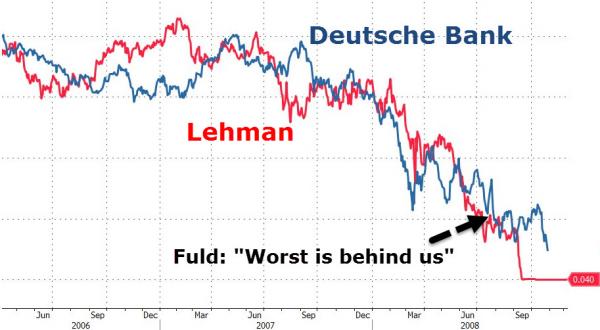
Kennedy and Johnson Morning of Nov 22 1963

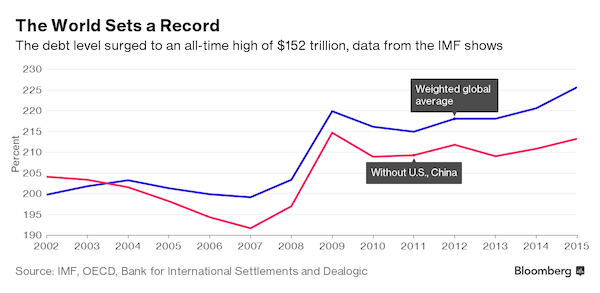
“So why the approximately $1.8 trillion surge in government borrowing? Because a robustly-healthy economy was necessary to help the party in power stay in power.”
• Another Election Year, Another Bunch Of Fake Growth Numbers (John Rubino)
Some pretty good economic reports have energized various parts of the financial markets lately. Consumer spending is up, GDP is exceeding expectations and even factory orders, that perennial downer, popped this morning. In response the dollar is soaring and interest rates are at breaking out of their multi-decade down-channel. The economy is clearly recovering, implying a return to normality. Right? Nah, it’s just the usual election year illusion. When the presidency is at stake the party in power always pumps up spending in an attempt to put people back to work and create the impression of a well-run country whose leaders deserve more time in the spotlight. After the election, spending returns to trend and the resulting bad news gets buried in “political honeymoon” media coverage.
How do we know this year is following the script? By looking at the federal debt. If the government is borrowing more than usual and (presumably) spending the proceeds, then it’s likely that the economy is getting a bit more than its typical diet of stimulus. So here you go: Note that after seven years of massive increases, the federal debt plateaued in 2015, which is what you’d expect in the late stages of a recovery. With full employment approaching and asset prices high, there should be plenty of tax revenues flowing in and relatively few people on public assistance, so the budget should be trending towards balance. Well, more people are working this year than last, and stock, bond and home prices all rose in the first half of the year. So why the approximately $1.8 trillion surge in government borrowing? Because a robustly-healthy economy was necessary to help the party in power stay in power.
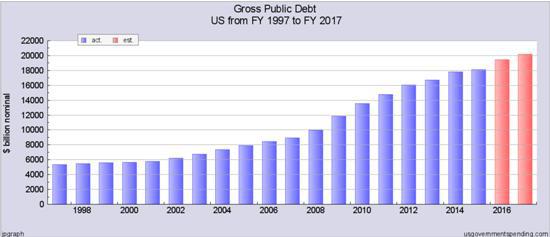
This is a huge jump in government debt, even by recent standards. And its impact is commensurately large, accounting for a big part of the “growth” seen in recent months. But it’s also unsustainable. You don’t double a government’s debt in a single decade (from an already historically high level) and then keep on borrowing. At some point an extreme event or policy choice will put an end to the orgy. Either the markets impose discipline through a crisis of some sort, or the government adopts a policy of currency devaluation or debt forgiveness. And – in a nice ironic twist – the people who did the insanely-excessive borrowing are leaving town, to be replaced by folks who will inherit something unprecedented, with (apparently) no clear idea of what’s coming or what will be necessary in response.

Protectionism and globalism in one.
• China Vows To Defend Trade Rights In Face Of Trump Tariff Threats (R.)
China will defend its rights under WTO tariff rules if US president-elect Donald Trump moves toward executing his campaign threats to levy punitive duties on goods made in China, a senior trade official has said. Zhang Xiangchen, China’s deputy international trade representative, also told a news conference in Washington on Wednesday that a broad consensus of academics, business people and government officials have concluded that China is not manipulating its yuan currency to gain an unfair trade advantage, as Trump has charged. “I think after Mr Trump takes office, he will be reminded that the United States should honour its obligations as a member of the WTO,” Zhang said through an interpreter. “And as a member of the WTO, China also has the right to ensure its rights as a WTO member.”
Trump has said China is “killing us” on trade and that he would take steps to reduce the large US goods trade deficit with China, including labelling Beijing as a currency manipulator soon after he takes office and levying duties of up to 45% on Chinese goods to level the playing field for US manufacturers. Trump said on Monday he will formally exit the 12-country TPP trade deal in January. China is not a signatory to the TPP. Zhang, who spoke at the closing news conference for a two-day technical meeting of US and Chinese trade officials in Washington, was not specific on what steps China would take to protect its rights under WTO rules. The global trading body prohibits members from unilaterally raising tariffs above levels that they have committed to maintain.
China’s state-run Global Times newspaper last week warned that a 45% Trump tariff would paralyse US-China bilateral trade. “China will take a tit-for-tat approach then. A batch of Boeing orders will be replaced by Airbus. US auto and [Apple] iPhone sales in China will suffer a setback, and US soybean and maize imports will be halted,” the newspaper warned.

Shadow securities. US redux.
• IMF: Chinese Banks Disguise A Massive Amount Of Bad Debt (BI)
China’s banks are disguising bad debts by turning them into “securitized packages” rather than writing them down as non-performing loans, according to the IMF. The “untradeable debt” comes from China’s “shadow credit” world, which has generated a massive amount of credit that has the potential to become suddenly illiquid. The debts consist of interbank loans in “a structure potentially susceptible to rapid risk transmission and destabilizing liquidity events,” the IMF says. The amount of “shadow credit” grew 48% in 2015, to RMB 40 trillion ($580 billion), the IMF says, “equivalent to 40% of banks’ corporate loans and 58% of GDP.” If any of this sounds familiar, that’s because it is. It’s similar in principal to the way American banks disguised bad mortgages inside securitized packages before the Great Financial Crisis of 2007-2008.
Back then, US mortgage providers gave out too many loans to people who couldn’t repay them. On its own, that should not have been a problem. A mortgage default only hurts the bank that made the loan. But banks bundled together packages of those mortgages and sold them as “mortgage-backed securities” to other institutions. Bad mortgages were mixed in with good ones, making it impossible for investors to judge their quality. When it became obvious that some of these packages were toxic, no one wanted to buy any them. The market became suddenly illiquid. And the credit derivative hedges and leveraged bets layered upon them magnified the problem throughout the entire banking system, creating the financial collapse that plunged most of the world into recession.

It was always just a fabricated dream.
• The ‘Ownership Society’ Came And Went – A Long Time Ago (MW)
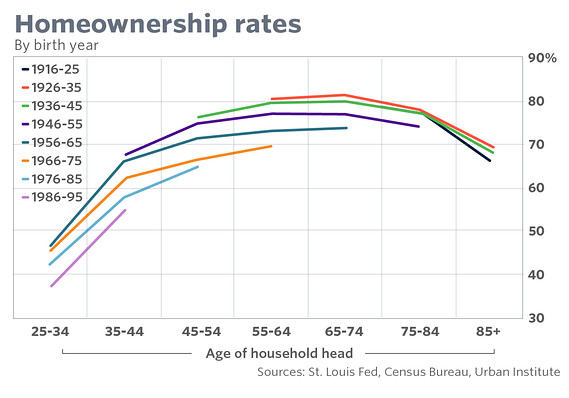
Of all the aftereffects of the housing bust and financial crisis, the steady decline in the homeownership rate might be among the most pernicious. Homeownership is traditionally one of the best means into the middle class, and it’s still popularly equated with the American Dream. But in a presentation last week, St. Louis Federal Reserve economist William Emmons demonstrated that homeownership has been losing ground for decades. What’s more, Emmons showed that higher ownership rates were likely coaxed along by government policies and national priorities appropriate for a certain moment in history and unsustainable beyond that. After the Depression, Emmons noted, New Deal policies “laid the foundation” for a huge increase in homeownership.
Those policies included the creation of a government financial system, such as the Federal Housing Administration, Fannie Mae, and the Federal Home Loan Banks. But just as important was the return of millions of service members from World War II, rising incomes and a prosperous economy, a national push for a country full of suburban single-family homes and highways to connect them all, as well as a national process of Americans “sorting themselves out” by race and class into the broad geographic outlines that would persist for decades. That meant the U.S. enjoyed robust growth – until it didn’t. Not only was there little room left to grow, but other changes began to influence ownership, Emmons said. Americans began to age, pushing off marriage, childbearing and home-buying until later.
The U.S. is also becoming more racially and ethnically diverse. Hispanics and African-Americans have traditionally had more limited opportunities to achieve homeownership – but as Emmons pointed out, citing research from the Harvard Joint Center for Housing Studies, “aspirations to own a home are higher among African-Americans and Latinos than among whites and Asians, despite homeownership rates that are 20 to 30 percentage points lower.” And while much of the impact of the 2008 crash has ebbed, it still continues to impact many people through diminished personal wealth, damaged credit scores, blighted neighborhoods, and some loss of trust in financial institutions.

How ‘little things’ add up.
• How (Slightly) Higher Mortgage Rates Maul Housing Bubble 2 (WS)
After the brutal beating following Election Day, US Treasuries took a breather early this week. But today, the beating resumed and will continue until the mood improves. Mid-day, the 10-year Treasury fell so hard that its yield, which moves in the opposite direction of price, spiked to 2.42%. By the end of the day, the 10-year yield was at 2.36%, up 4 basis points for the day, and up an entire percentage point from July this year: The market is 100% certain that the Fed will stop flip-flopping in mid-December and raise rates by moving the upper limit of the Fed funds target range to 0.75%. The markets see more rate hikes next year. A Fed funds rate with the first “1”-handle since 2008 would be a phenomenon a whole generation of Wall Street gurus has never seen in their professional lives.
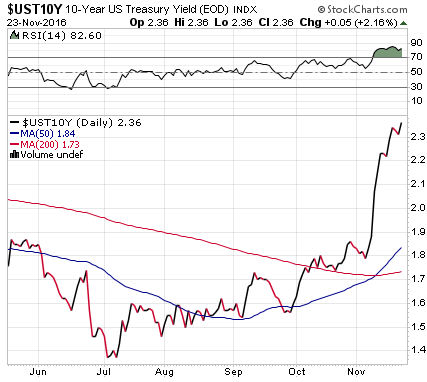
Mortgage rates are chasing after Treasury rates. The Mortgage Bankers Association reported today that the 30-year fixed-rate conforming mortgage ($417,000 or less) reached 4.16%, its “highest weekly average since the beginning of 2016.” This caused a flurry of activity. Last week, amid the post-election interest rate spike, mortgage applications plunged. But homebuyers may be trying to lock in whatever rate they can get, before they go even higher, and mortgage applications surged. Ironically, from a historical point of view, nothing major has happened so far. That spike is still small compared to what came before, including the spike during the Taper Tantrum in the summer of 2013, when the Fed started musing about ending QE Infinity. Compared to prior years, rates are still very, very low, but home prices have since soared, and for home buyers even a minor uptick makes a world of difference.
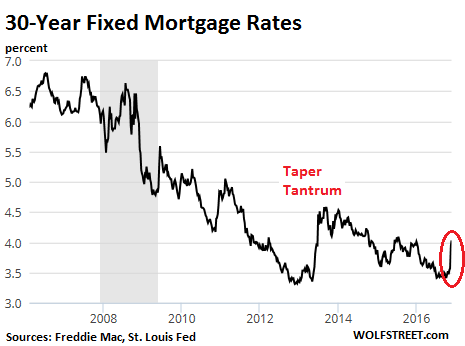
From the peak of Housing Bubble 1, which in San Francisco occurred in 2007, to Q3 2016, the median house price soared 45%. But due to plunging mortgage rates, the monthly housing costs increased only 14%. Now with rates rising, that process is going to reverse. The household income needed to qualify for a 30-year fixed rate mortgage with 20% down on that median $1.3 million house in San Francisco was $251,000 before Election Day. Paragon observes: “By Friday, November 18, the income requirement increased by $13,000. And if the interest rate goes up to 5% (and again, we are not saying it will), an additional $35,000 in annual income would be required.”
Hence, at 5%, a minimum qualifying household income of $286,000 a year. In this scenario, even in less costly markets, there are two things that happen: One, many people have to step down to a lower-priced home, or they don’t buy at all. A market-wide shift of this type puts downward pressure on prices and volume. And two, as people stretch more to buy homes at higher interest rates and higher monthly costs, they have even less money to spend on other things. This creates a new drag on consumer spending. It’s how low mortgage rates not only subsidized the house price bubble but the entire economy by giving consumers more money to spend – not just the US economy but exporter nations around the world.

Or will it?
• ‘Brexit Will Blow £59 Billion Hole In UK Public Finances’ (G.)
Philip Hammond conceded that Brexit will blow a £59bn black hole in the public finances over the next five years, as he outlined plans to boost investment in infrastructure and housing to equip the UK economy for life outside the EU. In his first fiscal statement, the chancellor, who had supported remain, sought to strike a cautiously upbeat tone about the country’s prospects, saying the economy had “confounded commentators at home and abroad with its strength and its resilience” since the referendum result last June. But the first official projections conducted after the vote of the likely impact of leaving the EU pointed to significantly weaker growth after Brexit. The Office for Budget Responsibility (OBR) announced that there would be a cumulative £122bn of extra borrowing over the next five years, with £59bn of that as a direct result of Brexit.
Other factors included weaker-than-expected tax revenues, and policy changes, including Hammond’s decision to spend more on infrastructure. George Osborne was expecting to achieve a surplus of £11bn on the public finances by 2020-21; instead, the OBR is now forecasting a £21bn deficit – and public debt is expected to peak at more than 90% of GDP. With little cash to spare, Hammond offered only modest handouts to the “just about managing” families (Jams) Theresa May’s government had said it wanted to help, although he repeatedly used the mantra of “building an economy that works for everyone”. The chancellor announced a renewed freeze in fuel duty, to help motorists – largely paid for with an increase in insurance premium tax from 10% to 12% – and a partial reversal of planned cuts to universal credit.
But Labour said there was no cash for either the NHS or social care, which are under increasing strain with winter approaching. Instead, the main thrust of Hammond’s first set-piece outing at the dispatch box was how to help Britain withstand the challenges of leaving the EU.

Agree to disagree.
• Pro-Brexit Lawmakers Attack Fiscal Watchdog’s Gloomy Outlook (BBG)
Conservative lawmakers attacked Britain’s fiscal watchdog after it warned that Brexit would cost £60 billion ($75 billion) in extra borrowing as the economy falters. The Office for Budget Responsibility’s forecast — the first official assessment of the costs related to leaving the bloc – also stated that exiting the EU would leave Britain with less potential for sustainable growth. Chancellor of the Exchequer Philip Hammond, who presented the forecasts alongside his Autumn Statement Wednesday, said the predictions showed there is an “urgent” need for Britain to tackle its long-term economic weaknesses. “We’ve had an endless slew of gloom and doom, and I just don’t buy it,” said Kwasi Kwarteng, a Tory lawmaker who backed the campaign to leave the EU. “They haven’t exactly had a brilliant track record. I’d take their predictions with a pinch of salt.”
Pro-Brexit lawmakers have been critical of both the OBR and the Treasury for overstating the negative consequences of Brexit. While Hammond made brief references to the opportunities that leaving may bring, his tone was one of caution, with few giveaways and a focus on creating a more productive economy that could weather future shocks. Responding to complaints from pro-Brexit politicians, Hammond told lawmakers that economic forecasting “is not a precise science.” He added: “The OBR very specifically says in its report that there is an unusually high degree of uncertainty in the forecasts it is making because of the unusual circumstances.”

It’s high time for Italy to go its own separate ways. There’s nothing to gain from the EU anymore, but lots to lose.
• Capital Flight From Italy (Reinhart)
Understandably, after the surprise victory in June of the “Leave” campaign in the United Kingdom’s Brexit referendum, and of Donald Trump in the United States’ presidential election, no one has much faith in polls in advance of the Italian vote. There is, however, a disquieting real-time poll of investors’ sentiment: capital flight from Italy has accelerated this year. There is a recent precedent for this. In the summer of 2015, Greece’s short-lived default on its IMF loan and the introduction of capital controls and deposit-withdrawal restrictions were at the center of the eurozone drama. Tensions between the Greek and German governments ran high, and speculation about whether Greece would remain in the eurozone escalated.
The stage has now shifted to the much larger Italian economy. In the current environment of uncertainty, yield spreads on Italian bonds have widened to about 200 basis points over German bunds. Economic and political conditions in the two debt-laden southern European economies differ in important respects; but there are also similarities. Economic growth in both countries has lagged far behind other advanced economies for more than a decade, but most markedly since the Global Financial crisis of 2008-2009. According to IMF estimates, real per capita income in Italy is about 12% below what it was in 2007, with only Greece faring worse. The problem of bank insolvency, endemic in Greece, where nonperforming loans account for more than one-third of bank assets, is not as generalized in Italy.
Still, the uncertain resolution of Italy’s third-largest bank, Monte dei Paschi, together with the Italian government’s limited resources to deal with weak banks, has fueled unease among depositors. Bankers also warn that the plan for Monte dei Paschi’s rescue may be jeopardized by the December referendum, which could trigger another round of decline in share prices. But, for all the talk of a looming banking crisis, the balance-of-payments crisis already underway in Italy since the first half of 2016 is the main factor driving the real-time poll of investors. Prior to the adoption of the euro, an unsustainable balance-of-payments position in Italy (as in other countries with their own currencies) would typically spur the central bank to raise interest rates, thereby making domestic financial assets more attractive to investors and stemming capital flight. With the ECB setting monetary policy for the eurozone as a whole, this is no longer an option for Banca d’Italia.

Nostalgia for hanging chads.
• Jill Stein Raises Over $2 Million To Request US Election Recounts (G.)
Jill Stein, the Green party’s presidential candidate, is prepared to request recounts of the election result in several key battleground states, her campaign said on Wednesday. Stein launched an online fundraising page seeking donations toward a a multimillion-dollar fund she said was needed to request reviews of the results in Michigan, Pennsylvania and Wisconsin. Before midnight EST on Wednesday, the drive had already raised more than the $2m necessary to file for a recount in Wisconsin, where the deadline to challenge is on Friday. Stein said she was acting due to “compelling evidence of voting anomalies” and that data analysis had indicated “significant discrepancies in vote totals” that were released by state authorities.
“These concerns need to be investigated before the 2016 presidential election is certified,” she said in a statement. “We deserve elections we can trust.” The fundraising page said it expected to need around $6m-7m to challenge the results in all three states. Stein’s move came amid growing calls for recounts or audits of the election results by groups of academics and activists concerned that foreign hackers may have interfered with election systems. The concerned groups have been urging Hillary Clinton, the defeated Democratic nominee, to join their cause.

As I said yesterday in “Trump Moves as America Stands Still”.
• Bernie Sanders Should Visit Trump Sooner Rather Than Later (NYDN)
Trump aside, evidently the most clairvoyant messenger of 2016 was Sanders, who got pitifully little support from the Democratic Party establishment — including a raw deal from the DNC, which tilted the scales against him in order to coronate Hillary. His brand of anti-Wall Street, anti-elite populism is ascendant. He is the tribune of the progressive youth, many of whom refused to back Hillary despite her repeated (and hollow) entreaties. So what should Sanders do now? Well, how about meeting with the new President-elect? It might seem incongruous. What would the nationalist, brash Trump have to gain from the aging socialist Sanders? Well, maybe quite a bit. Trump explicitly proclaimed during the campaign that he was going to take a page from Bernie’s playbook, much to the consternation of conservative pundits.
“I’m going to be taking a lot of the things Bernie said and using them,” Trump declared in April. And indeed, Trump followed through on the pledge: He made opposition to the Trans-Pacific Partnership a centerpiece of his campaign, thus emphasizing an area of agreement with Sanders. (Trump has since confirmed that the trade deal will be canceled.) He called for a reduced U.S. military presence abroad. And he even repeatedly defended Sanders before millions of people at the televised debates, pointing out that he’d been screwed over by the DNC and Clinton minions. Naturally, Trump and Sanders will never agree on everything, but where they do see eye-to-eye, why not take advantage?
Two days after the election, Sanders issued a statement noting Trump’s success at connecting with folks “sick and tired of establishment economics, establishment politics and the establishment media.” Sanders then offered to “work with” him on discrete initiatives. Trump has already announced that an infrastructure funding bill is one of his top priorities, so who better than Sanders to help steer the legislative process in the most fruitful possible direction? (Bernie this week characterized Trump’s plan as a “scam,” so why not register those concerns in person?)

Sounds desperate.
• Merkel Warns Against Fake News Driving Populist Gains (AFP)
German Chancellor Angela Merkel warned Wednesday against the power of fake news on social media to spur the rise of populists, after launching her campaign for a fourth term. Speaking in parliament for the first time since her announcement Sunday that she would seek re-election next year, Merkel cautioned that public opinion was being “manipulated” on the internet. “Something has changed – as globalisation has marched on, (political) debate is taking place in a completely new media environment. Opinions aren’t formed the way they were 25 years ago,” she said. “Today we have fake sites, bots, trolls – things that regenerate themselves, reinforcing opinions with certain algorithms and we have to learn to deal with them.”
Merkel, 62, said the challenge for democrats was to “reach and inspire people – we must confront this phenomenon and if necessary, regulate it.” She said she supported initiatives by her right-left coalition government to crack down on “hate speech” on social media in the face of what she said were “concerns about the stability of our familiar order”. “Populism and political extremes are growing in Western democracies,” she warned. Last week, Google and Facebook moved to cut off ad revenue to bogus news sites after a US election campaign in which the global misinformation industry may have influenced the outcome of the vote. But media watchers say more is needed to stamp out a powerful phenomenon seen by some experts as a threat to democracy itself.
Merkel’s conservative Christian Democrats are the odds-on favourites to win the German national election, expected in September or October 2017.

Well, we already knew the EU has gone crazy.
• Putin: EU Resolution Equating RT to ISIS A ‘Degradation Of Democracy’ (R.)
The European Parliament called on the EU and its states to do more to counter Russian “disinformation and propaganda warfare” on Wednesday, drawing an angry response from President Vladimir Putin. A motion endorsing a committee report, which also called for more effort against attempts by Islamic State to radicalize Europeans, passed by 304 votes to 179. Members on the far left and far right were opposed; many in the center-left abstained. “The European Parliament … expresses its strong criticism of Russian efforts to disrupt the EU integration process and deplores, in this respect, Russian backing of anti-EU forces in the EU with regard, in particular, to extreme-right parties, populist forces and movements that deny the basic values of liberal democracies,” the 59-point motion read.
With East-West relations in deep freeze since Moscow responded to an EU pact with Ukraine by annexing Crimea in 2014, the Parliament’s report accused the Kremlin of funding media outlets that spread falsehoods and of sponsoring eurosceptic movements in Western Europe which are growing in strength. Putin said that after lecturing Russia on democracy Europe was now trying to silence dissenting opinions. He told reporters in Moscow: “We are observing a certain, quite obvious, degradation … of how democracy is understood in Western society, in this particular case in the European Parliament.” In Strasbourg, center-left lawmakers said they could not endorse the report because Russia was not alone in posing such threats and they objected to the way it appeared to be given an equivalent status to the non-state militants of Islamic State.

Not a bug but a feature. Given the multibillion ‘trouble’ with the JSF, what do you think the odds are the military-industrial complex makes broken equipemnt on purpose, for profit?
• US Navy’s New $4 Billion Stealth Warship Breaks Down – Again (ZH)
For the second time in two months, The Navy’s new $4 billion stealth warship has broken down. As Military.com reports, the ripped-from-the-pages-of-a-sci-fi mag-looking USS Zumwalt is now in Panama for repairs after suffering a breakdown while passing through the Panama Canal on Monday evening. Military.com’s Hope Hodge Seck reports that a spokesman for U.S. 3rd Fleet, Cmdr. Ryan Perry, told Military.com that the commander of 3rd Fleet, Vice Adm. Nora Tyson, had instructed the USS Zumwalt, the first in a new class of stealthy destroyers, to remain at ex-Naval Station Rodman in Panama to address the engineering casualty. “The timeline for repairs is being determined now, in direct coordination with Naval Sea Systems and Naval Surface Forces,” he said in a statement.
“The schedule for the ship will remain flexible to enable testing and evaluation in order to ensure the ship’s safe transit to her new homeport in San Diego.” An official confirmed to Military.com that the ship had been transiting south through the canal en route to its new San Diego homeport when the incident occurred. The ship had to be towed to pier by the Panama Canal Authority, the official said. While details about what caused the breakdown were few, Navy Times – which first reported the incident – cited reports about problems with heat exchangers in the ship’s integrated power plant that had contributed to the mishap. [..]The ship also made headlines earlier this month when multiple outlets reported that the missiles fired from its 155mm Advanced Gun System, at $800,000 apiece, were too expensive for the Navy to buy in large quantities [..]

But they’ve accepted tons of others already?!
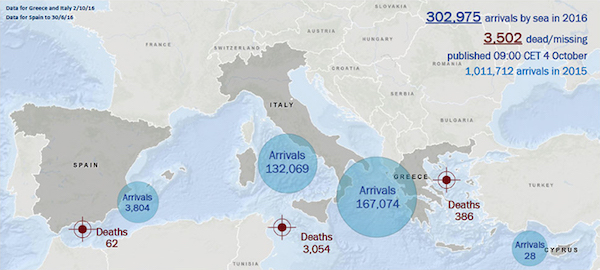
• Greece Wants To Conclude EU/IMF Review, Won’t Accept ‘Irrational’ Demands (R.)
Greece wants to conclude its bailout review but cannot accept what it sees as irrational demands on labor reform or for extra austerity, Prime Minister Alexis Tsipras said on Wednesday, in his first speech to lawmakers after a cabinet reshuffle. Negotiations between Greece and its official creditors – the EU and the IMF – hit a snag this week due to differences on fiscal targets, energy and labor reforms in the country, where one in four is unemployed. “The Greek government is fully consistent with what was agreed and has proven it has the political will to conclude the second bailout review without meaningless delays,” Tsipras told his Syriza party lawmakers. “But this does not mean we would discuss irrational demands.”
The mission chiefs overseeing Greece’s bailout program implementation left Athens on Tuesday. Government officials said talks would continue but the latest disagreements and a long-standing rift among the creditors on medium-term fiscal targets have clouded Greek hopes for a swift conclusion. Unpopular labor reforms, including collective bargaining, a mechanism to set the minimum wage and giving companies more freedom to lay off workers are the main sticking point in talks with lenders. Tsipras said differences could be bridged if there is political will on all sides, adding that an agreement could be reached by Dec. 5, when euro zone finance ministers will meet in Brussels.
“It is realistic but also absolutely necessary to conclude the talks soon to secure at the scheduled Dec. 5 … meeting the agreement needed on a political level in order to conclude the bailout review,” he said. Tsipras said this would pave the way for talks on debt relief measures, not only in the short term but also in the medium and long term, which would allow Greece to lower primary surplus targets beyond 2018, when its bailout program ends.

The Troika forces Greece to strangle itself.
• Greek Businesses Move Abroad To Escape Austerity (R.)
Greek businessman Prokopis Makris believes moving to Bulgaria three years ago was the best decision he ever made. The accountant shut his failing furniture company in Greece and opened a business helping other entrepreneurs move to Bulgaria to escape a 29% tax rate, which has jumped since Athens adopted austerity as part of an international bailout. “We are bombarded with taxes in Greece, businesses are being annihilated,” he says in his plush office overlooking the town square of Petritsi, a Bulgarian town about 12 km (seven miles) north of the border with Greece. The debt crises faced by Greece and several other European countries led to drastic spending cuts and tax increases to improve government finances.
But the higher taxes punished businesses forcing many to shut or move to lower tax jurisdictions such as Bulgaria or Cyprus, helping those economies but undermining the recovery needed to balance the books at home. The number of Greek owned businesses based in Bulgaria, where the corporate tax rate is only 10%, has risen to 17,000 from 2,000 in 2010, when Greece had its first bailout, according to Bulgarian authorities. The Greek government is concerned. It plans a series of tax audits in cooperation with Bulgaria to determine if these business defections are merely changes of address designed to avoid tax rather than a physical relocation of operations. [..] Six hundred kilometers north of Athens, the Greek-Bulgarian border is teeming with traffic. A ravine through mountains on the Greek side gives way to a sweeping valley where agriculture and vineyards are the mainstay of the local economy.
At two small industrial parks 5 km inside Bulgaria, Greek signs are everywhere, advertising storage and office space. “There are dozens of Greek businesses just in this area alone, from transport companies to textile businesses and construction materials,” said Yiorgos Kalaitzoglou who runs a logistics business out of one of the industrial parks where a sign reads, “Land of Opportunities”. Three years ago, his business was stuttering in Greece. He moved to Bulgaria, leaving his wife and family in Thessaloniki, Greece’s second largest city an hour’s drive away. “The taxman in Greece takes 70 to 90% of earnings, Greece simply doesn’t let you live,” the 50-year-old said as he walked through a warehouse stacked with ladders and paint tubs.