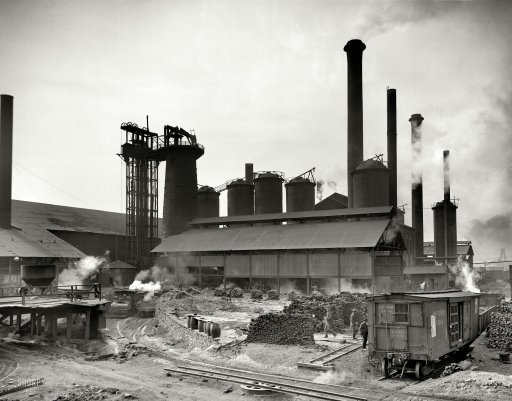
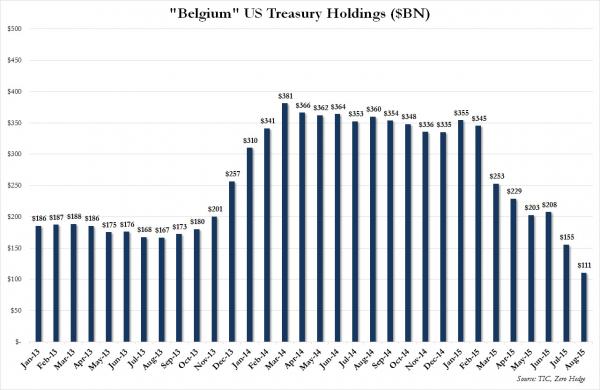
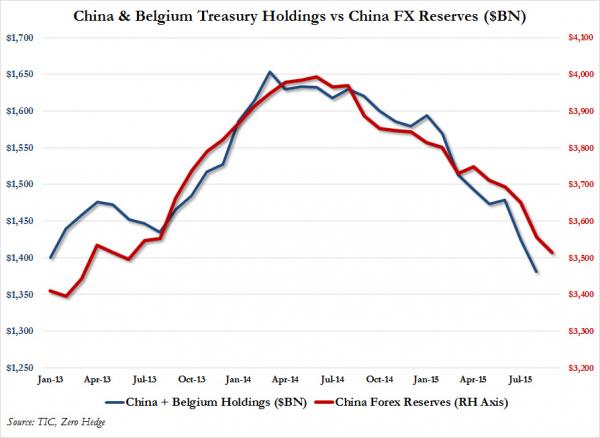
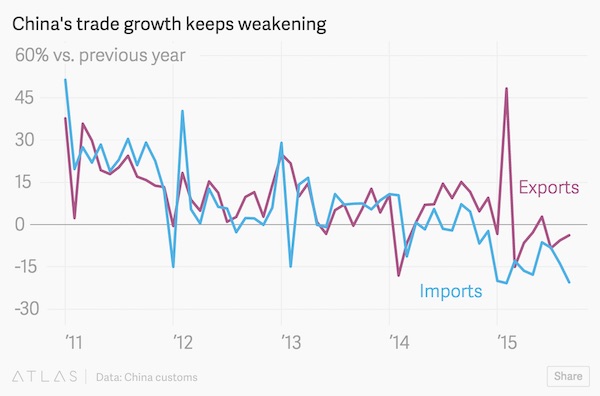
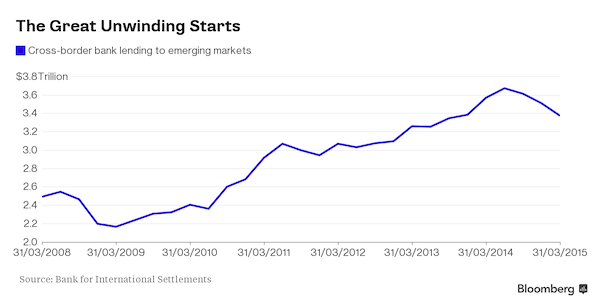
DPC Sloss City furnaces, Birmingham, Alabama 1906



Forward looking.
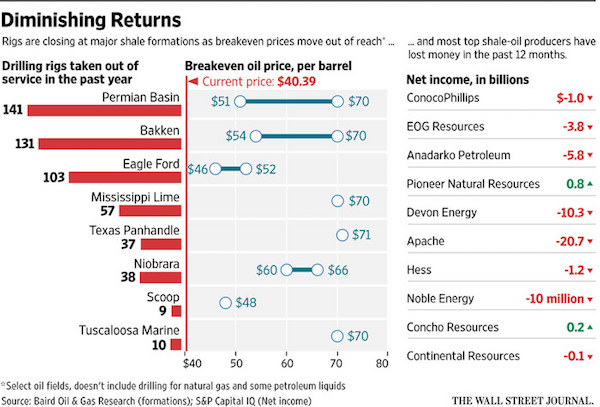
• Weak Demand, Vessel Surplus Mean Horror 2016 For Commodities Shipping (Reuters)
Shipping companies that transport commodities such as coal, iron ore and grain face a painful year ahead, with only the strongest expected to weather a deepening crisis caused by tepid demand and a surplus of vessels for hire. The predicament facing firms that ship commodities in large unpackaged amounts – known as dry bulk – is partly the result of slower coal and iron ore demand from leading global importer China in the second half of 2015. The Baltic Exchange’s main sea freight index – which tracks rates for ships carrying dry bulk commodities – plunged to an all-time low this month. In stark contrast, however, tankers that transport oil have in recent months enjoyed their best earnings in years. As crude prices have plummeted, bargain-buying has driven up demand, while owners have moved more aggressively to scrap vessels to head off the kind of surplus seen in the dry bulk market.
Symeon Pariaros, chief administrative officer of Athens-run and New York-listed shipping firm Euroseas, said the outlook for the dry bulk market was “very challenging”. “Demand fundamentals are so weak. The Chinese economy, which is the main driver of dry bulk, is way below expectations,” he added. “Only companies with very strong balance sheets will get through this storm.” The dry bulk shipping downturn began in 2008, after the onset of the financial crisis, and has worsened significantly this year as the Chinese economy has slowed. The Baltic Exchange’s main BDI index – which gauges the cost of shipping such commodities, also including cement and fertiliser – is more than 95% down from a record high hit in 2008. The index is often regarded as a forward-looking economic indicator. With about 90% of the world’s traded goods by volume transported by sea, global investors look to the BDI for any signs of changes in sentiment for industrial demand.

Very thin trading.
• Energy Stocks Fall Along With Oil Prices (WSJ)
A fresh selloff in the oil market weighed down U.S. stocks, with energy shares posting sharp losses. Major U.S. indexes pared their steepest declines but still ended the day in negative territory, returning some of last week’s gains. The Dow Jones Industrial Average lost 23.90 points, or 0.1%, to 17528.27, after falling as much as 115 points intraday. The S&P 500 index fell 4.49, or 0.2%, to 2056.50. The Nasdaq Composite Index declined 7.51, or 0.1%, to 5040.99. Just 4.8 billion shares changed hands Monday, marking the lowest full day of U.S. trading volume this year, in a holiday-shortened week. Markets in London and Australia were closed Monday for Boxing Day. The U.S. stock market will be closed Friday for New Year’s Day. Energy stocks notched some of the steepest declines across the market. Chevron posted the heaviest loss among Dow components, falling $1.69, or 1.8%, to $90.36.
Marathon Oil shed 95 cents, or 6.8%, to 12.98. “We’re just following the price of oil,” said Peter Cardillo, chief market economist at brokerage First Standard Financial. December has been marked by unusually wide swings in U.S. stocks. A long-awaited interest-rate increase by the Federal Reserve earlier in the month has failed to quiet the recent volatility. A respite from the decline in oil prices last week helped lure investors into the energy sector. U.S. stocks last week posted their biggest weekly gains in more than a month, driven by the energy sector. But both oil prices and energy stocks remain sharply lower this year, even with last week’s rally. A global glut of crude oil has contributed to a 30% fall in U.S. oil prices this year. On Monday, U.S. crude prices fell 3.4% to $36.81 a barrel. Energy stocks in the S&P 500 are down 23% so far in 2015, while the S&P 500 is on track for a loss of 0.1%.

if the dollar stays strong, the peg is history.
• Saudi Riyal In Danger As Oil War Escalates (AEP)
Saudi Arabia is burning through foreign reserves at an unsustainable rate and may be forced to give up its prized dollar exchange peg as the oil slump drags on, the country’s former reserve chief has warned. “If anything happens to the riyal exchange peg, the consequences will be dramatic. There will be a serious loss of confidence,” said Khalid Alsweilem, the former head of asset management at the Saudi central bank (SAMA). “But if the reserves keep going down as they are now, they will not be able to keep the peg,” he told The Telegraph. His warning came as the Saudi finance ministry revealed that the country’s deficit leapt to 367bn riyals (£66bn) this year, up from 54bn riyals the previous year. The IMF has suggested Saudia Arabia could be running a deficit of around $140bn.
Remittances by foreign workers in Saudi Arabia are draining a further $36bn a year, and capital outflows were picking up even before the oil price crash. Bank of America estimates that the deficit could rise to nearer $180bn if oil prices settle near $30 a barrel, testing the riyal peg to breaking point. Dr Alsweilem said the country does not have deep enough pockets to wage a long war of attrition in the global crude markets, whatever the superficial appearances. Concern has become acute after 12-month forward contracts on the Saudi Riyal reached 730 basis points over recent days, the highest since the worst days of last oil crisis in February 1999. The contracts are watched closely by traders for signs of currency stress. The latest spike suggests that the riyal is under concerted attack by hedge funds and speculators in the region, risking a surge of capital flight.
A string of oil states have had to abandon their currency pegs over recent weeks. The Azerbaijani manat crashed by a third last Monday after the authorities finally admitted defeat. The dollar peg has been the anchor of Saudi economic policy and credibility for over three decades. A forced devaluation would heighten fears that the crisis is spinning out of political control, further enflaming disputes within the royal family. Foreign reserves and assets have fallen to $647bn from a peak of $746bn in August 2014, but headline figures often mean little in the complex world of central bank finances and derivative contracts. Dr Alsweilem, now at Harvard University, said the Saudi authorities have taken a big gamble by flooding the world with oil to gain market share and drive out rivals. “The thinking that lower oil prices will bring down the US oil industry is just nonsense and will not work.”
The policy is contentious even within the Saudi royal family. Optimists hope that this episode will be a repeat of the mid-1980s when the kingdom pursued the same strategy and succeeded in curbing non-OPEC investment, and preperaring the ground for recovery in prices. But the current situation is sui generis. The shale revolution has turned the US into a mid-cost swing producer, able to keep drilling at $50bn a barrel, according to the latest OPEC report. US shale frackers can switch output on and off relatively quickly, acting as a future headwind against price rises.

End of free money.
• Saudis Plan Unprecedented Subsidy Cuts to Counter Oil Plunge (BBG)
Confronting a drop in oil prices and mounting regional turmoil, Saudi Arabia reduced energy subsidies and allocated the biggest part of government spending in next year’s budget to defense and security. Authorities announced increases to the prices of fuel, electricity and water as part of a plan to restructure subsidies within five years. The government intends to cut spending next year and gradually privatize some state-owned entities and introduce value-added taxation as well as a levy on tobacco. The biggest shake-up of Saudi economic policy in recent history coincides with growing regional unrest, including a war in Yemen, where a Saudi-led coalition is battling pro-Iranian Shiite rebels.
In attempting to reduce its reliance on oil, the kingdom is seeking to put an end to the population’s dependence on government handouts, a move that political analysts had considered risky after the 2011 revolts that swept parts of the Middle East. “This is the beginning of the end of the era of free money,” said Ghanem Nuseibeh, founder of London-based consulting firm Cornerstone Global Associates. “Saudi society will have to get used to a new way of working with the government. This is a wake-up call for both Saudi society and the government that things are changing.” This is the first budget under King Salman, who ascended to the throne in January, and for an economic council dominated by his increasingly powerful son, Deputy Crown Prince Mohammed bin Salman.
In its first months in power, the new administration brought swift change to the traditionally slow-moving kingdom, overhauling the cabinet, merging ministries and realigning the royal succession. The new measures are the beginning of a “big program that the economic council will launch,” Economy and Planning Minister Adel Fakeih told reporters in Riyadh. The subsidy cuts won’t have a “large effect” on people with low or middle income, he said.

Immediate danger for House of Saud.
• Saudi Arabia Plans Subsidy Cuts as King Unveils 2016 Budget (BBG)
Saudi Arabia said it plans to gradually cut subsidies and sell stakes in government entities as it seeks to counter a slump in oil revenue. The government expects the 2016 budget deficit to narrow to 326 billion riyals ($87 billion) from 367 billion in 2015. Spending, which reached 975 billion riyals this year, is projected to drop to 840 billion. Revenue is forecast to decline to 513.8 billion riyals from 608 billion riyals. The budget is the first under King Salman, who ascended to the throne in January, and an economic council dominated by his increasingly powerful son, Deputy Crown Prince Mohammed bin Salman. The collapse in oil prices has slashed government revenue, forcing officials to draw on reserves and issue bonds for the first time in nearly a decade.
“The budget was approved amid challenging economic and financial circumstances in the region and the world,” the Finance Ministry said. “The deficit will be financed through a plan that considers the best available options, including domestic and external borrowing.” The 2015 deficit is about 16% of GDP, according to Alp Eke, senior economist at National Bank of Abu Dhabi. The median estimate of 10 economists in a Bloomberg survey was a shortfall of 20%. Oil made up 73% of this year’s revenue, according to the Finance Ministry. Non-oil income rose 29% to 163.5 billion riyals. The government has managed to reign in “some spending in the second half of the year,” Monica Malik at Abu Dhabi Commercial Bank said. “With the further fiscal retrenchment that we expect in 2016, we think that the fiscal deficit should narrow to about 10.8% of GDP.”
For 2016, the government allocated 213 billion riyals for military and security spending, the largest component of the budget as the kingdom fights a war in Yemen against Shiite rebels. “In terms of defense expenditure in particular there’s the burden of the war in Yemen,” Nasser Saidi, president of Nasser Saidi & Associates, said by phone. The outcome for 2016 depends on “the course of the war in Yemen, oil prices, how much will subsidies actually get reduced, how effective are they in reigning in public spending and rationalizing some of the spending on large projects, and finally how good are they at reigning in current spending,” he said.

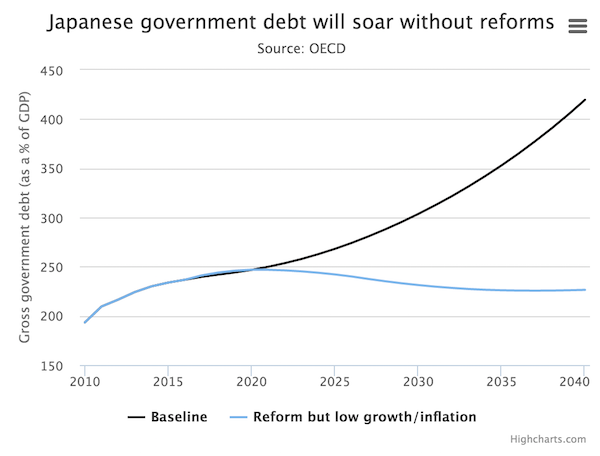
” Japan’s debt pile is huge, at around 240pc of GDP, and the OECD warned this year that it could balloon to 400pc of GDP..”
• Where Next For The Three Arrows Of Abenomics? (Telegraph)
The last sales tax increase threw the world’s third largest economy into recession. For this reason, things may start getting more complicated at the checkout. Policymakers announced last week that they plan to exempt food from the next hike. This would be the first time Japan has adopted different consumption tax rates since it was introduced in 1989. The government estimates this will cost about one trillion yen (£5.5bn) in lost revenues – equivalent to about a fifth of what it expects the increase to bring in. While cynics highlight the move as a ploy to win votes ahead of next year’s upper house elections, it is also a reminder that steering Japan out of its two-decade malaise remains a challenge. It’s been three years since prime minister Shinzo Abe took power with a promise to smash deflation and “take back Japan”.
Under the stewardship of Bank of Japan governor Haruhiko Kuroda, the country launched a multi trillion yen quantitative easing programme in 2013 that was beefed up to ¥80 trillion (£446bn) annually last October. Pessimists argue that Japan’s monetary steroids have had little impact. As economists at BNP Paribas highlight, real GDP has grown by just 2.2pc between the fourth quarter of 2012 and the third quarter of this year – or an average of just 0.8pc per year – a poor performance compared with its G7 peers. Japan’s recovery has been lacklustre since the 2008 crisis, and the economy would currently be in a quintuple-dip recession if growth for the third quarter of 2015 had not been revised up this month. This month, the Bank of Japan revised down its growth forecast for the year ending next March to 1.2pc, from 1.7pc, citing weaker global growth.
It also pushed back its expectation of achieving 2pc inflation to the second half of the year or early 2017, from a previous forecast of mid-2016. This is the second time the target date has been moved since Mr Kuroda pledged in April 2013 to lift consumer inflation to 2pc in “around two years”. Policymakers are already talking down their chances of reflating the economy. Consumer prices rose by just 0.3pc in the year to October, while core inflation, which strips out the impact of volatile food and energy prices, stood at 0.7pc. “If consumer prices were rising more than 1.5pc then I don’t think you could complain when talking about the price target,” said Akira Amari, Japan’s economy minister.
On a brighter note, nominal GDP, or the cash size of the economy, has risen at a more robust pace. This is important because nominal GDP determines a country’s ability to pay down its debt, most of which is fixed in cash terms. Japan’s debt pile is huge, at around 240pc of GDP, and the OECD warned this year that it could balloon to 400pc of GDP unless policymakers implemented vital structural reforms.

M&A as a means to hide one’s indebtedness.
• Record Merger Boom Won’t Stop In 2016, Because Money Is Still Cheap (Forbes)
It was a year for the record books when it comes to merger and acquisition activity. Nearly $5 trillion in deals were cut globally, a new all-time high, as dealmakers used consolidation to uncover cost cuts, bolster their scale and take advantage of historically low borrowing costs. Though 2016 may be a tougher year if emerging market growth slows further and the impact of a sharp rout in commodities hits North America, few expect today’s merger boom to slow. After all, most of the reasons M&A climbed from $3 trillion to $4 trillion and now a rounding error below $5 trillion remain. Corporations are using cheap debt financing to buy competitors and wrench out synergies that can quickly grow their earnings. Amid a mostly halting economic recovery in the United States, M&A has proven far more attractive and easy to pitch to investors than an expansion, which might require increased plant and equipment and rising expenses.
For the nation’s largest companies, there’s also been a race to increase market power, or respond to consolidation among competitors. In pharmaceuticals, these trends have manifest themselves in the race to merge with European-domiciled drugmakers who can access cash stockpiles without triggering repatriation tax and aren’t charged at U.S. rates globally. This has spurred a pharma merger wave that hit new records in 2015 and it isn’t expected to slow anytime soon. In technology, mergers are yet to hinge on tax savings. Instead, semiconductors facing tectonic shifts such as the adoption wireless devices and cloud computing are merging in an effort to round out their services. Consolidation in cable and telecommunications is being used to adapt to the commoditization of once lucrative services like video and data bundles.
The combination of overlapping wireless and broadband networks is also seen as an efficient way to build the infrastructure that’s needed to serve consumers’ shift to streaming media. Spongy financing markets have aided the M&A boom. Low economic growth, modest inflation and weak pricing power are all causing CEOs to look at engineering profits through share buybacks and mergers. Meanwhile, activist shareholders are putting pressure on C-Suites to provide a clear plan on how they reinvest profits. Bold bets have to be justified with credible return expectations and these days it seems the returns by way of M&A, not capital expenditure or expansion.

Casino control.
Can authorities in China really take a back seat? In the midst of a bull market (stocks are up more than 20% from their August lows), Beijing appears to be handing control over to companies for all new initial public offerings from March onward. The shift toward a more U.S.-style disclosure system, where any company can list so long as they provide the requisite information, has been a long time coming. In a more market-oriented system, the regulator concentrates on supervising publicly traded firms rather than acting as a gatekeeper. Such a system would give China’s cash-strapped corporates a funding alternative to shadow banks and online peer-to-peer lenders, and help clear a logjam of almost 700 companies waiting to sell shares for the first time. The question is, can Beijing truly stop its tinkering?
According to KPMG, China has imposed moratoriums on IPOs nine times in the A-share market’s relatively short 25-year history – four of those in the last decade during periods when things were heading south. The most recent halt, enforced in July after several blockbuster share sales and some stomach-churning stock declines, ended only last month when a government-engineered rally revived the market.Even when IPOs have been approved, social policy dominates. A few years ago, when China was trying to cool its then-heady real estate sector and rein in burgeoning bad loans, no developer or city commercial bank would have stood a chance getting listing approval. Instead, some went to Hong Kong to raise funds. The conundrum for the China Securities Regulatory Commission is that letting any (qualified) company sell shares would result in a glut and damp appetite for the state-owned firms that dominate the market.
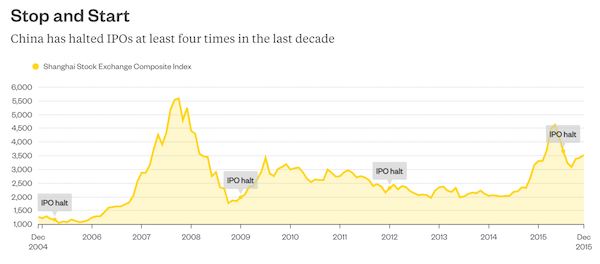
However, rationing admittance to the IPO market means bureaucrats rather than investors are making the decisions, and has resulted in an insatiable demand for new stock. An even bigger challenge for the CSRC, whose seven-member listing committee currently vets IPO applications, is managing investor expectations. In a nation where investment options tend to be limited to volatile wealth management products, equally choppy real estate or low-yielding bank accounts, people have little recourse for their some $22 trillion in savings beyond stocks. That explains why retail investors own about 80% of publicly traded companies’ tradeable shares unlike the U.S., where institutional investors dominate. Such a prevalence of individuals, who don’t have class action lawsuits to fall back on in cases of corporate malfeasance, also makes for a stock market more akin to a casino than a funding tool.

Shadow banking clamp down.
• China Clamps Down on Online Lenders, Vows to Cleanse Market (BBG)
China’s banking regulator laid out planned restrictions on thousands of online peer-to-peer lenders, pledging to “cleanse the market” as failed platforms and suspected frauds highlight risks within a booming industry. Online platforms shouldn’t take deposits from the public, pool investors’ money, or guarantee returns, the China Banking Regulatory Commission said on Monday, publishing a draft rule that will be its first for the industry. The thrust of the CBRC’s approach is that the platforms are intermediaries – matchmakers between borrowers and lenders – that shouldn’t themselves raise or lend money. It rules out P2P sites distributing wealth-management products, a tactic that some hoped would diversify their revenue sources, and limits their use for crowdfunding.
“The rule is quite strict,” Shanghai-based Maizi Financial Services, which operates a P2P site and other investment platforms, said in a statement. “The industry’s hope of upgrading itself with wealth management products and adopting a diversified business model is completely dashed.” The banking regulator issued its plan at the same time as the central bank put out a rule to tighten oversight of online-payment firms. The looming clampdown – the regulator asked for feedback by Jan. 27 – comes as the police probe Ezubo, an online site that raised billions of dollars from investors according to Yingcan Group, a company which provides industry data. It also follows a stock boom and bust that was fueled by leverage, including some channeled through online lenders.
China had 2,612 online lending platforms operating normally as of November, with more than 400 billion yuan ($61.7 billion) of loans outstanding, while another 1,000 were “problematic,” the CBRC said. Firms such as Tiger Global Management, Standard Chartered and Sequoia Capital are among those to invest in the industry, which China initially allowed to develop without regulation. Under the planned rule, P2P platforms will need to register with local financial regulators and cannot help borrowers who want to raise money to invest in the stock market. They’re banned from crowdfunding “for equities and physical items,” a description that wasn’t clarified in the CBRC statement. “Many online lenders have strayed from the role of information intermediary,” the CBRC said in a separate statement, adding that it wanted to protect consumers and “cleanse the market.”

Control clowns: “..a goal of doubling GDP and per capita income by 2020 from 2010..”
• China Central Bank Says To Keep Reasonable Credit Growth, Yuan Stable (Reuters)
China’s central bank said on Monday that it would “flexibly” use various policy tools to maintain appropriate liquidity and reasonable growth in credit and social financing. The People’s Bank of China will keep the yuan basically stable while forging ahead with reforms to help improve its currency regime, it said in a statement summarizing the fourth-quarter monetary policy committee meeting. The PBOC said it would maintain a prudent monetary policy, keeping its stance “neither too tight nor too loose”. The prudent policy has been in place since 2011. “We will improve and optimize financing and credit structures, increase the proportion of direct financing and reduce financing costs,” it said. The central bank said it would closely watch changes in China’s economy and financial markets, as well as international capital flows.
Top leaders at the annual Central Economic Work Conference pledged to make China’s monetary policy more flexible and expand its budget deficit in 2016 to support a slowing economy as they seek to push forward “supply-side reform”. The PBOC has cut interest rates six times since November 2014 and lowered banks’ reserve requirements, or the amount of cash that banks must set aside as reserves. But such policy steps have yielded limited impact on the economy, as the government has been struggling to reach its growth target of about 7% this year. President Xi Jinping has said China must keep annual average growth of no less than 6.5% over the next five years to hit a goal of doubling GDP and per capita income by 2020 from 2010.

Betcha Cameron is more concerned right now with London’s flood control than Lancashire’s.
• Cost Of UK Floods Tops £5 Billion, Thousands Face Financial Ruin (Guardian)
The cost of the UK’s winter floods will top £5bn and thousands of families and businesses will face financial ruin because they have inadequate or non-existent insurance, a leading accountant has warned, as the government defended its record on flood defences. The prime minister faced growing anger from politicians in the north of England who accused the government of creating “a north-south gap” in financial support for flood-prevention schemes. On a tour of the region, David Cameron defended spending levels amid mounting criticism from MPs and council leaders. “We are spending more in this parliament than the last one and in the last parliament we spent more than the one before that,” he said during a stop in York.
“I think with any of these events we have to look at what we are planning to spend and think: ‘Do we need to do more?’ We are going to spend £2.3bn on flood defences in this parliament but we will look at what’s happened here and see what needs to be done. We have to look at what’s happened in terms of the flooding, what flood defences have worked and the places where they haven’t worked well enough.” But Judith Blake, leader of Leeds city council, said a flood prevention scheme for the city was ditched by the government in 2011, and warned that there was “a very strong feeling” across the region that the north was being short-changed.
“I think there’s a real anger growing across the north about the fact that the cuts have been made to the flood defences and we’ll be having those conversations as soon as we are sure that people are safe and that we start the clean-up process and really begin the assess the scale of the damage. “So there are some very serious questions for government to answer on this and we’ll be putting as much pressure on as possible to redress the balance and get the funding situation equalised so the north get its fair share.” Labour MP Ivan Lewis, meanwhile, challenged Cameron to back up his vision of the Northern Powerhouse by sending immediate help to residents and businesses in his Bury South constituency.
[..] On Monday, as the waters receded in the worst hit areas, residents began to face up the scale of the damage. In York telephone lines and internet connections were down and some cash machines were not working. Many of the bars and shops that were open were only taking cash. In Hebden Bridge in Calderdale, volunteers spent the day clearing out schools, shops and homes that had been overwhelmed by filthy floodwater – a scene repeated in scores of towns and cities across the region. Forecasters warned another storm – Storm Frank – is expected to bring more rain to the west and north of the UK on Wednesday. It is feared that up to 80mm (3in) will fall on high ground and as much as 120mm (4.7in) in exposed locations, accompanied by gale force winds..

Oh yeah, an economy others are jealous of.
• UK Factories Forecast To Shed Tens Of Thousands Of Jobs In 2016 (Guardian)
British manufacturers will shed tens of thousands of jobs next year as they battle a tough export market, the fallout from steel plant closures and a collapse in demand from the embattled North Sea oil industry, an industry group has forecast. The manufacturers’ organisation EEF said the factory sector will shrug off this year’s recession and eke out modest growth in 2016 but it warned a number of risks loom on the horizon, chief among them a sharper downturn in China that could trigger a global slump. A cautious mood has prompted many firms to plan cuts to both jobs and investment in a further blow to George Osborne, after the latest official figures showed UK economic growth had faltered and that his “march of the makers” vow had failed to translate into a manufacturing revival.
EEF said its latest snapshot of manufacturers’ mood shows some bright spots for 2016, however, particularly in the car, aerospace and pharmaceutical sub-sectors. They will be the main drivers behind overall manufacturing growth of 0.8% in 2016, following an expected 0.1% contraction this year. Those sub-sectors will also buck the wider manufacturing trend of job cuts with an employment increase in 2016, EEF predicts. “Some of the headwinds have been a consistent theme over 2015 – the collapse in oil and gas activity, weakness in key export markets, and strong sterling. Others, like disappointing construction activity and the breakdown in the steel industry, have piled on the pain since the second quarter of 2015,” said EEF’s chief economist, Lee Hopley, in the report. “It’s not all doom and gloom however, with the resilience of the transport sectors and the rejuvenation of the pharmaceuticals industry providing reasons for cheer in UK manufacturing.”

“..it would require dedication to clear goals and the hard work of altering all our current arrangements – and giving up these childish fantasy distractions about space and technology.”
• Questions and Answers (Jim Kunstler)
The really big item in last night’s 60-Minutes newsbreak was that the latest Star Wars movie passed the billion dollar profit gate a week after release. That says just about everything you need to know about our floundering society, including the state of the legacy news media. The cherry on top last week was Elon Musk’s SpaceX company’s feat landing the first spent stage of its Falcon 9 rocket to be (theoretically) recycled and thus hugely lowering the cost of firing things into space. The media spooged all over itself on that one, since behind this feat stands Mr. Musk’s heroic quest to land humans on Mars. This culture has lost a lot in the past 40 years, but among the least recognized is the loss of its critical faculties. We’ve become a nation of six-year-olds.
News flash: we’re not going Mars. Notwithstanding the accolades for Ridley Scott’s neatly-rationalized fantasy, The Martian (based on Andy Weir’s novel), any human journey to the red planet would be a one-way trip. Anyway, all that begs the question: why are we so eager to journey to a dead planet with none of the elements necessary for human life when we can’t seem to manage human life on a planet superbly equipped to support us? Answer: because we are lost in raptures of techno-narcissism. What do I mean by that? We’re convinced that all the unanticipated consequences of our brief techno-industrial orgy can be solved by… more and better technology! Notice that this narrative is being served up to a society now held hostage to the images on little screens, by skilled people who, more and more, act as though these screens have become the new dwelling place of reality.
How psychotic is that? All of this grandstanding about the glories of space goes on at the expense of paying attention to our troubles on this planet, including the existential question as to how badly we are fucking it up with burning the fossil fuels that power our techno-industrial activities. Personally, I don’t believe that any international accord will work to mitigate that quandary. But what will work, and what I fully expect, is a financial breakdown that will lead to a forced re-set of human endeavor at a lower scale of technological activity. The additional question really is how much hardship will that transition entail and the answer is that there is plenty within our power to make that journey less harsh.
But it would require dedication to clear goals and the hard work of altering all our current arrangements – and giving up these childish fantasy distractions about space and technology. Dreaming about rockets to Mars is easy compared to, say, transitioning our futureless Agri-Biz racket to other methods of agriculture that don’t destroy soils, water tables, ecosystems, and bodies. It’s easier than rearranging our lives on the landscape so we’re not hostage to motoring everywhere for everything. It’s easier than educating people to both think and develop real hands-on skills not dependent on complex machines and electric-powered devices.

Wild theories welcome.
• Qatari Royals Rush To Switzerland In Nine Planes After Emir Breaks Leg (AFP)
Unidentified individuals travelling in as many as nine planes belonging to Qatar’s royal family made an emergency trip to Switzerland over the weekend for medical reasons, according to a Swiss official. A spokesman for Switzerland’s federal office of civil aviation confirmed local media reports that multiple aircraft made unscheduled landings at the Zurich-Kloten airport overnight from 25 to 26 December and that the planes were part of the Qatari royal fleet. He gave no details as to who was on board or who any of the potential patients may have been. “The emergency landing clearance was given by the Swiss air force,” he told AFP, explaining that the civil aviation office was closed during the hours in question.
Qatari authorities later said that the country’s former ruler, Sheikh Hamad bin Khalifa Al Thani, had been flown to Switzerland over the weekend for surgery after breaking a leg. The Qatari government’s communications office said early on Tuesday that Sheihk Hamad suffered “a broken leg while on holiday” and was flown to Zurich on Saturday to receive treatment. The office says the 63-year-old sheikh underwent a successful operation and was in Zurich “recovering and undergoing physiotherapy.” The government declined to say how or where Sheikh Hamad broke his leg but the royal family had reportedly been on holiday in Morocco at a resort in the Atlas mountains. Night landings and takeoffs are typically forbidden at Zurich-Kloten to avoid disturbing local residents.
Swiss foreign ministry spokesman Georg Farago told AFP in an email that the federation was informed about the “stay of members of Qatar’s royal family in Switzerland”, without giving further details. According to Zurich’s Tages Anzeiger newspaper, the first Qatari plane, an Airbus, landed in Zurich from Marrakesh shortly after midnight on 26 December. A second flight landed at Zurich-Kloten at 5am (0400 GMT) on 26 December, with a third plane coming 15 minutes later, both having originated in Doha, the paper reported. According to Tages Anzeiger, the medical emergency in question was so significant that six more planes linked to the Qatari royal family and government landed in Zurich through the weekend. Sheikh Hamad is believed to have been in poor health for years. He ruled the oil-and-gas-rich Qatar from 1995 until handing over power to his son, Sheikh Tamim, in 2013.

“It’s as if a bomb went off. And, in fact, it did.”
• Freak Storm In Atlantic To Push Arctic Temps Over 50º Above Normal (WaPo)
The vigorous low pressure system that helped spawn devastating tornadoes in the Dallas area on Saturday is forecast to explode into a monstrous storm over Iceland by Wednesday. Big Icelandic storms are common in winter, but this one may rank among the strongest and will draw northward an incredible surge of warmth pushing temperatures at the North Pole over 50 degrees above normal. This is mind-boggling. And the storm will batter the United Kingdom, reeling from recent flooding, with another round of rain and wind. Computer model simulations show the storm, sweeping across the north central Atlantic today, rapidly intensifying along a jet stream ripping above the ocean at 230 mph. The storm’s pressure is forecast by the GFS model to plummet more than 50 millibars in 24 hours between Monday night and Tuesday night, easily meeting the criteria of a ‘bomb cyclone’ (a drop in pressure of at least 24 mb in 24 hours),
By Wednesday morning, when the storm reaches Iceland and nears maximum strength, its minimum pressure is forecast to be near 923 mb, which would rank among the great storms of the North Atlantic. (Note: there is some uncertainty as to how much it will intensify. The European model only drops the minimum pressure to around 936 mb, which is strong but not that unusual). Winds of hurricane force are likely to span hundreds of miles in the North Atlantic. Environmental blogger Robert Scribbler notes this storm will be linked within a “daisy chain” of two other powerful North Atlantic low pressure systems forming a “truly extreme storm system.” He adds: “The Icelandic coast and near off-shore regions are expected to see heavy precipitation hurled over the island by 90 to 100 mile per hour or stronger winds raging out of 35-40 foot seas. Meanwhile, the UK will find itself in the grips of an extraordinarily strong southerly gale running over the backs of 30 foot swells.”
[..] Ahead of the storm, the surge of warm air making a beeline towards the North Pole is astonishing. [..] It’s as if a bomb went off. And, in fact, it did. The exploding storm acts a remarkably efficient heat engine, drawing warm air from the tropics to the top of the Earth. The GFS model projects the temperature at the North Pole to reach near freezing or 32 degrees early Wednesday. Consider the average winter temperature there is around 20 degrees below zero. If the temperature rises to freezing, it would signify a departure from normal of over 50 degrees.

Hope some of that goes toward giving them jobs.
• German States To Spend At Least €17 Billion On Refugees In 2016 (Reuters)
Germany’s federal states are planning to spend around €17 billion on dealing with the refugee crisis in 2016, newspaper Die Welt said on Tuesday, citing a survey it conducted among their finance ministries. The sum, bigger than the €15.3 billion that the central government planned to allocate to its education and research ministry in 2015, is a measure of the strain that the influx is causing across the country as a whole. Germany is the favoured destination for many of the hundreds of thousands of refugees fleeing conflict and poverty in the Middle East and Africa, partly due to the generous benefits that it offers.
The German states have repeatedly complained that they are struggling to cope, and Chancellor Angela Merkel’s open-door policy has caused tensions within her conservative camp. Die Welt said that excluding the small city state of Bremen, which did not provide any details, current plans suggested the states’ combined expenditure would be €16.5 billion. The paper said actual costs would probably be even higher because the regional finance ministries had based their budgets on an estimate from the federal government that 800,000 refugees would come to Germany in 2015. In fact, 965,000 asylum seekers had already arrived by the end of November.

Finance ministers have no place intervening in politics.
• Schaeuble Slams Greece Over Refugee Crisis, Aims For Joint EU Army (Reuters)
Germany’s finance minister Wolfgang Schaeuble and a senior Bavarian politician criticized Greece on Sunday over the way it is managing its role in Europe’s biggest migration crisis since World War Two. Schaeuble, who has clashed repeatedly with Greek officials this year over economic policy, told Bild am Sonntag that Athens has for years ignored the rules that oblige migrants to file for asylum in the European Union country they arrive in first. He said German courts had decided some time ago that refugees were not being treated humanely in Greece and could therefore not be sent back there. “The Greeks should not put the blame for their problems only on others, they should also see how they can do better themselves,” Schaeuble said.
Greece, a main gateway to Europe for migrants crossing the Aegean sea, has faced criticism from other EU governments who say it has done little to manage the flow of hundreds of thousands of people arriving on its shores. Joachim Herrmann, the interior minister of the southern state of Bavaria, that has taken the brunt of the refugee influx to Germany, criticized the way Greece is securing its external borders. “What Greece is doing is a farce,” Herrmann said in an interview with Die Welt am Sonntag newspaper, adding any that any country that does not meet its obligations to secure its external borders should leave the Schengen zone, where internal border controls have been abolished.
[..] In contrast to his criticism of Greece, Schaeuble sought to offer to compromise with eastern European countries that have voiced reluctance to accept migrants under EU quotas. “Solidarity doesn’t start by insulting each other,” Schaeuble said. “Eastern European states will also have to take in refugees, but fewer than Germany.” The influx of hundreds of thousands of migrants, many fleeing war and poverty in the Middle East, also means that European countries will have to increase spending on defense, he said. “Ultimately our aim must be a joint European army. The funds that we spend on our 28 national armies could be used far more effectively together,” Schaeuble said.

No, EU indifference on refugees has brought it down.
• Selfishness On Refugees Has Brought EU ‘To Its Knees’ (IT)
The “ruinously selfish” behaviour of some member states towards refugees has brought the European Union to its knees, former attorney general Peter Sutherland has said. In a sharp denunciation of Europe’s failures on migration and social integration, Mr Sutherland, who is special representative to the United Nations secretary general for migration, said political “paralysis and ambivalence” was threatening the future of the EU and resulting in the rise of xenophobic and racist parties. With a population of 508 million, the EU should have had no insuperable problem welcoming even a million refugees “had the political leadership of the member states wanted to do so and had the effort been properly organised,” Mr Sutherland said. “But instead, ruinously selfish behaviour by some member states has brought the EU to its knees.”
There were several “honourable exceptions”, most notably German chancellor Angela Merkel, who he described as “a heroine” for showing openness and generosity towards refugees. Mr Sutherland made the remarks in the Littleton memorial lecture, which was broadcast on RTÉ radio on St Stephen’s Day. More than a million refugees and migrants arrived in the EU by land and sea in 2015, according to the International Organisation for Migration, making this the worst crisis of forced displacement on the continent since the second World War. Half of those arriving were Syrians fleeing a conflict that has left almost 250,000 people dead and displaced half the country’s pre-war population. A European Commission plan to use quotas to relocate asylum seekers arriving in southeastern Europe was adopted in the autumn against strong opposition from several states, including Hungary, Poland and the Czech Republic.
Slovakia said it would take in only a few hundred refugees, and they would have to be Christians. Mr Sutherland said the razor and barbed wire fences being erected on the Hungarian border to keep out migrants and refugees “are not just tragic but they are also particularly ironic, as Hungarians were for so long confined by the Iron Curtain.” He recalled that in 1956, after their failed revolution, 200,000 Hungarian refugees were immediately given protection throughout Europe and elsewhere. “Yet now, prime minister Viktor Orbán is the most intransigent and vociferous opponent of taking refugees in the EU.” Mr Sutherland accused some heads of government of “stoking up prejudice” by speaking of barring Muslim migrants and said the absence of EU agreement on a refugee-sharing scheme meant a Europe of internal borders was increasingly likely to become a reality across the continent.

Waiting for the next surge as soon as the weather gets better.
• Refugee Arrivals In Greece Rise More Than Tenfold In A Year (Kath.)
Over 800,000 refugees and migrants entered Greece between the start of the year and the end of November, with the number of arrivals increasing more than tenfold compared to last year’s total of 72,632, data published by the Greek Police showed Monday. The number tallies with figures from the United Nations High Commission for Refugees (UNHCR), which puts total arrivals in Greece from January 1 to December 24 at 836,672. The UNHCR also reported that in the three-day period from December 24 to 26, daily arrivals in Greece came to 2,950, with the monthly average at 3,400 per day, a significant drop from November’s average of 5,040. Most arrivals continue to enter Greece via the islands close to Turkey, the main transit point for refugees and migrants fleeing strife in the Middle East and South Asia and trying to enter the European Union.
On Lesvos alone, authorities estimate that they continue to receive from 2,000 to 2,500 arrivals every day, down from an average of over 5,000 in November. Police on the eastern Aegean island on Monday said that more than 3,500 refugees and migrants were waiting to be ferried to the mainland by this afternoon, while at the island’s main registration center in Moria, there are a further 4,000 people waiting to be processed and granted permission to leave for Athens, from where they will continue their journey north. In the capital, meanwhile, the Asylum Service of the Citizens’ Protection Ministry on Monday published data showing that only 82 of the 449 applications it has submitted so far for the relocation of refugees from Syria, Iraq and Eritrea to other parts of the European Union have been successful.
The initial plan drawn up by European authorities was for a total of 66,400 refugees to be transferred from Greece to other EU member-states, though only 13 countries have come forward, offering to take in a total of 565 asylum seekers. The repatriations that have been successful have been to Luxembourg, which took in 30 people, Finland (24), Portugal (14), Germany (10) and Lithuania, which accepted four relocations.