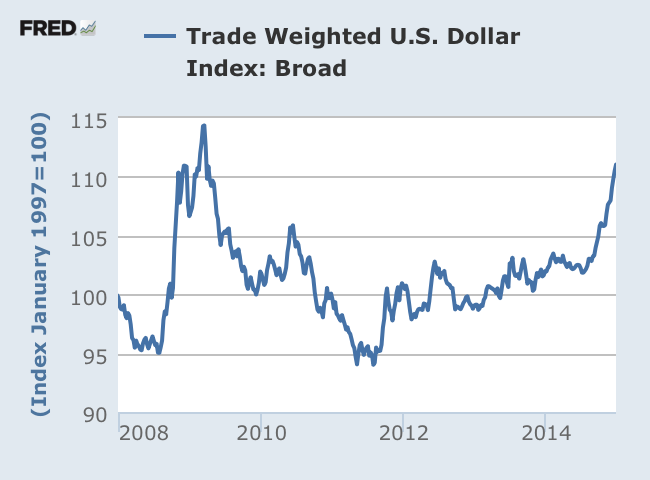
The broad trade-weighted dollar is up 9% this year, now at the highest point since March 2009, when financial crisis fears had risk-averse investors pouring into the U.S. currency. It’s well above its average historical price over the last 15 years and now just 3.6% away from reaching those crisis highs. This time though it’s not about a flight to safety. Investors are flocking to the dollar because they like it. The U.S. economy has outperformed and American assets are in vogue. The move has been absolutely stunning. Break apart the trade-weighted dollar into individual pairs – the currency has strengthened nearly 12% against the euro this year, 13% against the yen and 18 to 19% against the Norwegian and Swedish currencies. The move is more dramatic when weighed against the trouble spots of 2014. The dollar has gained 44% versus the Russian ruble and 24% versus the Argentine peso. In fact, the U.S. greenback has strengthened against all developed and emerging currencies in the past 12 months.
“The rise of the U.S. dollar in 2014 is remarkable both by its intensity and weak support from expectations of Fed tightening,” according to Sebastien Galy, FX strategist at Societe Generale. “It tells us much about the intensity with which other central banks have tried to weaken their currencies,” he said. In other words, it’s not just a story of U.S. economic strength in the face of global weakness, but also the contrast to major central banks seeking to weaken their own currencies in the name of growth and export competitiveness. That trend should continue in the new year and ultimately fuel more worrisome trade tensions.
“The odds are that the U.S. dollar strength can go much further than currently expected, similarly the odds of … trade barriers are steadily rising,” Galy warned. As if that wasn’t enough, expectations that the Fed will begin to raise interest rates in the second half of 2015 have many believing the dollar has plenty of room to run. “The strength of the U.S. labor market and U.S. economy are making the Fed more confident that it can begin to raise rates next year,” wrote Lee Hardman, currency strategist at Bank of Tokyo Mitsubishi in a note after the last Fed meeting in mid-December. “The market is still not convinced that the Fed will tighten even at that more modest pace … leaving scope for U.S. short rates to continue to increase in the year ahead, supporting a stronger U.S. dollar.” Beyond the stunning breakout of the buck, the move is significant because the dollar is the backbone of the global financial system. It influences prices of all major commodities, the largest and most liquid debt and equity markets, and the world’s largest economy.
Read more …

Much more to come.
• Commodities Head for Record Losing Run on Oil to Dollar (Bloomberg)
Commodities headed for the biggest annual loss since the global financial crisis in 2008, retreating for a record fourth year, as a global glut spurred a rout in oil prices and a stronger dollar cut the allure of raw materials. The Bloomberg Commodity Index dropped to the lowest level since March 2009 earlier today. It’s lost 16% this year, with crude, gasoline and heating oil the biggest decliners. A fourth year of losses would be the longest since at least 1991. Energy prices retreated in 2014 as a jump in U.S. drilling sparked a surge in output and price war with OPEC, which chose to maintain supplies to try to retain market share. The dollar climbed to the highest level in more than five years as a U.S. recovery spurred speculation that the Federal Reserve will start to raise borrowing costs next year. Commodities are set for a volatile year in 2015, with crude oil poised to extend its slump, according to Australia and New Zealand Bank.
“What we’re seeing is that supplies from North America have really outpaced worldwide demand growth and as a result, we have a supply glut,” Andy Lipow, president of Lipow Oil, said by phone. “And that of course has put pressure on prices over the last several months. And as a result, it’s dragging down commodities indexes as well.” Brent for February settlement traded at $57.01 a barrel on the London-based ICE Futures Europe exchange, with rice 49% lower this year. West Texas Intermediate dropped 1.1% to $53.55 a barrel on the New York Mercantile Exchange. Gasoline sank 49% this year. A slowdown in China also hurt demand for raw materials as policy makers grappled with a property slowdown, and data today showed a factory gauge at a seven-month low in December. The world’s biggest user of metals is headed for its slowest full-year economic expansion since 1990. China’s central bank cut interest rates last month for the first time since 2012.
Read more …

Bring back Sarah!
• As Oil Prices Fall, Alaska Governor Halts Project Spending (AP)
With oil prices dropping, Alaska Gov. Bill Walker has halted new spending on six high-profile projects, pending further review. Walker issued an order Friday putting the new spending on hold. He cited the state’s $3.5 billion budget deficit, which has increased as oil prices have dropped sharply. With oil prices now around a five-year low, officials in Alaska and about a half-dozen other states already have begun paring back projections for a continued gusher of revenues. Spending cuts have started in some places, and more could be necessary if oil prices stay at lower levels. How well the oil-rich states survive the downturn may hinge on how much they saved during the good times, and how much they depend on oil revenues.
Some states, such as Texas, have diversified their economies since oil prices crashed in the mid-1980s. Others, such as Alaska, remain heavily dependent on oil and will have to tap into sizeable savings to get by. The projects Walker halted spending on include a small-diameter gas pipeline from the North Slope, the Alaska Dispatch News reported. The other projects are the Kodiak rocket launch complex, the Knik Arm bridge, the Susitna-Watana hydroelectric dam, Juneau access road and the Ambler road. “The state’s fiscal situation demands a critical look and people should be prepared for several of these projects to be delayed and/or stopped,” Walker’s budget director Pat Pitney said in an email.
According to Walker’s order, the hold on spending is pending further review. The administration intends to decide on project priorities near the start of Alaska’s legislative session Jan. 20, and no later than a Feb. 18 legal budgeting deadline, Pitney said. State lawmakers have final authority to decide whether the projects should continue to be funded, Pitney said. Contractually required spending and employee salaries will continue. Walker’s order asks each agency working on the projects to stop hiring new employees, signing new contracts and committing any new funding from other sources, including the federal government. The action follows a letter sent Tuesday by the state Legislature’s Republican leadership, who urged the governor to immediately cut spending levels in light of the budget crunch.
Read more …

Why is this so hard to understand?
• Falling Energy Costs And Economic Impacts (STA)
“If you repeat a falsehood long enough, it will eventually be accepted as fact.” In the financial markets and economics it is a common occurrence that the media and commentators will latch on to a statement that supports a cognitive bias and then repeat that statement until it is a universally accepted truth. When such a statement becomes universally accepted and unquestioned, well, that is when I begin to question it. One of those statements has been in regards to plunging oil prices. The majority of analysts and economists have been ratcheting up expectations for the economy and the markets on the back of lower energy costs. The argument is that lower oil prices lead to lower gasoline prices that give consumers more money to spend. The argument seems to be entirely logical since we know that roughly 80% of households in America effectively live paycheck-to-paycheck meaning they will spend, rather than save, any extra disposable income. As an example, Steve LeVine recently wrote:
“US gasoline prices have dropped for more than 90 straight days. They now average $2.28 a gallon, which is remarkable considering that just a few months ago, some of us were routinely paying $4 and sometimes close to $5. Not so coincidentally, the US economy surged by 5% last quarter, and does not appear to be slowing down. “
If you read the statement, how could one possibly disagree with such a premise? If I spend less money at the gas pump, I obviously have more money to spend elsewhere. Right? The problem is that the economy is a ZERO-SUM game and gasoline prices are an excellent example of the mainstream fallacy of lower oil prices.
Example:
• Gasoline Prices Fall By $1.00 Per Gallon
• Consumer Fills Up A 16 Gallon Tank Saving $16 (+16)
• Gas Station Revenue Falls By $16 For The Transaction (-16)
• End Economic Result = $0
Now, the argument is that the $16 saved by the consumer will be spent elsewhere. This is the equivalent of “rearranging deck chairs on the Titanic.” Increased consumer spending is a function of increases in INCOME, not SAVINGS. Consumers only have a finite amount of money to spend.
Read more …

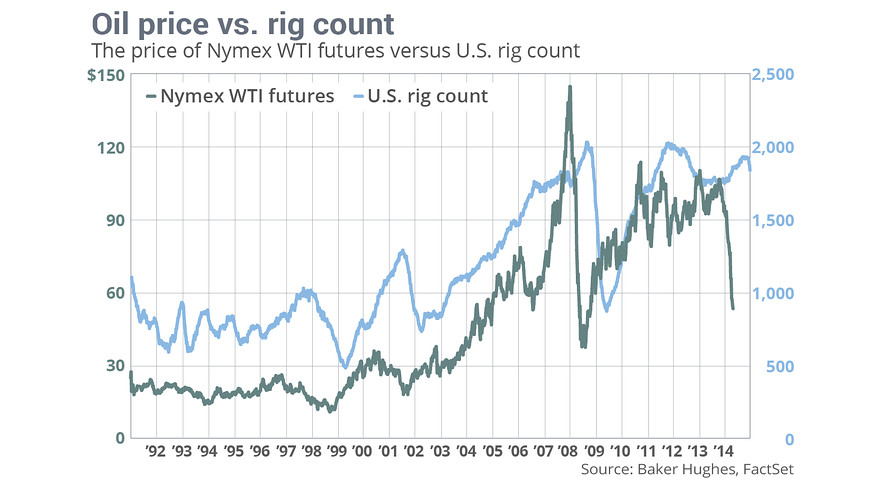
If you ask me, if there’s one thing this chart shows, it’s how much further the rig count has to fall.
• Chart Shows How US Drillers Respond To Oil Price Drop (MarketWatch)
It’s no surprise that the number of U.S. oil rigs moves up and down with the price of oil, but the chart above offers an interesting glance at the relationship. Baker Hughes on Monday said the total number of U.S. rotary rigs fell by 35 to 1,840 in the week ended Dec. 26, the fifth consecutive weekly decline, bringing the total to its lowest level since April. “If OPEC’s goal is to slow U.S. oil production by dumping cheap oil into our market, they are having some success,” said Phil Flynn, senior market analyst Price Futures in Chicago. OPEC in November accelerated oil’s free fall when it refrained from cutting crude production. Saudi Arabia’s oil minister said earlier this month that a plunge to as low as $20 wouldn’t be enough to prompt a production cut.
The move has been described as a price war aimed primarily at North American shale producers, who had responded to high oil prices by ramping up production in recent years at a breakneck clip. Oil’s slide, which has seen Nymex futures, the U.S. benchmark, fall 50% from their June high above $107 to trade at five-and-a-half year lows below $54 a barrel, has been the fastest since 2008. That means rig counts will continue to decline, but the impact on supply will likely take “weeks if not months” to be reflected in hard production figures, said analysts at Commerzbank.
Read more …

“Europe’s government bond markets all closed on Tuesday after another stellar year that has seen Italian and Spanish borrowing costs hit record lows and unglamorous but ultra-safe German debt enjoy its strongest year in six.”
• Chinese Stocks, Dollar And Debt The Stars Of 2014 (Reuters)
Chinese and U.S. stocks headed the list of 2014 top performers while markets elsewhere ended the year on Wednesday on a cautionary note as worries about Greece’s future served as an excuse to take profits. The U.S. dollar lost a little of the recent gains that have made it the year’s star major currency, but European bonds yields scored all-time lows following a shockingly sharp fall in Spanish inflation on Tuesday. European stocks had a steady start as they wrapped up a year that has seen a 3.5% rise for the region as a whole but also sharp divergence, with near 30% losses for debt-strained Greece and Portugal. The stand-out global equity performer has been China, where the CSI300 index looked set to end 2014 with gains of nearly 50%.
Almost all of China’s rise came in the last couple of months, as hopes for more aggressive policy stimulus to counter its economic slowdown boosted banks and brokerages. Featuring on Wednesday were hefty gains for China’s biggest train makers, China CNR and CSR Corp, after they confirmed a $26 billion merger. “China stocks have done really well this year and the dollar move has also been very interesting,” said Alvin Tan, an FX strategist at Societe Generale in London. “It barely moved against the other major currencies in the first of the year and all the big gains came in the second half.” Trade elsewhere was thinned by holidays in Japan, Thailand, South Korea and the Philippines, while many markets in Europe were either shut or finishing early.
Europe’s government bond markets all closed on Tuesday after another stellar year that has seen Italian and Spanish borrowing costs hit record lows and unglamorous but ultra-safe German debt enjoy its strongest year in six. Among the scraps of news in Europe, two polls in Greece published late on Tuesday showed the anti-bailout party Syriza’s lead over the ruling conservatives had narrowed. The dollar was on track to end 2014 with a gain of 12% against a basket of major currencies, its best performance since 2005, and anticipated U.S. interest rate hikes may strengthen its appeal in the new year. It eased against the safe haven yen to stand at 119.64 from Tuesday’s peak of 120.69, as futures prices pointed to small gains for Wall Street when trading resumes following its 13% jump to an all-time high this year. The euro was undermined by sliding European yields amid intense speculation the European Central Bank will have to start buying government bonds to avert deflation. The single currency was stuck at $1.2154 having touched a 29-month trough of $1.2123.
Read more …

But it’s how they’ll be portrayed.
• We’re Not Communists, Greek Opposition Insists (CNBC)
Accusations that Greece’s far-left opposition party Syriza is “worse than communism” are propaganda, its head of economic policy insisted on Tuesday, arguing instead that the party would solve Greece’s “humanitarian crisis” if it came to power in January. Speaking to CNBC on Tuesday, John Milios said Syriza planned to stabilize Greece’s society and boost the economy. “We have to combat first the humanitarian crisis, people who don’t have the necessities — houses, food or the money for transportation,” he said. “We are confident that if we do this the economy will start to stabilize and the present turmoil will be past.” Greece’s political establishment was thrown into chaos on Monday, when its parliament’s failure to elect a president triggered an early general election – something that credit ratings agency Fitch warned on Tuesday would increase the risks to the country’s credit worthiness.
Anti-austerity Syriza appears confident that it can win the forthcoming election in January, however. Opinion polls released late on Monday showed Syriza had a 3% lead over Prime Minister Antonis Samaras’ party, although the lead has narrowed of late. But although attractive to voters, the party does not appear to be popular within the investment community. In November, an email written by Joerg Sponer, an investment analyst at Capital Group, was leaked in which he said Syriza’s policies were “worse than communism.” Sponer reportedly wrote the email after attending a conference in London in which Milios presented the party’s economic manifesto. But Milios was quick to defend his policies, saying that such comments were “government propaganda.” “This saying that we are worse than communists was not something that represented the whole climate of discussions in London. I think this… had to do with the present government and to do with propaganda,” he told CNBC Europe’s “Squawk Box” on Tuesday.
Investors are particularly concerned that a Syriza-led government could result in the undoing of the austerity policies implemented under Samaras’ present government. The party has always said it would “tear up” the tough conditions of Greece’s bailout, which were required by the troika of international creditors, the EU, IMF and ECB. The Athens stock exchange fell up to 10% on Monday, before paring some losses, and was trading 0.3% lower on Tuesday. Meanwhile, Greece’s borrowing costs remained above 9.5%. With a public debt to GDP ratio of 175.5%, the country has the highest debt in the euro zone, but Greece’s politicians are keen to calm European lenders that Greece isn’t about to default – or leave the single currency union.
Read more …

Start the horror campaign.
• ‘Snap Elections Will Be Decisive For Greece’s Eurozone Future’ (Guardian)
Next month’s snap elections in Greece will be decisive for the country’s future in the eurozone, the prime minister, Antonis Samaras, said on Tuesday after requesting parliament’s dissolution. “People don’t want these elections and they aren’t necessary,” the beleaguered leader told the nation’s outgoing head of state Karolos Papoulias. “They are happening because of party self-interest … and this struggle will determine whether Greece stays in Europe.” Signalling market concerns, credit rating agency Fitch said prolonged political uncertainty could “increase the risks to Greece’s creditworthiness”. The country was forced into holding early elections after parliament failed on Monday to endorse Stavros Dimas, the government’s candidate for president.
With the debt-burdened country dependent on international rescue funds, officials said the radical left main opposition Syriza party would “pay a heavy price” for triggering the elections after joining forces with the far-right Golden Dawn to block Dimas from becoming president. Late on Monday the IMF said it would suspend aid instalments until after the 25 January poll. “People will punish those who have triggered this unnecessary turmoil, because it is obvious that Syriza has no solution [to economic problems]. It neither says where it will find the money, nor will it find the money,” said government spokeswoman Sophia Voultepsi, referring to the party’s pledge of wide-ranging social benefits if it wins power.
On the back of popular discontent over gruelling austerity, the price of €240bn (£188bn) in aid, Syriza has led polls since European elections in May. But the gap has narrowed since Samaras gambled by bringing forward the presidential election. An opinion poll on Tuesday showed a 3% lead for Syriza over Samaras’ New Democracy party. This followed the Greek finance minister Gikas Hardouvelis’ warning of economic sanctions by the European Central Bank if the anti-austerity Syriza won. Analysts predicted that Samaras, who has better personal ratings than Syriza’s leader, Alexis Tsipras, could win the elections yet.
Read more …

Deflation is a fact, not a fear.
• Europe Deflation Fears Back After Weak Spain, Greece Data (CNBC)
Fears of deflation in the euro zone were heightened once again on Tuesday, after both Spain and Greece reported worse-than-expected price declines. A flash reading for consumer price index (CPI) inflation in Spain showed that prices fell by 1.1% year-on-year in December. This was below forecasts of a 0.7% drop, and followed November’s decline of 0.5%. Analysts said this month’s fall was mainly driven by weakening oil prices which could mean that other large euro zone members fall victim to deflation soon. “With a Spanish reading this low, euro area inflation might well turn negative as early as December,” said Robert Kuenzel, director of euro area economic research at Daiwa Capital Markets, in a research note on Tuesday.
Meanwhile, data out from Greece showed that producer prices declined 2.3% year-on-year in November way below October’s 0.9% fall. Consumer prices in the country fell by 1.2% in the same period. Kuenzel told CNBC that the producer price drop in Greece was worse than he expected, and was “one of the largest fall we have seen for years.” “As producer prices are more energy price-sensitive, this is still not out of line with today’s downside Spanish CPI surprise, even though that was numerically smaller,” he said via email. Brent crude oil prices fell to a 5-1/2-year low under $57 per barrel on Tuesday, extending losses into a fourth trading session. Oxford Economics has warned that a multitude of European countries face deflation next year if oil prices remain below $60, including the U.K., France, Switzerland and Italy.
Read more …

Bloomberg has it all upside down.
• Will the Real Angela Merkel Please Stand Up? (Bloomberg)
If anything is certain about the new year, it is that much of the world’s stability and economic health will depend on what is done, or not done, in Europe. And what happens in Europe will depend, in large part, on German Chancellor Angela Merkel. Merkel’s leadership in 2014 was a curious mixture of boldness and timidity. It fell to her, more than any other European leader, to confront Russian President Vladimir Putin. And her efforts are what secured the unanimity among the European Union’s 28 fractious nations that was needed to impose meaningful economic sanctions to deter further Russian aggression in Ukraine. Regardless of whether those sanctions ultimately succeed, they have already served an important purpose by helping to hold the EU – with its Russophile Italians and Austrians, its Russophobe Poles and Balts – together.
As helpful as Merkel has been with Russia, however, she has so far only harmed efforts to address the faltering European economy. In 2015, as new elections in Greece bring fresh turmoil, she will need to apply some of the clarity and decisiveness she has showed in dealing with Putin to the euro zone. On both fronts, next year will be harder. Europe’s Russia challenge will get tougher, because the pressure to repeal sanctions will rise. The current measures against Russia begin to expire in March, and many European leaders will be looking for reasons not to renew them as long as something resembling a cease-fire is in place; the reduction in lending, investment and sales to Russia has hurt the European economy as well as the Russian one. Yet until there is a more meaningful settlement that ensures Putin can’t continue his semi-covert war in Ukraine, sanctions need to stay.
As for the EU, new forces for disunion will emerge. U.K. Prime Minister David Cameron will be pushing for changes in the way the bloc works that help him persuade Britons to vote against leaving it. Merkel will need to simultaneously rein Cameron in and convince other EU leaders that it would be in their interests, too, to return some powers to national governments. At the same time, the euro crisis threatens to heat up again. The favorite to win early elections in Greece next month, the neo-Marxist Syriza party, says it will refuse to carry out the further austerity measures required for the country’s remaining bailout funds. Syriza also promises to roll back economic reforms that were put in place under the terms of the country’s 240 billion euro loan program, as well as to demand a restructuring of the country’s enormous public debt. Europe’s banking system may not be as vulnerable to a Greek default as it once was, but markets have been jittery at the revived possibility of a Greek exit from the euro.
So far, Merkel has resisted relenting on austerity policies for Greece. She has been unwilling to stimulate demand in the euro area, either by boosting investment in Germany’s own low-growth economy or by letting the European Central Bank engage in large-scale quantitative easing. She should not wait for the dawn of a new government in Greece to change course on all fronts. Otherwise, Merkel may end next year not as the German leader who held Europe together, but as the one who put such strain on Europe’s currency and democracies that they began to break apart.
Read more …

Sure, Barry …
• Obama Suggests Putin ‘Not So Smart’ (BBC)
President Barack Obama has said Vladimir Putin made a “strategic mistake” when he annexed Crimea, in a move that was “not so smart”. Those thinking his Russian counterpart was a “genius” had been proven wrong by Russia’s economic crisis, he said. International sanctions had made Russia’s economy particularly vulnerable to changes in oil price, Mr Obama said. He also refused to rule out opening a US embassy in Iran soon. “I never say never but I think these things have to go in steps” he told NPR’s Steve Inskeep in the Oval Office. Mr Obama was giving a wide-ranging interview with NPR shortly before leaving for Hawaii for his annual holiday. He criticised his political opponents who claimed he had been outdone by Russia’s president.
“You’ll recall that three or four months ago, everybody in Washington was convinced that President Putin was a genius and he had outmanoeuvred all of us and he had bullied and strategised his way into expanding Russian power,” he said. “Today, I’d sense that at least outside of Russia, maybe some people are thinking what Putin did wasn’t so smart.” Mr Obama argued that sanctions had made the Russian economy vulnerable to “inevitable” disruptions in oil price which, when they came, led to “enormous difficulties”. “The big advantage we have with Russia is we’ve got a dynamic, vital economy, and they don’t,” he said. “They rely on oil. We rely on oil and iPads and movies and you name it.”
Read more …

“There’s still bit of way to go before we see the Chinese economy reviving ..”
• China Factory Activity Shrinks (BBC)
China’s manufacturing activity shrank for the first time in seven months in December, a private survey showed on Wednesday. The final HSBC/Markit Purchasing Managers’ Index (PMI) was at 49.6, just below the 50 level that separates growth from contraction in the sector. The reading was slightly higher than an initial “flash” number of 49.5 released earlier this month. But, the result was still down from a final reading of 50 in November. The most recent data paints an even weaker picture of the slowing Chinese economy, which has been heralded as the “factory of the world”. New factory orders contracted for the first time since April. The economic data also backs the series of surprising moves by its government to boost growth in the past two months.
In November, the country’s central bank unexpectedly cut interest rates to 2.75% for first time since 2012 in an attempt to revive the economy. Whether the world’s second biggest economy will be able to reach its growth target of 7.5% after not missing the mark for 15 years has economists questioning if more needs to be done by policymakers. While the downbeat data is not a surprise considering the preliminary reading released earlier this month, Ryan Huang, market strategist at broker IG Asia said it just adds more pressure on Beijing to introduce more measures. “There’s still bit of way to go before we see the Chinese economy reviving,” he told the BBC. “They [the central bank] have been doing [banks’] reserve requirement ratio cuts, loan to deposit ratios have been lowered to help lending conditions – we’ll probably see more of this happening.”
Read more …

Boom and bust and basket.
• Japan Is Writing History As A Prime Boom And Bust Case (Grass)
Recently, we wrote a paper about the dynamics behind the boom and bust cycles, based on the view of the Austrian School (the Austrian Business Cycle Theory, or ABCT). The key takeaway was that central banks don’t help in smoothing the amplitude of the cycles, but rather are the cause of cycles. Business cycles are a direct result of excessive credit flow into the market, facilitated by an intentionally low interest rate set by the government. The problem with ongoing monetary policies is that the excessive money supply sends the wrong signals to the market, which ultimately leads to misallocation of investments or ‘malinvestments’.
On the one hand, entrepreneurs invest more and increase the depth of the production process. On the other hand, consumers spend more as saving becomes unattractive. When the excess products created through the cheap money-induced investments reach the market, consumers are unable to buy them due to the lack of prior savings. At this point the bust occurs. It is key to understand that by manipulating interest rates (particularly by lowering them), central banks create bubbles that end in busts. Japan is an excellent case study depicting the scenario discussed by the Austrian Business Cycle Theory (ABCT). In this article, we will examine the course of the economic and monetary situation in Japan from the ABCT’s point of view.
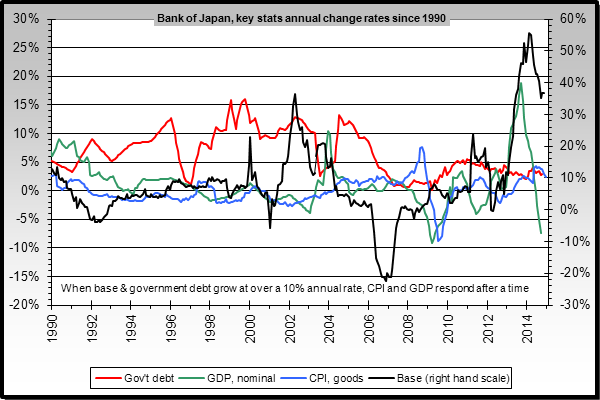
The latest quarterly GDP release in Japan was a real disaster. Economists had forecast a GDP growth between 2.2% and 2.5% but the result was a contraction of 1.6% on an annualized basis (i.e., -0.5% on a quarterly basis). That comes after a quarter in which GDP had already fallen 7.3% on an annualized basis (i.e., -1.9% on a quarterly basis). The money printing frenzy has taken gigantic proportions, and the (lack of) effectiveness of the excessive money creation is visible in the charts. The first chart below shows the annual monetary base expansion (the black line) since 1990. The GDP year-on-year growth is shown in the green line. Notice how the monetary base had exploded in 2013 but the steepness of the rise was slightly reduced in 2014. Even with this slight pull back in monetary growth, the GDP growth is truly collapsing.
Read more …

The Bloomberg piece is in yesterday’s Debt Rattle. Zero Hedge has a go at digging deeper.
• The Rigging Triangle Exposed: The JPMorgan-BP-BOE Cartel (Zero Hedge)
The name Dick Usher is familiar to regular readers: he was the head of spot foreign exchange for JPMorgan, and the bank’s alleged chief FX market manipulator, who was promptly fired after it was revealed that JPM was the bank coordinating the biggest FX rigging scheme in history, as initially revealed in “Another JPMorganite Busted For “Bandits’ Club” Market Manipulation.” Subsequent revelations – which would have been impossible without the tremendous reporting of Bloomberg’s Liam Vaughan – showed that JPM was not alone: as recent legal actions confirmed, virtually every single bank was also a keen FX rigging participant. However, the undisputed ringleader was always America’s largest bank, which would make sense: having a virtually unlimited balance sheet, JPM could outlast practically any margin call, and make money while its far smaller peers were closed out of trades… and existence.
But while the past year revealed that FX rigging was a just as pervasive, if not even more profitable industry for banks than the great Libor-fixing scandal, the conventional wisdom was that it involved almost exclusively bankers at the largest global banks including JPM, Goldman, Deutsche, Barclays, RBS, HSBC, and UBS. Now, courtesy of some more brilliant reporting by Vaughan, we can finally link banks with the other two facets of what has emerged to be an unprecedented FX-rigging “triangle” cartel: private sector companies that have no direct banking operations yet who have intimate prop trading exposure, as well as central banks themselves. By “banks” we, of course, refer to the ringleader itself: JP Morgan, and its former head of spot forex trading in London, Dick Usher. As for the company that benefited from its heretofore secret participation in the biggest FX rigging scandal in history, it is none other than British Petroleum.
We learn about all this thanks to a story that begins with, of all thing, a story about freshwater fishing at a lake in Essex called “Wharf Pool.” As Bloomberg reports, “an hour away by train, in London’s financial district, the lake’s owners ply their trade. Wharf Pool was purchased for about 250,000 pounds ($388,000) in 2012 by Richard Usher, the former JPMorgan Chase & Co. trader at the center of a global investigation into corruption in the foreign-exchange market, and Andrew White, a currency trader at oil company BP Plc. ” The plot thickens: was there more than a passing connection between the head FX trader at JPM and White “who’s known in the market as Tubby, is one of half a dozen spot currency traders working for British Petroleum (BP) in London. He and his colleagues, most of them ex-bankers, decide which firms will carry out their foreign-exchange transactions. That makes them prized clients for banks seeking a slice of the business and a glimpse into potentially market-moving trades. Passing on information was a way to curry favor.”
In short, a typical Over The Counter relationship between a banker and a buyside client, one which is largely unregulated and where the bank hopes to be able to frontrun the client’s orders by providing the client with confidential market moving information, thus generating more business with the client in the future. In this case, however, the buyside client was not a typical hedge fund, but the FX trading group at one of the world’s largest energy companies: a group which trades enormous amounts of FX every single day, both with intent to hedge, and to generate a profit.
Read more …

Because BP had no idea!
• BP Probes In-House Foreign Exchange Traders (FT)
BP is investigating whether in-house financial traders at the oil and gas group were involved in a foreign exchange manipulation scandal that has led regulators to levy $4.3 billion in fines on six banks. The UK group launched an internal review of its currency trading operations in London last year when regulators first started probing banks over their foreign exchange activities. A person familiar with the situation said the inquiry was “ongoing”. Additional questions about the potential involvement of BP’s traders in alleged attempts to rig the world’s $5.3 trillionn-a-day forex markets have been prompted by a Bloomberg report that bank employees tipped off the oil and gas group ahead of some big currency trades.
Bloomberg cited three undated messages sent to BP’s traders by the powerful network of senior foreign-exchange traders calling themselves “The Cartel” at four banks — JPMorgan, Barclays, UBS and Citigroup. It said BP was given “valuable information” about planned currency trades “sometimes hours before they happened”. But it could not be determined whether any BP employees acted on any information received. BP is not being investigated by financial regulators, said people familiar with the situation. But the report raises uncomfortable questions for the group at a time when it is being scrutinised as part of the European Commission probe into potential price fixing in oil markets.
Read more …

Familiar topic, good story.
• The Prison State of America (Chris Hedges)
Prisons employ and exploit the ideal worker. Prisoners do not receive benefits or pensions. They are not paid overtime. They are forbidden to organize and strike. They must show up on time. They are not paid for sick days or granted vacations. They cannot formally complain about working conditions or safety hazards. If they are disobedient, or attempt to protest their pitiful wages, they lose their jobs and can be sent to isolation cells. The roughly 1 million prisoners who work for corporations and government industries in the American prison system are models for what the corporate state expects us all to become. And corporations have no intention of permitting prison reforms that would reduce the size of their bonded workforce. In fact, they are seeking to replicate these conditions throughout the society.
States, in the name of austerity, have stopped providing prisoners with essential items including shoes, extra blankets and even toilet paper, while starting to charge them for electricity and room and board. Most prisoners and the families that struggle to support them are chronically short of money. Prisons are company towns. Scrip, rather than money, was once paid to coal miners, and it could be used only at the company store. Prisoners are in a similar condition. When they go broke—and being broke is a frequent occurrence in prison—prisoners must take out prison loans to pay for medications, legal and medical fees and basic commissary items such as soap and deodorant. Debt peonage inside prison is as prevalent as it is outside prison.
States impose an array of fees on prisoners. For example, there is a 10% charge imposed by New Jersey on every commissary purchase. Stamps have a 10% surcharge. Prisoners must pay the state for a 15-minute deathbed visit to an immediate family member or a 15-minute visit to a funeral home to view the deceased. New Jersey, like most other states, forces a prisoner to reimburse the system for overtime wages paid to the two guards who accompany him or her, plus mileage cost. The charge can be as high as $945.04. It can take years to pay off a visit with a dying father or mother.
Fines, often in the thousands of dollars, are assessed against many prisoners when they are sentenced. There are 22 fines that can be imposed in New Jersey, including the Violent Crime Compensation Assessment (VCCB), the Law Enforcement Officers Training & Equipment Fund (LEOT) and Extradition Costs (EXTRA). The state takes a percentage each month out of prison pay to pay down the fines, a process that can take decades. If a prisoner who is fined $10,000 at sentencing must rely solely on a prison salary he or she will owe about $4,000 after making payments for 25 years. Prisoners can leave prison in debt to the state. And if they cannot continue to make regular payments—difficult because of high unemployment—they are sent back to prison. High recidivism is part of the design.
Read more …

The gift that never stops giving.
• Recolonizing Africa: A Modern Chinese Story? (CNBC)
China, one of the world’s largest ’emerging’ investors, is ramping up investment in Sub Saharan Africa as it searches for natural resources, but whether the benefits are mutually beneficial is questionable. China’s economic growth has been a key narrative in the story of economic miracle over the past two decades. (Its foreign direct investment) FDI in particular has played a prominent role in economic interactions with many developing countries. Once a major recipient of FDI, it’s now one of the largest ’emerging’ investors, especially in Sub Saharan Africa countries, it has investments being in Nigeria, Sudan, South Africa and Angola among others.
The Asian economic super power is in pursuit of oil, gas, precious metals and mining to diversify its energy resource import’s pool; it requires other resources to sustain its manufacturing capabilities. Africa can offer all of these things to the world’s second largest economy: about 40% of global reserves of natural resources, 60% of uncultivated agricultural land, a billion people with rising purchasing power and a potential army of low-wage workers. Like many emerging markets, African countries are one of the fastest growing markets and profitable outlets for exported manufactured goods. In the past, the U.K. and France were the prime trade partners for Africa, however, today, China is Africa’s top bi-lateral trading partner with trade volume exceeding $166 billion. Between years 2003 and 2011, its FDI in the continent has increased thirty fold from $491 million to $14.7 billion.
This is more than just a trend. Not a long time ago, China eyed areas in Africa where resources were abundant and easy to extract. It focused on resource-rich countries such as Algeria, Nigeria, South Africa, Sudan and Zambia. Today, Sino-African investment focus has become broader. China is branching out into non-resource-rich investments, focusing on countries such as Ethiopia and Congo. Higher margins have attracted many state-owned enterprises and private companies to compete on gaining dominion in the vast continent. Oil, gas, metals and minerals constitute three-quarters of African-exports to China. Chinese Imports to Africa are more diverse, mostly comprised of manufactured goods.
Read more …

The impact of Ebola will take us completely back to it being a basket case ..”
• Ebola Wrecks Years Of Aid Work In Worst-Hit Countries (Reuters)
Ebola is wrecking years of health and education work in Sierra Leone and Liberia following their civil wars, forcing many charity groups to suspend operations or re-direct them to fighting the epidemic. More than a decade of peace and quickening economic growth had raised hopes that the nations could finally reduce their dependency on foreign aid and budgetary support; now Ebola has undermined those achievements, charity workers and officials say. “The impact of Ebola will take us completely back to it being a basket case,” said Rocco Falconer, CEO of educational charity Planting Promise in Sierra Leone. “The impact on some activities have been simply catastrophic.”
The two countries worst hit by Ebola have struggled to recover from the wars that raged through the 1990s until early in the 21st century, killing and maiming tens of thousands, and devastating already poor infrastructure. In Sierra Leone, aid made up one-fifth of economic output in 2010, according to officials, though this had been shrinking as growth accelerated thanks to a boom in the country’s commodities exports. Britain and the European Union are the main donors with funds directed to health, education and social assistance. But Planting Promise’s experience typifies the problems of non-government organisations (NGOs) since Ebola hit West Africa, infecting more than 20,000 people and killing nearly 8,000.
It had spent six years in Sierra Leone developing farms and using the profits to fund local schools. The project had just become self-financing for the first time when the outbreak was detected in March. After that, things fell apart. Planting Promise was forced to withdraw its expatriate staff in June and the following month it closed its five primary schools where nearly 1,000 pupils had studied. It has also shut down its food processing factory. Though sales have dived, it continues to pay about 120 staff, eating into its reserves. This has forced the group to return “cap in hand” to donors to ask for more money, Falconer said.
Read more …

MUST. READ.
• Protecting Money or People? (James K. Boyce)
The latest round of international climate talks this month in Lima, Peru, melting glaciers in the Andes and recent droughts provided a fitting backdrop for the negotiators’ recognition that it is too late to prevent climate change, no matter how fast we ultimately act to limit it. They now confront an issue that many had hoped to avoid: adaptation. Adapting to climate change will carry a high price tag. Sea walls are needed to protect coastal areas against floods, such as those in the New York area when Superstorm Sandy struck in 2012. We need early-warning and evacuation systems to protect against human tragedies, such as those caused by Typhoon Haiyan in the Philippines in 2013 and by Hurricane Katrina in New Orleans in 2005.
Cooling centers and emergency services must be created to cope with heat waves, such as the one that killed 70,000 in Europe in 2003. Water projects are needed to protect farmers and herders from extreme droughts, such as the one that gripped the Horn of Africa in 2011. Large-scale replanting of forests with new species will be needed to keep pace as temperature gradients shift toward the poles. Because adaptation won’t come cheap, we must decide which investments are worth the cost. A thought experiment illustrates the choices we face. Imagine that without major new investments in adaptation, climate change will cause world incomes to fall in the next two decades by 25% across the board, with everyone’s income going down, from the poorest farmworker in Bangladesh to the wealthiest real estate baron in Manhattan. Adaptation can cushion some but not all of these losses.
What should be our priority: reduce losses for the farmworker or the baron? For the farmworker, and a billion others in the world who live on about $1 a day, this 25% income loss will be a disaster, perhaps the difference between life and death. Yet in dollars, the loss is just 25 cents a day. For the land baron and other “one-percenters” in the U.S. with average incomes of about $2,000 a day, the 25% income loss would be a matter of regret, not survival. He’ll find a way to get by on $1,500 a day. In human terms, the baron’s loss pales compared with that of the farmworker. But in dollar terms, it’s 2,000 times larger.
Read more …

Here’s what increasing debt can give you – until it no longer can.
• Goodbye To One Of The Best Years In History (Telegraph)
Newspapers can seem like a rude intrusion into the Christmas holidays. We celebrate peace, goodwill and family – and then along come the headlines, telling us what’s going wrong in the world. Simon and Garfunkel made this point in 7 O’Clock News/Silent Night, a song juxtaposing a carol with a newsreader bringing bad tidings. But this is the nature of news. Whether it’s pub gossip or television bulletins, we’re more interested in what’s going wrong than with what’s going right. Judging the world through headlines is like judging a city by spending a night in A&E – you only see the worst problems. This may have felt like the year of Ebola and Isil but in fact, objectively, 2014 has probably been the best year in history.
Take war, for example – our lives now are more peaceful than at any time known to the human species. Archaeologists believe that 15% of early mankind met a violent death, a ratio not even matched by the last two world wars. Since they ended, wars have become rarer and less deadly. More British soldiers died on the first day of the Battle of the Somme than in every post-1945 conflict put together. The Isil barbarity in the Middle East is so shocking, perhaps, because it comes against a backdrop of unprecedented world peace. We have recently been celebrating a quarter-century since the collapse of the Berlin Wall, which kicked off a period of global calm.
The Canadian academic Steven Pinker has called this era the “New Peace”, noting that conflicts of all kinds – genocide, autocracy and even terrorism – went on to decline sharply the world over. Pinker came up with the phrase four years ago, but only now can we see the full extent of its dividends. With peace comes trade and, ergo, prosperity. Global capitalism has transferred wealth faster than foreign aid ever could. A study in the current issue of The Lancet shows what all of this means. Global life expectancy now stands at a new high of 71.5 years, up six years since 1990. In India, life expectancy is up seven years for men, and 10 for women. It’s rising faster in the impoverished east of Africa than anywhere else on the planet. In Rwanda and Ethiopia, life expectancy has risen by 15 years.
This helps explain why Bob Geldof’s latest Band Aid single now sounds so cringingly out-of-date. Africans certainly do know it’s Christmas – a Nigerian child is almost twice as likely to mark the occasion by attending church than a British one. The Ebola crisis has led to 7,000 deaths, each one a tragedy. But far more lives have been saved by the progress against malaria, HIV and diarrhoea. The World Bank’s rate of extreme poverty (those living on less than $1.25 a day) has more than halved since 1990, mainly thanks to China – where economic growth and the assault on poverty are being unwittingly supported by any parent who put a plastic toy under the tree yesterday.
Read more …