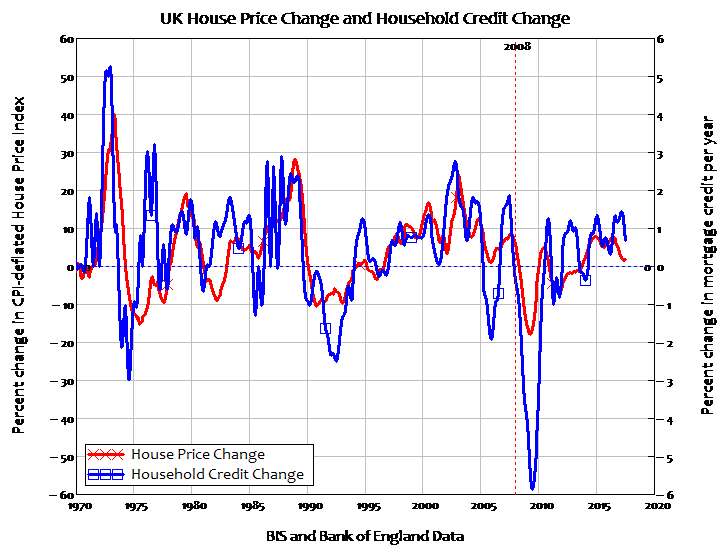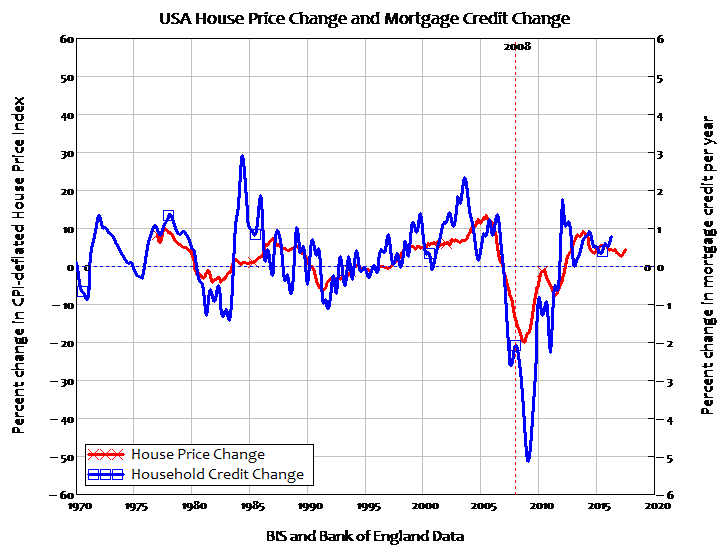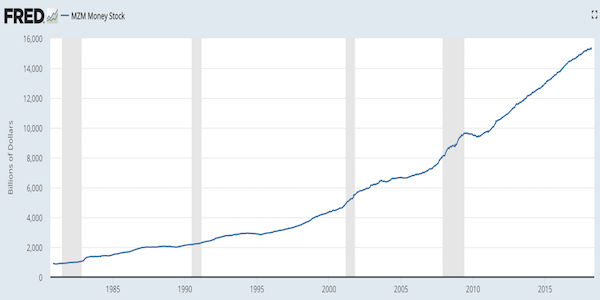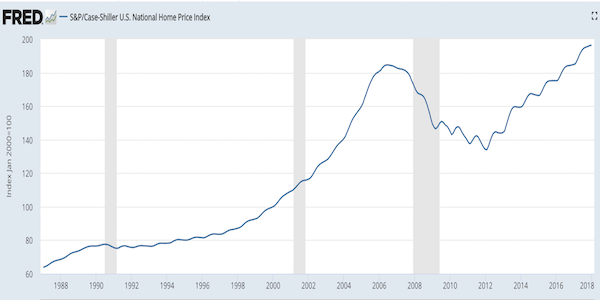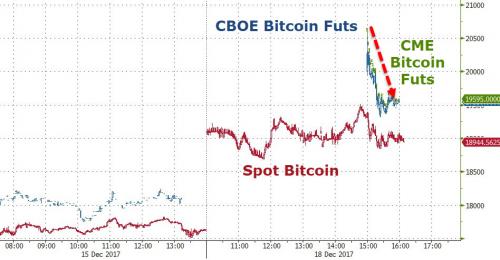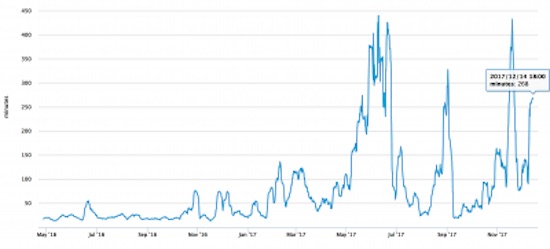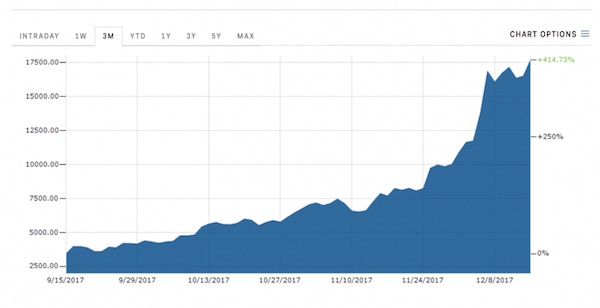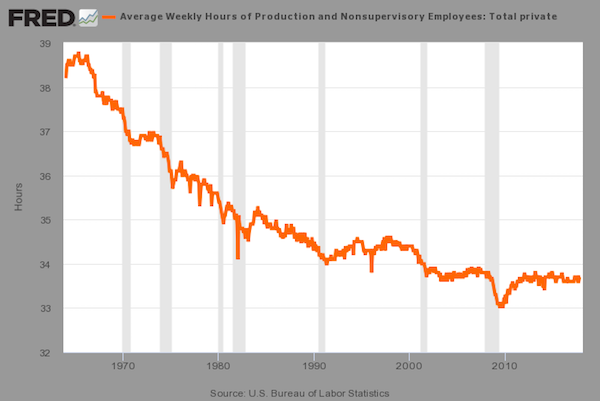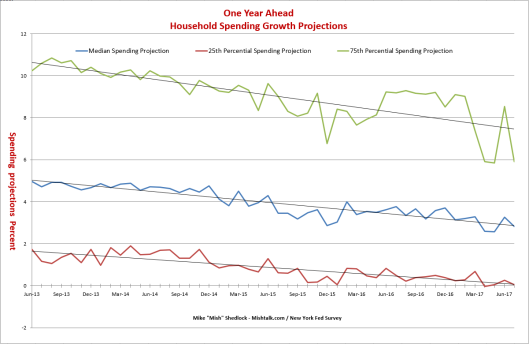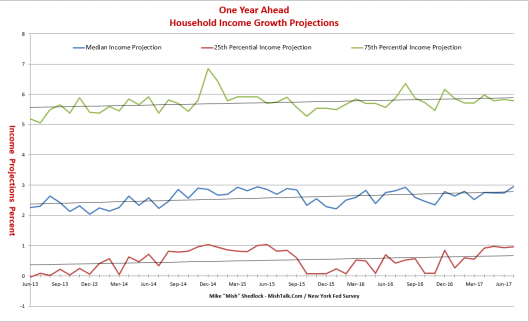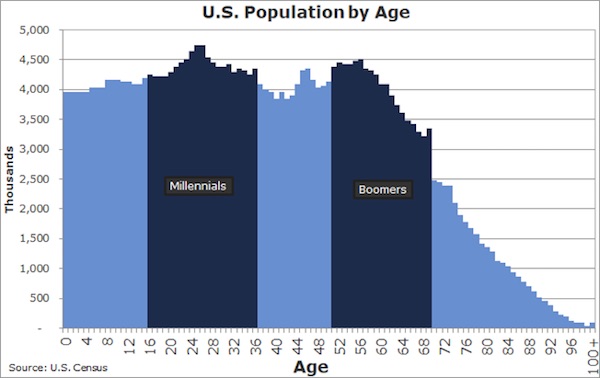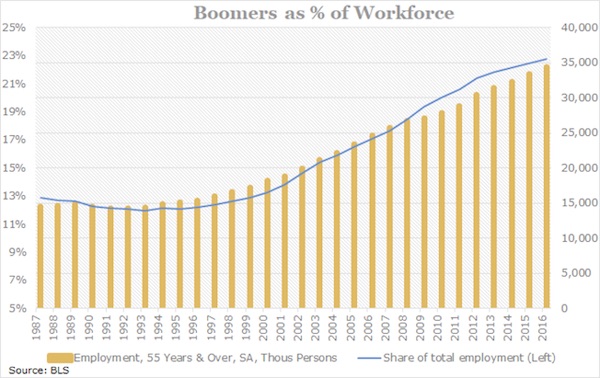
Pablo Picasso Etude Pour Mercure 1924

“..the end may come to resemble more closely a financial boom gone wrong..”
• The Next Global Crash Could Arrive ‘With A Vengeance’ – BIS (CNBC)
A new financial crisis is brewing in the emerging economies and it could hit “with a vengeance”, an influential group of central bankers has warned. Emerging markets such as China are showing the same signs that their economies are overheating as the US and the UK demonstrated before the financial crisis of 2007-08, according to the annual report of the Bank for International Settlements (BIS). Claudio Borio, the head of the BIS monetary and economic department, said a new recession could come “with a vengeance” and “the end may come to resemble more closely a financial boom gone wrong”. The BIS, which is sometimes known as the central bank for central banks and counts Bank of England Governor Mark Carney among its members, warned of trouble ahead for the world economy.
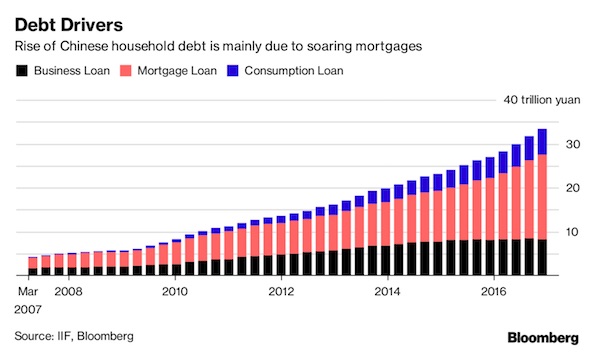
It predicted that central banks would be forced to raise interest rates after years of record lows in order to combat inflation which will “smother” growth. The group also warned about the threat poised by rising debt in countries like China and the rise in protectionism such as in the US under Donald Trump, City AM reported. Chinese corporate debt has almost doubled since 2007, now reaching 166% of GDP, while household debt rose to 44% of GDP last year. In May, Moody’s cut China’s credit rating for the first time since 1989 from A1 to Aa3 which could potentially raise the cost of borrowing for the Chinese government. The BIS’s credit-to-GDP gap indicator also showed debt, which is seen as an “early warning indicator” for a country’s banking system, is rising far faster than growth in other Asian economies such as Thailand and Hong Kong.
Read more …

“The BIS identified four main risks to the global outlook in the medium-term. A sudden flare-up of inflation which forces up interest rates and hurts growth, financial stress linked to the contraction phase of financial cycles, a rise in protectionism and weaker consumption not offset by stronger investment.”
• Push On With The ‘Great Unwinding’, BIS Tells Central Banks (R.)
Major central banks should press ahead with interest rate increases, the Bank for International Settlements said on Sunday, while recognizing that some turbulence in financial markets will have to be negotiated along the way. The BIS, an umbrella body for leading central banks, said in one of its most upbeat annual reports for years that global growth could soon be back at long-term average levels after a sharp improvement in sentiment over the past year. Though pockets of risk remain because of high debt levels, low productivity growth and dwindling policy firepower, the BIS said policymakers should take advantage of the improving economic outlook and its surprisingly negligible effect on inflation to accelerate the “great unwinding” of quantitative easing programs and record low interest rates.
New technologies and working practices are likely to be playing a roll in suppressing inflation, it said, though normal impulses should kick in if unemployment continues to drop. “Since we are now emerging from a very long period of very accommodative monetary policy, whatever we do, we will have to do it in a very careful way,” BIS’s head of research, Hyun Song Shin, told Reuters. “If we leave it too late, it is going to be much more difficult to accomplish that unwinding. Even if there are some short-term bumps in the road it would be much more advisable to stay the course and begin that process of normalization.” Shin added that it will be “very difficult, if not impossible” to remove all those bumps. The BIS identified four main risks to the global outlook in the medium-term. A sudden flare-up of inflation which forces up interest rates and hurts growth, financial stress linked to the contraction phase of financial cycles, a rise in protectionism and weaker consumption not offset by stronger investment.
Read more …

The death of the dollar has been greatly exaggerated.
• Japanese Banks at Risk as Borrowing in Dollars Doubles – BIS (BBG)
Japanese banks have more than doubled their borrowing and lending in dollars since 2007, leaving them vulnerable to funding shocks such as those that exacerbated the last financial crisis, the Bank for International Settlements warned in a report released Sunday. Assets denominated in dollars on the balance sheets of Japanese banks surged to about $3.5 trillion by the end of 2016, the coordinating body for the world’s central banks said in its annual report about the global economy. Those exceed liabilities in dollars by about $1 trillion, creating a massive so-called long position in the currency. The report also cited Canadian lenders for following a similar trend, almost doubling their dollar exposure since the crisis. Their net long positions reached almost $200 billion, the BIS said.
European firms, by contrast, have reduced exposure to dollars since the crisis, the report said. German banks, which had among the highest net dollar positions in 2007, now have matching assets and liabilities denominated in the currency after cutting dollar assets by about half. During the financial crisis, European banks’ net dollar exposures, which peaked at $2 trillion, ended up causing several firms to collapse when funding sources dried up and their efforts to dump U.S. mortgage-related assets led to huge losses. Even as post-crisis regulation has strengthened banks’ capital resources to cope with such losses and some funding has shifted to more stable sources, risks haven’t been completely eliminated, according to the Basel, Switzerland-based group.
[..] the biggest portion of dollar funding for non-U.S. banks – $4.1 trillion – now comes from deposits outside the U.S., according to BIS data. That shift toward offshore dollar deposits also presents risks because the Federal Reserve’s funding backstop during the 2008 crisis wouldn’t be present in non-U.S. jurisdictions if dollar funds became scant, the BIS said. The Fed provided $538 billion of emergency loans to European banks that lost dollar funding from U.S. sources during the 2008 crisis ..
Read more …

Is Mish missing out on confidence as a factor? You can lead a horse to water, but…
• Four Pronged Proposal to End Japanese Deflation (Mish)
Negative Sales Taxes People hoard cash, especially the miserly wealthy. We need to unlock that cash and put it to work. To free up this money, I propose negative sales taxes. The more you spend, the more money you get back as a direct tax credit against income taxes. I leave specific details to economists Larry Summers and Paul Krugman. What can possibly go wrong?
One Percent Tax Per Month on Government Bonds Negative interest rates are in vogue. However, all negative interest rates have done is to get those with money to hoard bonds. Bond buyers effectively bet on capital gains of still more negative rates. Phooey! Just yesterday I noted Bank of Japan Corners 33% of Bond Market: All Japanese Bonds, 40 Years and Below, Yield 0.3% or Less. 33% cornering of the bond market is truly inadequate as this sentiment implies: Makoto Yamashita, a strategist for Japanese interest rates at Deutsche Bank’s securities unit in Tokyo said “There are investors who have no choice but to buy.” We need to end this “no choice” hoarding sentiment right here, right now. I have just the solution. Tax government bonds at the rate of 1% per month.
No one will want them. Hedge funds and pension plans will dump sovereign bonds en masse. This will allow governments to buy every bond in existence immediately, if not sooner. As soon as the government corners the bond market (at effectively zero cost), debt and interest on the debt will truly be owed to itself. Once the bond market is 100% cornered, I propose government debt be declared null and void annually. This would effectively wipe out the entirety of Japan’s debt. Japan’s debt-to-GDP ratio would immediately plunge from 250% to 0%.
National Tax Free Lottery Japan desperately needs to get people to spend, continually. Once again, I have a logical proposal. For every purchase one makes on a credit card, that person gets a free lottery ticket for a weekly drawing worth $10,000,000 tax free. Each week, a random day of the week is selected and separately a random taxpayer ID is selected. If the person drawn made a credit card purchase exceeding $10 on the day of the week drawn, they win $10,000,000 tax free. If there is no winner, the amount rolls over. This beautiful plan will cost no more than $520 million annually, peanuts these days.
Hav-a-Kid Demographics in Japan are a huge problem. Although various incentives have been tried, none of them have gone far enough. I propose a reduction in income taxes for everyone starting a family. The following scale applies. One new child: 50% reduction in income taxes for a period of ten years. Two new children: 100% reduction in income taxes for a period of twenty years. Three new children: Subsidized housing, free healthcare, free schooling, and no income taxes for thirty years. Those with one new child in the last five years get full credit if they add at least one more child in the next five years.
Read more …

Well, Mish does have the answer to that above: One Percent Tax Per Month
• Japan’s Bond Market Grinds To A Halt (ZH)
The Bank of Japan may or may not be tapering, but that may soon be moot because by the time Kuroda decides whether he will buy less bonds, the bond market may no longer work. As the Nikkei reports, while the Japanese central bank ponders its next step, the Japanese rates market has been getting “Ice-9ed” and increasingly paralyzed, as yields on newly issued 10-year Japanese government bonds remained flat for seven straight sessions through Friday while the BOJ continued its efforts to keep long-term interest rates around zero. The 10-year JGB yield again closed at 0.055%, where it has been stuck since June 15m and according to data from Nikkei affiliate QUICK, this marks the longest period of stagnation since 1994, Because what comes after record low volatility? Simple: market paralysis.
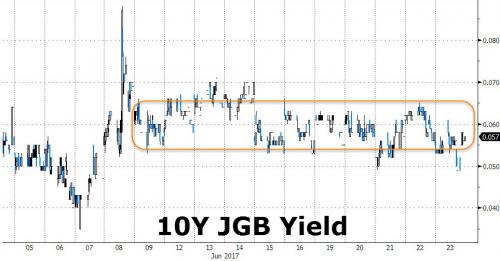
And that’s what Japan appears to be experiencing right now as private bondholders no longer dare to even breathe without instructions from the central bank. Meanwhile, the implied volatility of JGBs tumbled to the lowest level since January 2008 for the same reason we recently speculated may be the primary driver behind the global collapse in volatility: nobody is trading. This means that trading in newly issued 10-year debt has become so infrequent that broker Japan Bond Trading has seen days when no bonds trade hands. It’s not just cash bonds that find themselves in trading limbo: trading in short-term interest rate futures has also thinned and on Tuesday of last week the Nikkei reports that there were no transactions in three-month Tibor futures – the first time that has happened since such trading began in 1989.
As more market participants throw in the towel on a rigged, centrally planned market, the result will – no could – be a further loss of market function, and a guaranteed crash once the BOJ and other central banks pull out (which is why they can’t). As the Nikkei politely concludes, “if the bond and money markets lose their ability to price credit based on future interest rate expectations and supply and demand, the risk of sudden rate volatility from external shocks like a global financial crisis will rise.” Translation: in a world where only central banks trade, everyone else is destined to forget forget what trading, and certainly selling, means.
Read more …

“..when the global credit impulse reverses, it’ll be a cascade, an avalanche. And I pin the tail on that donkey to be Valentine’s Day 2018.”
• “It’ll Be An Avalanche”: Hedge Fund CIO Sets The Day Of The Next Crash (ZH)
While most asset managers have been growing increasingly skeptical and gloomy in recent weeks (despite a few ideological contrarian holdouts), joining the rising chorus of bank analysts including those of Citi, JPM, BofA and Goldman all urging clients to “go to cash”, none have dared to commit the cardinal sin of actually predicting when the next crash will take place. On Sunday a prominent hedge fund manager, One River Asset Management’s CIO Eric Peters broke with that tradition and dared to “pin a tail on the donkey” of when the next market crash – one which he agrees with us will be driven by a collapse in the global credit impulse – will take place. His prediction: Valentine’s Day 2018. Here is what Peters believes will happen over the next 8 months, a period which will begin with an increasingly tighter Fed and conclude with a market avalanche:
“The Fed hikes rates to lean against inflation,” said the CIO. “And they’ll reduce the balance sheet to dampen growing financial instability,” he continued. “They’ll signal less about rates and focus on balance sheet reduction in Sep.” Inflation is softening as the gap between the real economy and financial asset prices is widening. “If they break the economy with rate hikes, everyone will blame the Fed.” They can’t afford that political risk. “But no one understands the balance sheet, so if something breaks because they reduce it, they’ll get a free pass.”
“The Fed has convinced itself that forward guidance was far more powerful than QE,” continued the same CIO. “This allows them to argue that reversing QE without reversing forward guidance should be uneventful.” Like watching paint dry. “Balance sheet reduction will start slowly. And proceed for a few months without a noticeable impact,” he said. “The Fed will feel validated.” Like they’ve been right all along. “But when the global credit impulse reverses, it’ll be a cascade, an avalanche. And I pin the tail on that donkey to be Valentine’s Day 2018.”
Read more …

One must remember there are no markets left. That makes talking about them dicey.
• A Stock Market Crash Scenario (CH Smith)
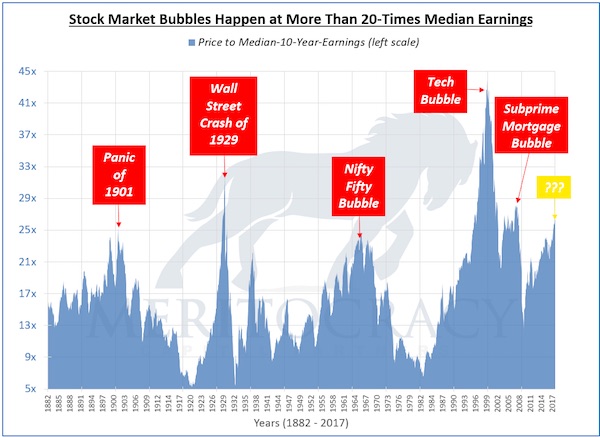
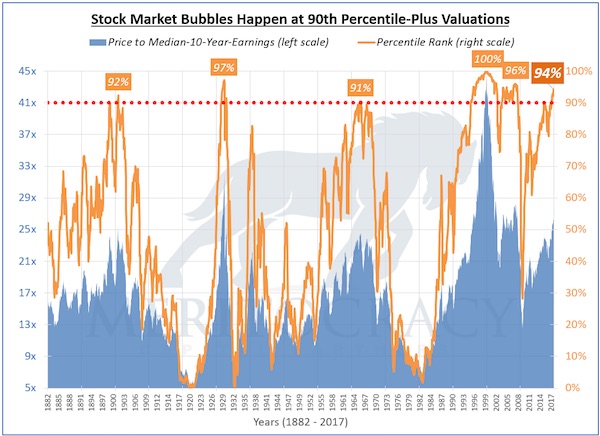
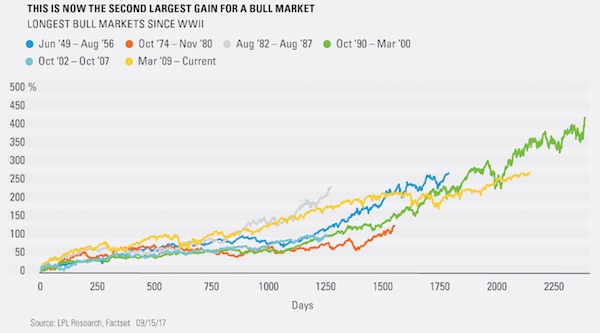
After 8+ years of phenomenal gains, it’s pretty obvious the global stock market rally is overdue for a credit-cycle downturn, and many research services of Wall Street heavyweights are sounding the alarm about the auto industry’s slump, the slowing of new credit and other fundamental indicators that a recession is becoming more likely. Next February is a good guess, as recessions and market downturns tend to lag the credit market by about 9 months. My own scenario is based not on cycles or technicals or fundamentals, but on the psychology of the topping process, which tends to follow this basic script:
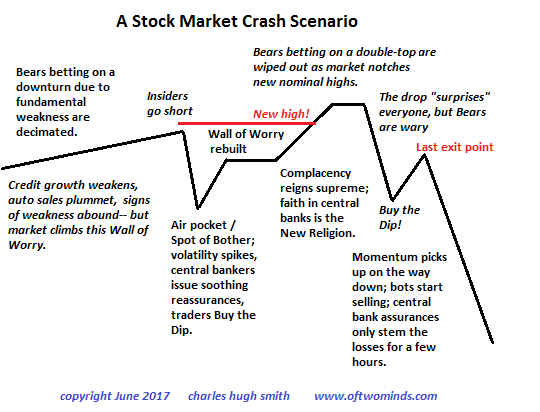
When there are too many bearish reports of gloomy data, and too many calls to go long volatility or go to cash, the market perversely goes up, not down. Why? This negativity creates a classic Wall of Worry that markets can continue climbing. (Central banks buying $300 billion of assets a month helps power this gradual ascent most admirably.) The Bears betting on a decline based on deteriorating fundamentals are crushed by the steady advance. As Bears give up, the window for a Spot of Bother decline creaks open, however grudgingly, as central banks make noises about ending their extraordinary monetary policies by raising interest rates a bit (so they can lower them when the next recession grabs the global economy by the throat). As bearish short interest and bets on higher volatility fade, insiders go short.
A sudden air pocket takes the market down, triggered by some bit of “news.” (Nothing like a well-engineered bout of panic selling to set up a profitable Buy the Dip opportunity.) And since traders have been well-trained to Buy the Dips, the Spot of Bother is quickly retraced. Nonetheless, doubts remain and fundamental data is still weak; this overhang of negativity rebuilds the wall of Worry. Some Bears will reckon the weakened market will double-top, i.e. be unable to break out to new highs given the poor fundamentals, and as a result we can anticipate a nominal new high after the Wall of Worry has been rebuilt, just to destroy all those who reckoned a double-top would mark The Top. Mr. Market (and the central banks) won’t make it that easy to reap a fortune by going short.
Read more …

I think the Fed has already done that. By manoeuvering themselves into a position they cannot escape from.
• The Fed Is Going to Cause a Recession (James Rickards)
Why did the Federal Reserve (Fed) hike rates last week, and what will its policy look like in the future? They’re trying to prepare for the next recession. They’re not predicting a recession, they never do, but they know a recession will come sooner rather than later. This expansion is 96 months old. It’s one of the longest expansions in U.S. history. It’s also the weakest expansion in U.S. history. A lot of people say, “What expansion? Feels like a depression to me.” I think it is a depression defined as depressed growth, but we’re not in a technical recession and haven’t been since June 2009. So it’s been an eight-year expansion at this point, but it won’t fare well, and the Fed knows that. When the U.S. economy goes into recession, you have to cut interest rates about 3% to get the United States out of that recession. Well, how do you cut interest rates by 3% when you’re only at 1%?
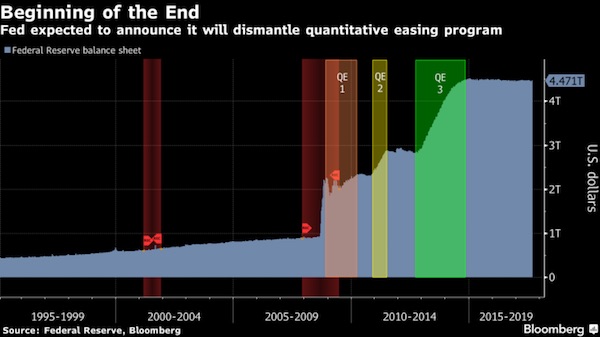
The answer is, you can’t. You’ve got to get them up to 3% to cut them back down, maybe to zero, to get out of the next recession. So that explains why the Fed is raising interest rates. That’s the fourth rate hike getting them up to 1%. They would like to keep going; they would like to get them up to 3, 3.5% by 2019. My estimate is that they’re not going to get there. The recession will come first. In fact, they will probably cause the recession that they’re preparing to cure. So let’s just say we get interest rates to 1% and now you go into recession. We can cut them back down to zero. Well, now what do you do? You do a new round of QE. The problem is that the Fed’s balance sheet is so bloated at $4.5 trillion. How much more can you do—$5 trillion, $5.5 trillion, $6 trillion—before you cause a loss of confidence in the dollar? There are a lot of smart people who think that there’s no limit on how much money you can print. “Just print money. What’s the problem?”
I disagree. I think there’s an invisible boundary. The Fed won’t talk about it. No one knows what it is. But you don’t want to find out the hard way. [..] You probably want to get from $4.5 trillion, down to $2.5 trillion. Well, you can’t sell any treasury bonds. You destroy the market. Rates would go up, putting us in recession, and the housing market would collapse. They’re not going to do that. What they’re going to do is just let them mature. When these securities mature, they won’t buy new ones. They won’t roll it over, and they actually will reduce the balance sheet and make money disappear. They’re going to do it in tiny increments, maybe $10 billion a month or $20 billion a month. They want to run this quantitative tightening in small increments and pretend nothing’s happening. But that’s nonsense. It’s just one more way of tightening money in a weak economy; it will probably cause a recession.
Read more …

Views on the dollar are all over the place.
• US Dollar Will Strengthen on Fed Hikes – Credit Agricole (CNBC)
While investors seem to have come to a consensus view that the U.S. dollar rally is coming to an end, Credit Agricole has offered a contrarian take: There is room for the greenback to strengthen. David Forrester, the bank’s FX strategist told CNBC Monday that markets have been predominantly focused on U.S. inflation data and pricing in an overly cautious Federal Reserve. But, he thinks the Fed will be more hawkish than what is currently expected, which will support the U.S. dollar. “The Fed seems to have changed its policy response function. Yes it’s going to pay attention to the data, but less so. It now wants to get its rates normalized so that it actually has room to cut rates in the next downturn,” Forrester said.
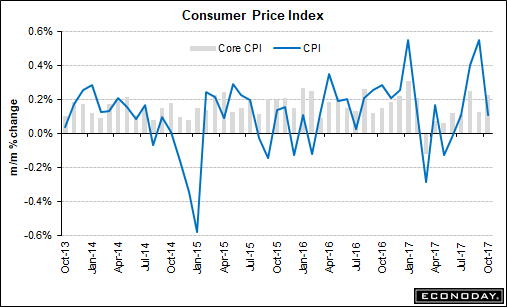
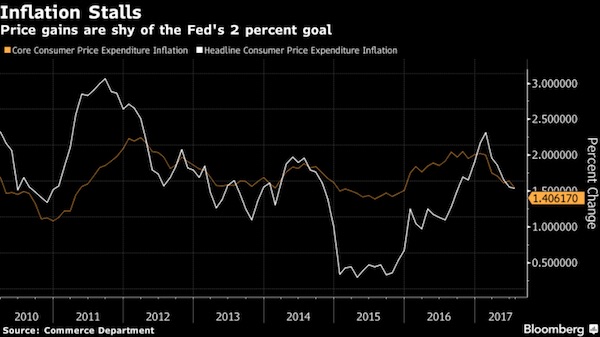
“Let’s not forget here: The U.S. expansion, while being soft, is actually pretty mature so the Fed is getting lined up here in preparation for the next downturn. That’s why we think they’re going to hike rates and we will see a steepening of the U.S. Treasury curve and that will be supportive of the U.S. going forward.” Credit Agricole expects the Fed to hike rates once more this year, followed by three times in 2018. U.S. inflation — still below its 2% target despite a low unemployment rate — has been a key point in the argument on whether the Fed should continue normalizing rates. Forrester said the divergence between the unemployment rate and inflation is not unique to the U.S. Globally, economies face structural issues such as ageing populations and automation replacing jobs, which could increase the risks of a recession.
But, he said U.S. inflation should pick up on the back of further wage growth and a rebound in oil prices. “We expect the U.S. economy to continue to recover and strengthen, we will believe in the Philips curve in the U.S. We do expect wages growth to accelerate and inflation expectation(s) to pick back up. So all-in-all, we do expect that re-steepening,” he said. The Philips curve relates to a supposed inverse relationship between the level of unemployment and the inflation rate. Forrester’s views are in contrast to that of many analysts, who expect weakness in the U.S. dollar. Ken Peng, Asia investment strategist at Citi Private Bank, told CNBC’s “Squawk Box” that the greenback is headed for a “new cycle” after a six-year rally since 2011. He added that the dollar weakness will be “one of the greatest market trends” for global investors.
Read more …

Desperately seeking something.
• The $1.5 Trillion US Business Tax Change Flying Under the Radar (WSJ)
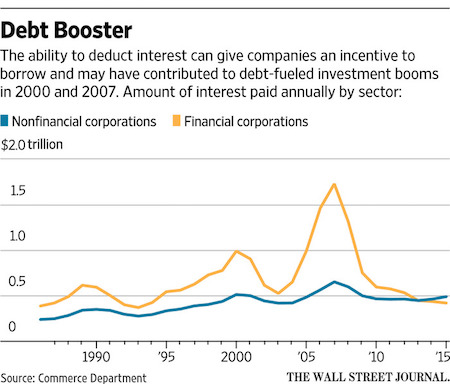
Republicans looking to rewrite the U.S. tax code are taking aim at one of the foundations of modern finance—the deduction that companies get for interest they pay on debt. That deduction affects everyone from titans of Wall Street who load up on junk bonds to pay for multibillion-dollar corporate takeovers to wheat farmers in the Midwest looking to make ends meet before harvest. Yet a House Republican proposal to eliminate the deduction has gotten relatively little sustained public attention or lobbying pressure. Thanks in part to the deduction, the U.S. financial system is heavily oriented toward debt, which because of the tax code is often cheaper than equity financing—such as sales of stock. It also is widely accessible. In 2015, U.S. businesses paid in all $1.3 trillion in gross interest, according to Commerce Department data, equal in magnitude to the total economic output of Australia.
Getting rid of the deduction for net interest expense, as House Republicans propose, would alter finance. It also would generate about $1.5 trillion in revenue for the government over a decade, according to the Tax Foundation, a conservative-leaning think thank. The plan would raise money to help offset Republicans’ corporate tax cuts and reduce a “huge bias” toward debt financing, said Robert Pozen, a senior lecturer at MIT’s Sloan School of Management. That bias, he said, hurts companies built around innovation, which tend to not have the physical assets that banks usually require as collateral. [..] Midsize businesses may also get squeezed. “The people that utilize debt, they utilize it because they don’t have the cash and they don’t have the access to equity,” said Robert Moskovitz, CFO of Leaf Commercial Capital, which finances businesses’ purchases of items like copiers and telephone systems.
“A dry cleaner in Des Moines, Iowa? Where is he going to get equity? He can’t do an IPO.” The idea behind the Republican plan is to pair the elimination of this deduction with immediate deductions for investments in equipment and other long-lived assets. Party leaders expect the capital write-offs would encourage more investment and growth and greater worker productivity, but not the debt often associated with it.
Read more …

Dijsselbloem et al made a big circus about how taxpayers would never again foot the bill. It was never worth a thing.
“German conservative MEP Markus Ferber (EPP): “With this decision, the European Commission accompanies the Banking Union to its deathbed. The promise that the tax payer will not stand in to rescue failing banks anymore is broken for good. I am very disappointed that the commission has approved this course of action. By doing so the Commission has massively undermined the credibility of the Banking Union. If the common set of rules governing banking resolution is so blatantly ignored, there is no point in negotiating any further on a common deposit insurance scheme. The precondition for a working Banking Union is a common understanding of its rules. If such a basic common understanding is lacking, there is no point in further deepening the Banking Union and mutualising risk.”
• Two Failed Italian Banks Split Into Good And Bad Banks, Taxpayers Pay (G.)
The Italian government is stepping in to wind up two failing lenders and prevent a bank run, at a total cost of up to €17bn. After an emergency cabinet meeting on Sunday, ministers agreed to a decree splitting Veneto Banca and Banca Popolare di Vicenza into ‘good’ and ‘bad’ banks, keeping branches open. The ‘good’ assets are being acquired by Italy’s biggest retail bank, Intesa Sanpaolo, with the Italian government handing about €5bn to Intesa as part of the deal. The lenders will then be liquidated, which leaves the state footing the bill for bad loans on both banks’ books, plus restructuring costs.
The Italian government would provide state guarantees worth up to €12bn to cover potential losses at the ‘bad’ bank, Pier Carlo Padoan, the finance minister, told reporters in Rome. That means the total cost could reach €17bn. Padoan added that both banks would operate normally on Monday. The deal is meant to ward off the threat of a bank run, by reassuring nervous savers and deterring them from withdrawing their funds when branches reopen. Paolo Gentiloni, Italy’s prime minister, insisted that the decree fully respected EU rules, even though taxpapers are no longer meant to stump the cost to rescue a failing bank. The funds will come from a €20bn fund created last year to help struggling lenders, so will not affect Italy’s public borrowing, according to the government.
Read more …

Lower pensions solve everything.
• Investors Call For Greece To Accelerate Reforms (K.)
The return of investor confidence in Greece will require time and the acceleration of the government’s reform program, foreign fund managers told Greek officials during two investment conferences that took place in the last couple of weeks in New York and London with the participation of Greek listed firms. In their meetings with hundreds of funds from the US and Europe, the representatives of Greek companies said that while the recent Eurogroup decision may have banished uncertainty about Greece, the government will need to put in some serious effort and work in addressing the issues of speed and efficiency. This was after Greece had failed to secure any debt-easing measures, while the entry of Greek bonds to the ECB’s QE remains pending.
The main subject at the two investment events was the titanic effort being made by Greek banks to reduce the bad loans in their portfolios. As for the Athens stock market, Alpha Finance noted in its presentation at the 6th Greek Investment Forum in New York on June 21-22 that “there is a light at the end of the tunnel.” The Alpha Bank subsidiary noted that “the Greek market has recorded bigger returns than its European peers and prospects appear very encouraging as Greece has beaten its fiscal targets and restored investor confidence in the timetable of the Greek [bailout] program.”
Read more …

“the U.S. will not be indifferent to the mistreatment of the long suffering Greece. That is America’s key strategic base in the Mediterranean, and a location of new military installations on the island of Crete to monitor the Middle East.”
• Germans Fearing China’s World Order? Worry About The EU Instead (CNBC)
Criticizing what he saw as Washington’s isolationist bent, German Finance Minister Wolfgang Schäuble voiced a concern in a speech earlier this month that the West could be threatened as China (and Russia) might fill the void. That, he feared, “would be the end of our liberal world order.” He also said that the U.S. was no longer willing to act as a “guardian of global order,” apparently because Washington withdrew from the agreement on climate change, and it allegedly showed no interest for cooperative migration and security policies. The U.S. Department of State has probably something to say about that, but I wish Schäuble were at least partly right. Arguably, the U.S. could cut back on some foreign engagements and pay more attention to pressing domestic problems.
That said, I wonder how the German minister fails to see that the U.S. is all over the map in active, proxy and hybrid warfare — Afghanistan, the Middle East and North Africa, Korean Peninsula, Central and Eastern Europe and the South China Sea. What else would he want? A nuclear war with China and Russia? Germany may wish to think about whether it is in its interest to fuel and broaden the points of friction with the United States. In my view, Berlin should leave the big power dealings alone. Washington and Beijing are engaged on a broad range of issues to build a historically unique relationship between an established superpower and a runner-up that needs space to develop and contribute to the world in peace and harmony. In trying to do that, the two countries are blazing totally new trails of modern statecraft.
Ubiquitous analogies of Sparta (an established power) and Athens (a rapidly developing strategic competitor), and their ensuing Peloponnesian War, are worthless in the case of countries with huge nuclear arsenals and ground, sea, air and airspace delivery vehicles. So, yes, Germany should leave that alone and get over its fury at Washington’s decision to stop the hemorrhage of foreign trade accounts that are killing jobs, incomes and whatever is left of American manufacturing industries. China got that message and is doing something about it. In the first four months of this year, American export sales to China soared 16.1%. By contrast, U.S. exports to the EU, which account for one-fifth of the total, barely eked out a 2.7% increase.
Germany has to make up its mind with regard to the European integration. Bullying the Visegrad Group (and Baltic States) — a task that Germany has subcontracted to France due to dark pages of its history — and pillorying Greece (a task Germany was eager to continue) won’t work. These countries will run to the U.S. for cover, as some of them are doing now by demanding large contingents of U.S. armed forces on their soil. Also, the U.S. will not be indifferent to the mistreatment of the long suffering Greece. That is America’s key strategic base in the Mediterranean, and a location of new military installations on the island of Crete to monitor the Middle East.
Read more …

Proud supporters of the Paris Agreement.
• China’s Hydropower Frenzy Drowns Sacred Mountains (AFP)
Beijing is building hydropower at a breakneck pace in ethnically Tibetan regions as part of an ambitious undertaking to reduce the country’s dependence on coal and cut emissions that have made it the world’s top polluter. China had just two dams in 1949, but now boasts some 22,000 – nearly half the world total – in all but one of the country’s major waterways. Mountains and rivers are revered as sacred in Tibetan Buddhism, and the extensive construction, which began in 2014, has alarmed locals who believe they can only live peacefully if the nature around them is protected. “Last year, people said that a big forest fire happened because they blasted a road into the holy mountain, and it took revenge,” said villager Tashi Yungdrung, who tends a small herd of yaks in the pastures above her stone, square-windowed home.
Most would not dare remove so much as a single stone from the mountain Palshab Drakar, an important pilgrimage site, she said. Villagers are bracing for mass relocations, an experience that has previously caused havoc elsewhere in China. Beginning in the 1990s, more than a million were moved for the Three Gorges Dam, the world’s largest in terms of capacity, with thousands still mired in poverty. Plans posted at the Lianghekou construction site showed that 22 power plants will be built along the Yalong, a Yangtze tributary, collectively capable of generating 30 gigawatts of electricity – a fifth of China’s current total installed hydropower capacity. Li Zhaolong, a Tibetan from Zhaba village, said he received 300,000 yuan ($44,000) in government compensation to build a new home on higher ground, where he will move next year.
But the 28,000 yuan moving fee his family received per person will not last long once their crops are submerged and they have no other sources of income. “Before we were farmers, and now we have no land,” said Li. [..] Some 80% of China’s hydropower potential lies along the high-flow, glacier-fed rivers of the Tibetan plateau, but dams there bring minimal local benefits because most of the power goes to smog-choked cities in the east, according to the non-governmental organisation International Rivers. Construction worker Zeng Qingtao said the state-owned Power Construction Corporation had brought in some 10,000 employees, but none are locals. “We can’t hire Tibetans. They aren’t reasonable,” he said.
Read more …