Jackson Pollock Male and female 1942

What a cesspool, what a shithole Washington has become. Actually, reading through today’s news, the whole world has.
Clinton, Podesta, Corker, Flake, Trump, Clapper, Comey, Mueller, Manafor, Ppmpeo, Sessions, people are simply going to walk away from it all.
And you can say good on the WaPo for publishing this, but they have thrown so much echo chamber stuff out there over the past year, this doesn’t make that right.
• Clinton Campaign, DNC Paid For Research That Led To Russia Dossier (WaPo)
The Hillary Clinton campaign and the Democratic National Committee helped fund research that resulted in a now-famous dossier containing allegations about President Trump’s connections to Russia and possible coordination between his campaign and the Kremlin, people familiar with the matter said. Marc E. Elias, a lawyer representing the Clinton campaign and the DNC, retained Fusion GPS, a Washington firm, to conduct the research. After that, Fusion GPS hired dossier author Christopher Steele, a former British intelligence officer with ties to the FBI and the U.S. intelligence community, according to those people, who spoke on the condition of anonymity. Elias and his law firm, Perkins Coie, retained the company in April 2016 on behalf of the Clinton campaign and the DNC.
Before that agreement, Fusion GPS’s research into Trump was funded by an unknown Republican client during the GOP primary. The Clinton campaign and the DNC, through the law firm, continued to fund Fusion GPS’s research through the end of October 2016, days before Election Day. Fusion GPS gave Steele’s reports and other research documents to Elias, the people familiar with the matter said. It is unclear how or how much of that information was shared with the campaign and the DNC and who in those organizations was aware of the roles of Fusion GPS and Steele. One person close to the matter said the campaign and the DNC were not informed by the law firm of Fusion GPS’s role.
The dossier has become a lightning rod amid the intensifying investigations into the Trump campaign’s possible connections to Russia. Some congressional Republican leaders have spent months trying to discredit Fusion GPS and Steele and tried to determine the identity of the Democrat or organization that paid for the dossier. Trump tweeted as recently as Saturday that the Justice Department and FBI should “immediately release who paid for it.”

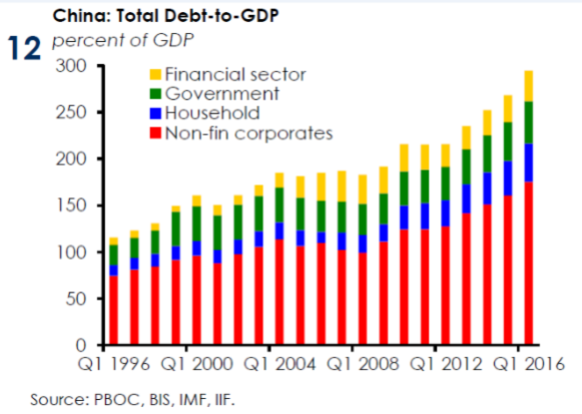
“Mathematically, as long as China runs surpluses, foreign holding of yuan will not match foreign holding of dollars.”
• Gold-Backed Petro-Yuan Silliness: Reserve Currency Curse? (Mish)
A massive amount of hype is spreading regarding China’s alleged ambitions to dethrone the dollar. The story this time involves China’s plan is to price oil in yuan using a gold-backed futures contract. Even if that were true, the impact would be zero. Nonetheless, CNBC is now in on the hype. CNBC reports China has grand ambitions to dethrone the dollar. It may make a powerful move this year. Yuan pricing and clearing of crude oil futures is the “beginning” of a broader strategic push “to support yuan pricing and clearing in commodities futures trading,” Pan Gongsheng, director of the State Administration of Foreign Exchange, said last month. To support the new benchmark, China has opened more than 6,000 trading accounts for the crude futures contract, Reuters reported in July. Yawn.
Jeff Brown, president at FGE, an international energy consultant has a more accurate assessment. “Most counterparties will not want anything to do with this contract as it adds in a layer of cost and risk. They also don’t like contracts with only a few dominant buyers or sellers and a government role.” Repeat after me: It’s meaningless what currency oil is quoted in. Once you understand the inherent truth in that statement, you immediately laugh at headlines like that presented on CNBC. For those who do not understand the simple logic, consider the fact that one does not need to have dollars to buy oil. Currencies are fungible. In less than a second, and at ant time day or night, one can convert any currency to any other currency. If countries want to hold dollars they can. If one wants to hold Swiss Francs, Euros, or Yen they can as well. Oil likely trades in all of those currencies right now.
Countries accumulate US dollars because the US runs a trade deficit, and those dollars will eventually return to the US. If China wants to assume the role of having the world’s reserve currency, something I highly doubt actually, it will need to have a free-floating currency and the world’s largest bond market . China will need property rights protection and a global willingness of countries to hold the yuan. To assume the role of China would have to be willing to run trade deficits instead of seeking trade surpluses via subsidized exports. Please read that last sentence over and over again until it sinks in. Mathematically, whether they like it or not, China and Japan have massive US dollar reserves as a result of cumulated trade surpluses. Mathematically, as long as China runs surpluses, foreign holding of yuan will not match foreign holding of dollars.

More on that cesspool. Nothing to do with ideas, or convictions, or voters. Just power.
• Do Democrats Really Need Wall Street? (BM)
Halloween is coming and fear mongering seems to be the order of the day — not just on the part of Republicans, but apparently no less so on the part of “centrist” and conservative Democrats who are expressing growing anxiety about offending big donors who see politics not as the pursuit of justice but as the pursuit of their interests. Douglas Schoen, said to have been Bill Clinton’s favorite pollster during his presidency, has taken to the op-ed page of The New York Times to warn center-right party members and friends that ‘all Hell will break loose’ if the Democrats embrace a platform promising “wealth redistribution through higher taxes and Medicare for all” and utilizing democracy to challenge the power of money.
Don’t be bewitched by the fantasies of folks such as Sens. Bernie Sanders (I-VT) and Elizabeth Warren (D-MA), Schoen counsels, for if you do, the American financial elite will not keep the party’s “coffers full.” Indeed, he argues, “Democrats should strengthen their ties to Wall Street,” for “America is a center-right, pro-capitalist nation.” “Memories in politics are short,” Schoen wrote. And he wrings his hands over the amnesia that robs people of remembering that the center-right assembled under Bill Clinton enabled him to balance the budget, limit government and protect essential programs “that make up the social safety net.” Leaving behind “that version of liberalism,” Schoen writes, has cost Democrats several elections. He even claims that Hillary Clinton lost in Michigan and Wisconsin in 2016 because she “lurched to the left.”
Yes, memories are short indeed, but they are made even shorter by the likes of Schoen. The horrors he prophesies make it clear that he does not want us to remember. He wants us to forget, and therefore to tame our aspirations for social democracy and an economy that serves everyday people instead of the 1%. Schoen wants us to forget that Hillary Clinton lost the Upper Midwest not because of her supposed “lurch to the left,” but because many working people could not erase from their minds her lavishly paid Wall Street engagements and her adamant refusal to “release the transcripts” of those flattering speeches to the bankers. To many a Rust Belt voter she was the “Goldman Sachs” candidate, something Schoen would consign to the memory hole.

You will see this wherever a housing bubble rules the economy.
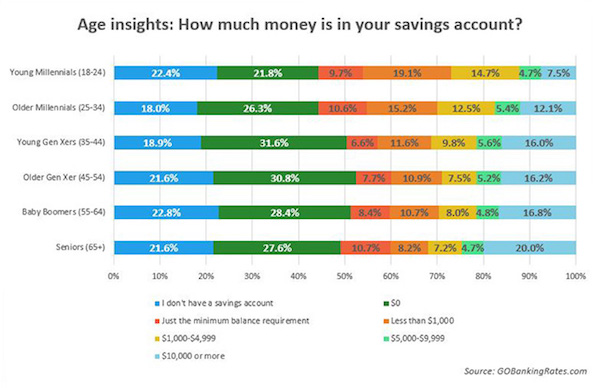
• 4 In 10 Canadians Can Not Cover Basic Expenses Without Adding More Debt (ZH)
[..] BNN reported that a survey released yesterday found that almost half of Canadian households don’t feel financially prepared for further interest rate increases. According to the Ipsos poll, conducted on behalf of MNP, 40% of respondents said they fear ending up in financial trouble if rates go up much higher, with one-in-three already feeling the impact of higher rates. “It’s clear that people are nowhere near prepared for a higher rate environment,” MNP President Grant Bazian said in a release. “The good news is that there seems to be at least the acknowledgement now that rates are going to climb which might make people reassess their spending habits – especially using credit.”
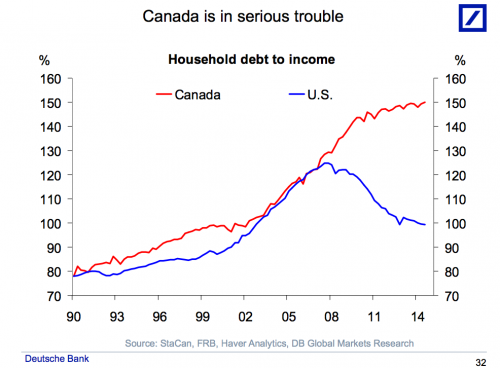
It gets worse: 42% of respondents said they don’t think they can cover basic expenses over the next year without going deeper into more debt. The same number said they’re within $200 of not being able to cover monthly expenses. This familiar “ponzi state” means that more than 4 in 10 Canadians effectively have no savings, which is ominously similar to US trends: as we reported earlier this year, a quarter of American adults can’t pay all their monthly bills, while 44% have less than $400 in cash. The Ipsos poll also found 70% of Canadians said they will take a more cautious approach to spending amid higher interest rates, which may be enough to choke off any economic growth and make the Canadian rate hikes a “one and one” affair.
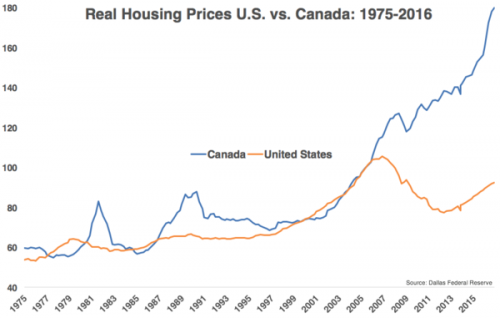
Concern about rising rates is greater among lower-income Canadians – those who tend to rely on credit cards – according to the survey, as opposed to homeowners who said they are a bit more optimistic they can absorb a rate increase of… a whopping 1%. Geographically, over half of Albertans say they’ll be more concerned about paying off debt if interest rates rise, which is more than those in British Columbia and Quebec, where less than half said they are worried. Meanwhile, Ontarians are the least concerned (44 per cent) about their ability to pay down their debts.
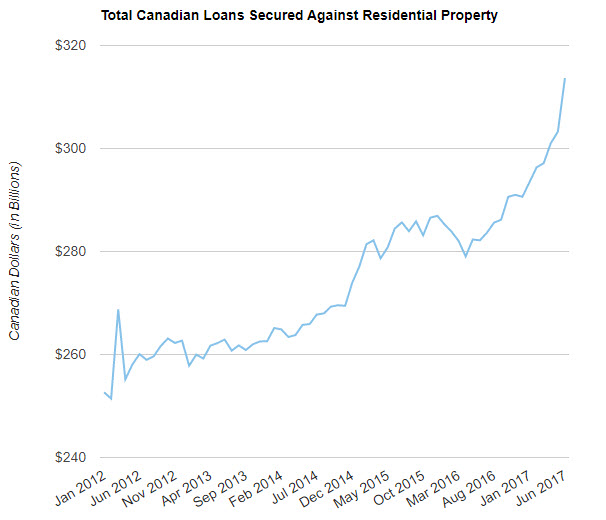

But .. but .. Draghi’s Italian… At one point, he wanted to be its PM.
• Italy Faces Worst Shock In Europe As ECB Prepares To Taper Bond Buys (MW)
The entire eurozone will face a crucial test when the European Central Bank begins to wind down its asset-buying program, but one country stands to lose the most as the monetary punch bowl is taken away: Italy. Saddled with mountains of debt and a looming election, the southern European nation will likely struggle to find buyers for its government bonds when the European Central Bank stops snapping up Italian debt over the coming years, according to Christian Schulz, European economist at Citigroup. That means yields are set to rise, potentially strangling the country’s nascent recovery. “It comes at a difficult time. At the moment political uncertainty is rising and the ECB pulling out of the market just makes [the end of quantitative easing] so much harder on Italy than other countries,” Schulz said.
“They have a huge pile of debt, which makes the country much more sensitive to interest rate changes than countries with smaller piles of debt,” he said. Italy has particularly benefited from the ECB’s quantitative easing program that began in 2015, as it’s been one of the biggest bond issuers in the currency union. The central bank has purchased 300 billion euros ($352.9 billion) of Italian bonds under the program, which is more than three times the net bond issuance for the country during that period, according to Schulz. That means the ECB has not only bought pretty much all new bonds issued in Italy since 2015, but also existing bonds from other investors. The ECB is widely expected to announce some sort of tapering at its monetary policy setting meeting on Thursday, and most economists expect the asset purchases to end altogether in late 2018.

” Schaeuble said Greece had decided to cut pensions instead of taxing wealthy ship-owners..” Not true.
• Don’t Blame Others For Your Problems, Germany’s Schaeuble Tells Greece (R.)
Outgoing German Finance Minister Wolfgang Schaeuble urged debt-wracked Greece to stop blaming others for its financial woes and stick to a reform agenda instead of relying on debt relief. Schaeuble, a leading advocate of Greece’s tough austerity programs and one of Germany’s most powerful politicians, was elected speaker of its lower house of parliament on Tuesday. The 75-year-old lawyer, whose no-nonsense approach on austerity made him a popular hate figure among Greeks, told Greek Skai TV that Athens must take responsibility for its fiscal difficulties and act on them. “When you ask others for loans, you cannot insult them for granting the loans. It doesn’t make sense. Greece’s problems are Greece’s problems,” the conservative Christian Democrat said in an interview aired in Greece on Tuesday.
Asked if he ever suggested a “time out” on Greece’s participation in the euro zone, he said he had discussed the option “as a currency devaluation tool” with a former finance minister, who rejected it saying Greece would implement reforms. Schaeuble said he warned Prime Minister Alexis Tsipras while the latter was still in opposition in 2014 that the Greek politician would not be able to meet his pre-election platform of zero austerity. Tsipras, Schaeuble said, told him he wanted to remain in the euro without any conditions. “I responded that I wished, for his sake, that he didn’t win that election because he wouldn’t be able to keep his promises,” Schaeuble said in comments translated from German to Greek.
Seven months after he was elected, Tsipras was forced to cave into lenders’ demands for more belt-tightening. He was re-elected saying the bailout, the country’s third since 2010, was a product of blackmail. Greece is eyeing a bailout exit in 2018. Asked if the Greek case had become a personal issue for him, Schaeuble said: “Obviously in Greece I was a bogeyman, or at least for some media.” Politicians, he said, had a habit of using lenders as an excuse to impose cutbacks. “That saddened me somewhat, because nobody ever wanted to harm Greece,” he said. By way of example, Schaeuble said Greece had decided to cut pensions instead of taxing wealthy ship-owners – contrary to what the leftist Syriza party promised before elections. “This wasn’t a German parliament decision, it was a Greek government decision,” he said.

Anything to say on this, Wolfgang? Where I come from this is called ordinary blackmail.
• What Happened To The €8 Billion Europe Took From Greece? (EN)
In 2012 with Greece on the verge of bankruptcy, fellow Eurozone states rallied round to rescue one of their own. Part of the bailout package they agreed was to use almost 27 billion euros to buy up Greek debt to prevent a vicious circle that would see the country facing more and more expensive borrowing costs. At the time, the countries agreed that they should not profit from this action and that the interest paid to them by Athens linked to the bonds they had bought should be returned. To this day, that interest amounts to almost €8 billion (More precisely €7,838,000,000, according to an email sent by EU finance commissioner Pierre Muscovici to MEPs). Some of this money has been sent back to Greece but much of it remains in the hands of other European countries. And they seem determined not to reveal how much.
“For legal reasons, it’s not possible for member states to declare the amounts paid by their central banks to Greece,” said a source at the European Commission, citing the principle that central banks should not disclose details about their investments to avoid unduly influencing the behaviour of markets. For once, it seems, that Europe is united on the issue – Ireland, Italy, Spain and even Greece all refused to disclose how much had been returned and how much they were still holding. In Luxembourg, the press revealed that the government had handed back to Greece €28.3 million and was committed to returning the entire €40.2 million of interest it had accrued.
According to Euronews’ calculations, the Bundesbank, due to its position as the largest of Europe’s central banks earned €2 billion of interest since 2012 on the debt they purchased from Greece. France took €1.58 billion and Italy €1.37 billion. Documents obtained by Euronews confirm the figure for France, officials from other countries would not confirm or deny the amounts by the time this story was published.
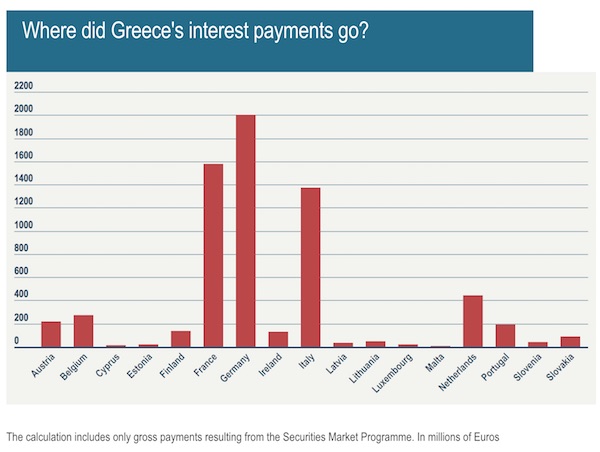
Under the Securities Market Programme, Eurozone central banks bought up Greek government bonds, pushing up the prices for that debt and thereby lowering the interest rates Athens needed to pay to borrow. This offset to a degree the impact of market fears about the country’s economy which had obliged the government to pay significantly higher rates to secure the money it needed to keep operating. As a result of this programme, the countries participating received interest from Greece on the bonds they had purchased.
It was this money that they agreed to return under the 2012 bailout deal. When Alexis Tsipras swept to power in 2015 and rejected a proposed deal to extend the bailout, Eurozone finance ministers agreed to freeze these payments, having returned €4.3 billion relating to the debt buyup and a separate programme known as ANFA. The withholding of this money, according to Christopher Dembik, an economist at Saxo Bank, serves as a “kind of punishment” combined with a “means to pressure” Greece to fulfill its bailout obligations.

What Greece moves close to the US.
• Turkey Says Doesn’t Want Greece To Become ‘Safe Haven’ For Coup Plotters (R.)
Turkish Foreign Minister Mevlut Cavusoglu urged Greece on Tuesday to not become a “safe haven” for plotters of last year’s coup attempt, citing the 995 people who have applied for asylum since the failed putsch. Speaking at a joint news conference with his Greek counterpart, Nikos Kotzias, Cavusoglu said asylum seekers needed to be evaluated to determine those linked to the network of U.S.-based cleric Fethullah Gulen, blamed by Turkey for masterminding the putsch. “We would not want our neighbor Greece, with whom we are improving our ties, to be a safe haven for Gulenists. We believe these applications will be evaluated meticulously and that traitors will not be given credit,” Cavusoglu said.
Responding to Cavusoglu’s comments, Kotzias said the decisions on asylum seekers were made by the Greek judiciary and had to be respected even if “it doesn’t please some”. Relations between Turkey and Greece were further strained in May after a Greek court ruled to not extradite eight Turkish soldiers who fled to Greece following last year’s coup attempt. Turkey alleges the men, who fled to Greece in a military helicopter as the July coup unfolded, were involved in efforts to overthrow President Tayyip Erdogan and has repeatedly demanded they be sent back. Greek courts have blocked two extradition requests by Ankara, drawing an angry rebuke from Turkey and highlighting the tense relations between the NATO allies, who remain at odds over issues from territorial disputes to ethnically split Cyprus.

Lies, threats and ghostwriting.
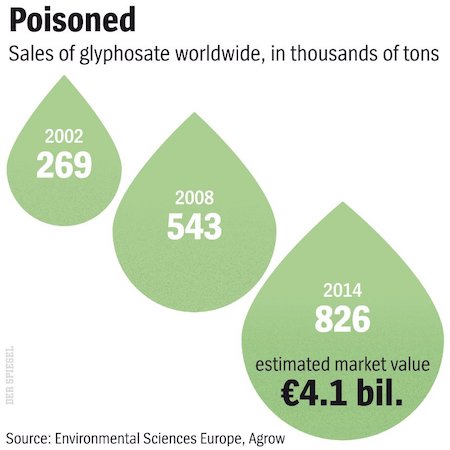
• Monsanto Faces Blowback Over Cancer Cover-Up (Spiegel)
Some companies’ reputations are so poor that the public already has low expectations when it comes to their ethics and business practices. That doesn’t make it any less shocking when the accusations against them are confirmed in black and white. Agricultural chemicals giant Monsanto is under fire because the company’s herbicide, Roundup (active ingredient: glyphosate), is suspected of being carcinogenic. Permission to sell the chemical in the European Union expires on December 15 with member states set to decide on Wednesday whether to renew it for another 10 years. And now, the longstanding dispute about glyphosate has been brought to a head by the release of explosive documents. Monsanto’s strategies for whitewashing glyphosate have been revealed in internal e-mails, presentations and memos.
Even worse, these “Monsanto Papers” suggest that the company doesn’t even seem to know whether Roundup is harmless to people’s health. “You cannot say that Roundup is not a carcinogen,” Monsanto toxicologist Donna Farmer wrote in one of the emails. “We have not done the necessary testing on the formulation to make that statement.” The email, sent on Nov. 22, 2003, is one of more than 100 documents that a court in the United States ordered Monsanto to provide as evidence after about 2,000 plaintiffs demanded compensation from Monsanto in class-action suits. They claim that Roundup has caused non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma, a form of lymph node cancer, in them or members of their family.
The documents suggest the company concealed risks, making their publication a disaster for the company. The matter is also likely to be a topic of discussion at Bayer, the German chemical company in the process of acquiring Monsanto. “The Monsanto Papers tell an alarming story of ghostwriting, scientific manipulation and the withholding of information,” says Michael Baum, a partner in the law firm of Baum, Hedlund, Aristei & Goldman, which is bringing one of the US class actions. According to Baum, Monsanto used the same strategies as the tobacco industry: “creating doubt, attacking people, doing ghostwriting.”

First of multiple steps. The European Commission has totally different ideas.
• EU Parliament Votes To Ban Controversial Weedkiller Glyphosate By 2022 (AFP)
The European Parliament Tuesday called for the controversial weedkiller glyphosate to be banned by 2022 amid fears it causes cancer, a day before EU states vote on whether to renew its licence. MEPs approved a resolution which is not binding but will add fresh pressure on the European Commission, the bloc’s executive arm, which has recommended the licence for the herbicide be renewed for 10 years. Glyphosate critics, led by environmental campaigners Greenpeace, are calling for an outright ban in Europe and on Monday activists handed the EU a petition signed by more than 1.3 million people backing such a move.
Experts from the EU’s 28 member states are due to vote on the commission recommendation on Wednesday, just as a row escalates over claims that US agro giant Monsanto unduly influenced research into its weedkiller’s safety. MEPs criticised the commission’s proposal, saying it “fails to ensure a high level of protection of both human and animal health and the environment (and) fails to apply the precautionary principle”. They called for a halt to non-professional use of glyphosate when its licence runs out in December 15 and for its use to end near public parks and playgrounds. Opponents of glyphosate, used in Monsanto’s best-selling herbicide Roundup, point to a 2015 study by the World Health Organization’s (WHO) International Agency for Research on Cancer that concluded it was “probably carcinogenic”.

Madrid better be careful.
• Spain’s Government Prepared To ‘Discipline Disobedient Catalans’ (CNBC)
Spain’s central government is prepared to discipline Catalan citizens who chose to disobey direct rule from Madrid, the Spanish government’s official representative in Catalonia told CNBC. “The Spanish government is going to have the responsibility of taking decisions of a disciplinary nature if there is a rejection, by any functionaries, of any of the orders that they receive,” Enric Millo told CNBC on Monday, according to a translation. Prime Minister Mariano Rajoy invoked unprecedented constitutional powers on Saturday, vowing to curtail some of the freedoms of Catalonia’s parliament, sack some of its political players and force regional elections within six months. A vote in the national Senate to implement this direct rule is scheduled for Friday.
In response, the far-left CUP party — a key supporter of Catalonia’s pro-independence minority government in the regional parliament — described Madrid’s actions as an aggression against all Catalans. The secessionist group also urged Catalan citizens to engage in “massive civil disobedience.” Millo said he was hopeful the “large majority” of public servants based in the northeast of Spain would resist calls from separatist leaders to disobey the constitution. However, when he was asked what preparations had been made for those who ignored Madrid’s direct rule, Millo said that it would be the politicians who had decided to break with “democratic legality” that would be dealt with first. “These people will resign … And therefore, although they may not agree, they will not have any type of responsibility, validity, nor any type of authorization in any institutional decision. They will be left without any responsibilities,” he said.

Colonialism 2.0
• US Military Is Conducting Secret Missions All Over Africa (Vice)
U.S. troops are now conducting 3,500 exercises, programs, and engagements per year, an average of nearly 10 missions per day, on the African continent, according to the U.S. military’s top commander for Africa, General Thomas Waldhauser. The latest numbers, which the Pentagon confirmed to VICE News, represent a dramatic increase in U.S. military activity throughout Africa in the past decade, and the latest signal of America’s deepening and complicated ties on the continent. With the White House and the Pentagon facing questions about an Oct. 4 ambush in Niger in which four U.S. Special Forces soldiers were killed, Secretary of Defense James Mattis reportedly indicated to two senior members of the Senate Armed Services Committee Friday that these numbers are only likely to increase as the U.S. military shifts even greater attention to counterterrorism in Africa.
“You’re going to see more actions in Africa, not less,” said Sen. Lindsey Graham after the briefing. “You’re going to see more aggression by the United States toward our enemies, not less; you’re going to have decisions being made not in the White House but out in the field.” But the U.S. military has already seen significant action in Africa, where its growth has been sudden and explosive. When U.S. Africa Command, the umbrella organization for U.S. military operations on the continent, first became operational in 2008, it inherited 172 missions, activities, programs, and exercises from other combatant commands. Five years in, that number shot up to 546. Today’s figure of 3,500 marks an astounding 1,900 percent increase since the command was activated less than a decade ago, and suggests a major expansion of U.S. military activities on the African continent.

But…
• Yes, The US Leads All Countries In Reducing Carbon Emissions (Rapier)
Last week, in an interview with Fox News, Environmental Protection Agency Administrator Scott Pruitt claimed: “We are leading the nation – excuse me – the world with respect to our CO2 footprint in reductions.” The Washington Post fact-checked this claim and rated it “Three Pinocchios,” which means they rate the claim mostly false. They further wrote that Pruitt’s usage of data appeared to be a “deliberate effort to mislead the public.” I agree that this is a nuanced issue, but the data mostly support Pruitt’s claim. According to the 2017 BP Statistical Review of World Energy, since 2005 annual U.S. carbon dioxide emissions have declined by 758 million metric tons. That is by far the largest decline of any country in the world over that timespan and is nearly as large as the 770 million metric ton decline for the entire EU.
By comparison, the second largest decline during that period was registered by the United Kingdom, which reported a 170 million metric ton decline. At the same time, China’s carbon dioxide emissions grew by 3 billion metric tons, and India’s grew by 1 billion metric tons. Thus, I don’t think it’s the least bit misleading to claim that the U.S. is leading the world in reducing carbon dioxide emissions. The Washington Post gets into per capita emissions, and indeed despite the decline, U.S. per capita emissions are still among the highest in the world. However, the Washington Post story claimed: “The United States may have had the largest decrease in carbon emissions, but it is still the largest per capita emitter.” That’s not accurate either. According to World Bank data, U.S. per capita carbon dioxide emissions rank 11th among countries.
So, we are not the largest per capita emitter, but we do emit 2.2 times as much on a per capita basis as China. But, China has 4.3 times as many people, and that matters from an overall emissions perspective. China’s lower per capita carbon dioxide emissions are more than offset by its greater population, so China emits over 70% more carbon dioxide annually than the U.S. The story quoted Pruitt a second time: “We have reduced our CO2 footprint by over 18%, almost 20%, from 2000 to 2014.” The Post also disputes this claim, citing EPA numbers that stated “energy-related CO2 emissions” have fallen by 7.5% since 2000. I am not sure why anyone is using numbers from 2000, as U.S. carbon dioxide emissions continued to rise until 2005. That’s when they began to fall.

Can’t say that makes me feel happy.
• Global Wine Output Hits 50-Year Low (AFP)
Worldwide wine production tumbled 8.2% this year to hit a 50-year low due to unfavourable climate conditions, the International Organisation of Vine and Wine (OIV) said Tuesday. The total output of 246.7 million hectolitres was due in large part to steep drops in the top three wine producing countries: Italy, France and Spain. “This drop is consecutive to climate hazards, which affected the main producing countries, particularly in Europe,” said the Paris-based OIV, an intergovernmental organisation that provides scientific and technical advice on vines and wine. In Italy production slumped 23% to 39.3 mhl, while in France the drop was 19% to 36.7 mhl. Production in Spain fell 15% to 33.5 mhl.

Symbol of all our troubles as a species.
• Ancient Amazon Tribe Vow To Defend Their Territory Against Mining (AFP)
They appear silently, seemingly from nowhere: a dozen figures, naked except for bright red loincloths, blocking the dirt road. These are the Waiapi, an ancient tribe living in Brazil’s Amazon rainforest but now fearing invasion by international mining companies. Leading AFP reporters to a tiny settlement of palm-thatched huts hidden in foliage, the tribesmen streaked in red and black dye vow to defend their territory. They brandish six-foot (two-meter) bows and arrows to reinforce the point. “We’ll keep fighting,” says Tapayona Waiapi, 36, in the settlement called Pinoty. “When the companies come we’ll keep resisting. If the Brazilian government sends soldiers to kill people, we’ll keep resisting until the last of us is dead.”
The Waiapi indigenous reserve is in pristine rainforest near the eastern end of the Amazon river. It is part of a much larger conservation zone called Renca, covering an area the size of Switzerland. Surrounded by rivers and towering trees, the tribe operates almost entirely according to its own laws, with a way of life at times closer to the Stone Age than the 21st century. Yet modern Brazil is barely a few hours’ drive away. And now the center-right government is pushing to open Renca to international mining companies who covet the rich deposits of gold and other metals hidden under the sea of green.