Piet Mondriaan The Flowering Apple Tree 1912

If they would stick their heads together, they could hammer out a single payer plan for less than what this competition in incompetence costs. But they won’t.
• US Senate Will Vote To Repeal Obamacare Without Replacement (G.)
Senate majority leader Mitch McConnell has announced that the Senate will vote on a clean repeal of Obamacare without any replacement, after two Republican senators broke ranks to torpedo the current Senate healthcare bill. Senators Mike Lee of Utah and Jerry Moran of Kansas came out on Monday night in opposition to McConnell’s Better Care Reconciliation Act (BCRA), the Senate version of the controversial healthcare reform bill that passed the House in May. Senate Republicans hold a bare 52-48 majority in the Senate and two members of the GOP caucus, the moderate Susan Collins of Maine and the libertarian Rand Paul of Kentucky, already opposed the bill, along with all 48 Democrats. The announcement from Moran and Lee made it impossible for Republicans to muster the 50 votes needed to bring the BCRA bill to the floor.
Instead, McConnell announced late on Monday night that the Senate would vote on a bill to simply repeal Obamacare without any replacement in the coming days. The Kentucky Republican said in a statement: “Regretfully, it is now apparent that the effort to repeal and immediately replace the failure of Obamacare will not be successful.” He added that “in the coming days” the Senate would vote on repealing the Affordable Care Act with a two-year-delay. The Senate passed a similar bill in 2015, which was promptly vetoed by Barack Obama. McConnell’s plan echoes a statement made by Donald Trump in a tweet on Monday night, in which the president urged a repeal of Obamacare with any replacement to come in the future. “Republicans should just REPEAL failing ObamaCare now & work on a new Healthcare Plan that will start from a clean slate. Dems will join in!” Trump wrote.
In January, an analysis by the nonpartisan Congressional Budget Office (CBO) estimated that repealing Obamacare without a replacement would result in 32 million people losing insurance by 2026, including 19 million who would lose Medicaid coverage. It would also cause premiums to rise by as much as 50% in the year following the elimination of key planks of the healthcare law, including the repeal of Medicaid expansion and cost-sharing subsidies. Premiums would nearly double over a decade.

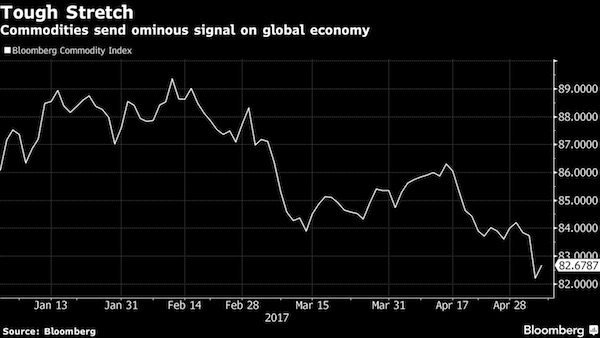
This is your entire economy. Companies refusing to invest in themselves. Why do anything useful if you can simply borrow your share price higher?
• There Has Been Just One Buyer Of Stocks Since The Financial Crisis (ZH)
When discussing Blackrock’s latest quarterly earnings (in which the company missed on both the top and bottom line, reporting Adj. EPS of $5.24, below the $5.40 exp), CEO Larry Fink made an interesting observation: “While significant cash remains on the sidelines, investors have begun to put more of their assets to work. The strength and breadth of BlackRock’s platform generated a record $94 billion of long-term net inflows in the quarter, positive across all client and product types, and investment styles. The organic growth that BlackRock is experiencing is a direct result of the investments we’ve made over time to build our platform.”
While the intention behind the statement was obvious: to pitch Blackrock’s juggernaut ETF product platform which continues to steamroll over the active management community, leading to billions in fund flow from active to passive management every week, if not day, he made an interesting point: cash remains on the sidelines even with the S&P at record highs. In fact, according to a chart from Credit Suisse, Fink may be more correct than he even knows. As CS’ strategist Andrew Garthwaite writes, “one of the major features of the US equity market since the low in 2009 is that the US corporate sector has bought 18% of market cap, while institutions have sold 7% of market cap.” What this means is that since the financial crisis, there has been only one buyer of stock: the companies themselves, who have engaged in the greatest debt-funded buyback spree in history.
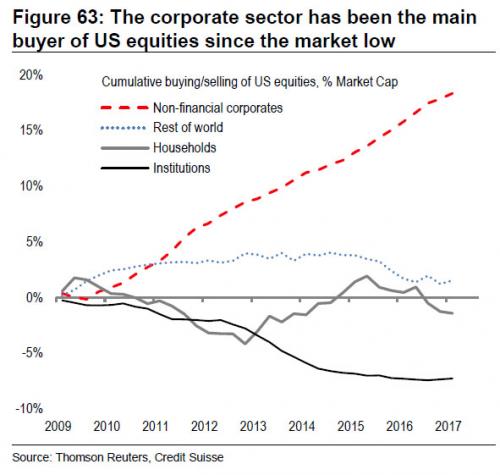
Why this rush by companies to buyback their own stock, and in the process artificially boost their Eearning per Share? There is one very simple reason: as Reuters explained some time ago, “Stock buybacks enrich the bosses even when business sags.” And since bond investor are rushing over themselves to fund these buyback plans with “yielding” paper at a time when central banks have eliminated risk, who is to fault them. More concerning than the unprecedented coordinated buybacks, however, is not only the relentless selling by institutions, but the persistent unwillingness by “households” to put any new money into the market which suggests that the financial crisis has left an entire generation of investors scarred with “crash” PTSD, and no matter what the market does, they will simply not put any further capital at risk.
As to Fink’s conclusion that “investors have begun to put more of their assets to work”, we will wait until such time as central banks, who have pumped nearly $2 trillion into capital markets in 2017 alone, finally stop doing so before passing judgment.

Real estate across the globe is on the edge of a cliff. Entire economies will follow it down.
• People Buy Payments – Not Houses (Roberts)
When the average American family sits down to discuss buying a home they do not discuss buying a $125,000 house. What they do discuss is what type of house they “need” such as a three bedroom house with two baths, a two car garage, and a yard. That is the dream part. The reality of it smacks them in the face, however, when they start reconciling their monthly budget. Here is a statement I have not heard discussed by the media. People do not buy houses – they buy a payment. The payment is ultimately what drives how much house they buy. Why is this important? Because it is all about interest rates. Over the last 30-years, a big driver of home prices has been the unabated decline of interest rates. When declining interest rates were combined with lax lending standards – home prices soared off the chart. No money down, ultra low interest rates and easy qualification gave individuals the ability to buy much more home for their money.
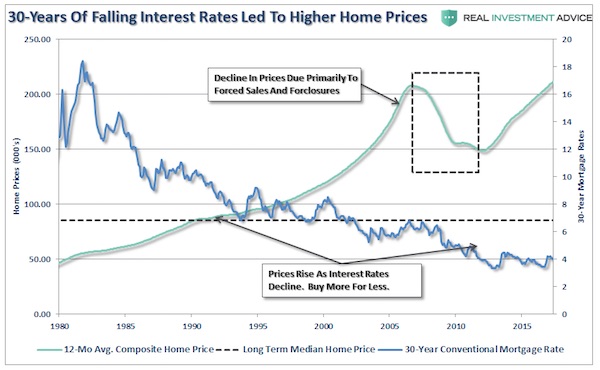
[..] With this in mind let’s review how home buyers are affected. If we assume a stagnant purchase price of $125,000, as interest rates rise from 4% to 8% by 2027 (no particular reason for the date – in 2034 the effect is the same), the cost of the monthly payment for that same priced house rises from $600 a month to more than $900 a month – more than a 50% increase. However, this is not just a solitary effect. ALL home prices are affected at the margin by those willing and able to buy and those that have “For Sale” signs in their front yard. Therefore, if the average American family living on $55,000 a year sees their monthly mortgage payment rise by 50% it is a VERY big issue.
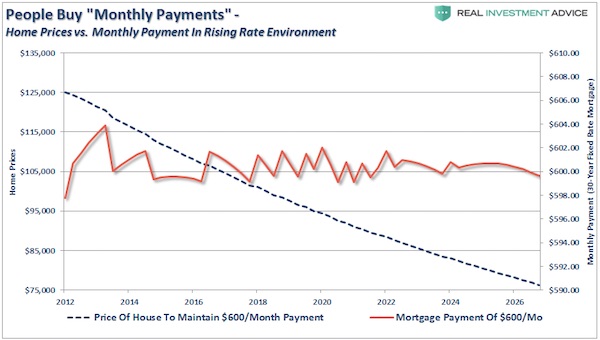
Assume an average American family of four (Ward, June, Wally and The Beaver) are looking for the traditional home with the white picket fence. Since they are the average American family their median family income is approximately $55,000. After taxes, expenses, etc. they realize they can afford roughly a $600 monthly mortgage payment. They contact their realtor and begin shopping for their slice of the “American Dream.” At a 4% interest rate, they can afford to purchase a $125,000 home. However, as rates rise that purchasing power quickly diminishes. At 5% they are looking for $111,000 home. As rates rise to 6% it is a $100,000 property and at 7%, just back to 2006 levels mind you, their $600 monthly payment will only purchase a $90,000 shack. See what I mean about interest rates?

Home prices will have to come down enormously to cover this issue. And therefore they will. The losses will be crippling.
• Student Debt Is a Major Reason Millennials Aren’t Buying Homes (BBG)
College tuition hikes and the resulting increase in student debt burdens in recent years have caused a significant drop in homeownership among young Americans, according to new research by the Federal Reserve Bank of New York. The study is the first to quantify the impact of the recent and significant rise in college-related borrowing—student debt has doubled since 2009 to more than $1.4 trillion—on the decline in homeownership among Americans ages 28 to 30. The news has negative implications for local economies where debt loads have swelled and workers’ paychecks aren’t big enough to counter the impact. Homebuying typically leads to additional spending—on furniture, and gardening equipment, and repairs—so the drop is likely affecting the economy in other ways.
As much as 35% of the decline in young American homeownership from 2007 to 2015 is due to higher student debt loads, the researchers estimate. The study looked at all 28- to 30-year-olds, regardless of whether they pursued higher education, suggesting that the fall in homeownership among college-goers is likely even greater (close to half of young Americans never attend college). Had tuition stayed at 2001 levels, the New York Fed paper suggests, about 360,000 additional young Americans would’ve owned a home in 2015, bringing the total to roughly 2.9 million 28- to 30-year-old homeowners. The estimate doesn’t include younger or older millennials, who presumably have also been affected by rising tuition and greater student debt levels.
There’s a good chance the number of millennials kept from buying homes because of their student loans has only grown since the period the economists studied. As tuition has risen, total student debt has increased 13%, and every new class graduates with more student debt than the preceding one. The consequences could reverberate for decades as more young Americans are locked out of purchasing property, the primary way that U.S. households build wealth. With less wealth, millennials could cut their spending as they attempt to build up their net worth. The U.S. economy has historically depended on household spending for roughly 70% of its growth.

Who gets stuck with the empty bag here? The piper must be paid.
• US Student Loans Worth Billions Are Getting Erased On A Technicality (ZH)
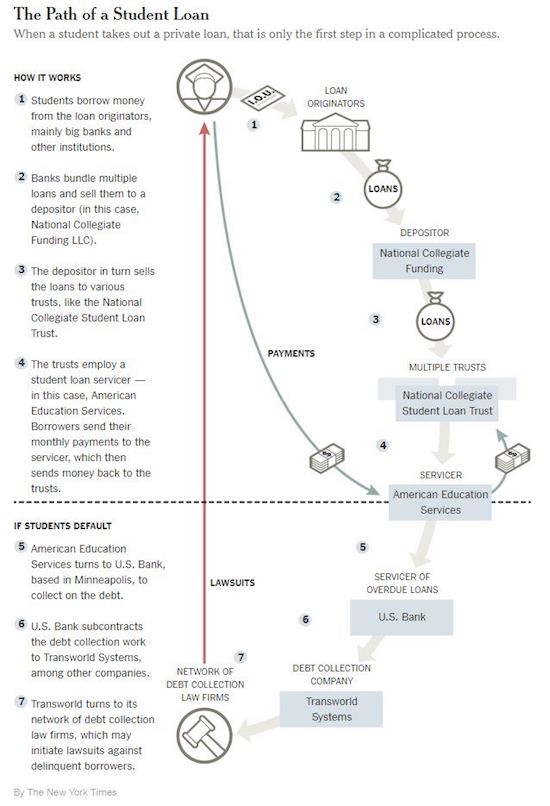
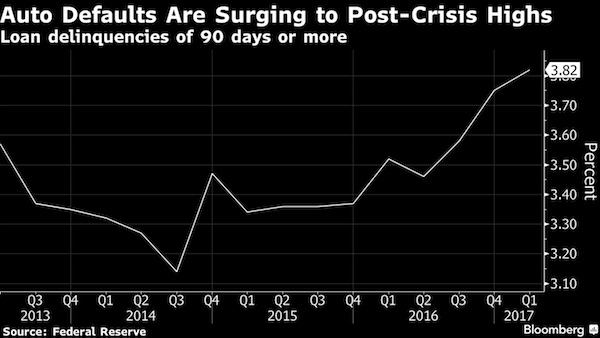
National Collegiate Funding (NCF) is an umbrella name for 15 trusts that collectively hold 800,000 private student loans, totaling some $12 billion in outstanding obligations. The only problem is that roughly $5 billion worth of those loans, or over 40%, are currently in default (and you thought auto delinquencies were bad). Now, ordinarily when a student defaults on their loan, NCF simply files a lawsuit in local or state court as a means for negotiating a settlement or payment plan with the borrower. Often times, NCF wins these cases automatically as the borrowers don’t even bother to show up for their court date. In cases like that, NCF can use their court victory to garnish wages and/or federal benefits from entitlement programs like Social Security which can haunt borrowers for decades.
That said, NCF is increasingly finding that, much like the subprime mortgage debacle from 10 years ago, student lending institutions apparently had a really hard time keeping tracking of paperwork over the years and/or processed deeply flawed contracts with incomplete ownership records and mass-produced documentation (who can forget that whole robo-signing catastrophe). As the New York Times points out today, student loans, much like mortgages, are often originated at large commercial banks before being sold to numerous other financial institutions and ultimately ending up in a securitization owned by some unsuspecting European pension funds. And while pooling these student loans in such a complicated way into securitizations apparently magically eradicates all default risk associated with the underlying loans (just ask any 22 year old on the JPM securitization desk and he/she will confirm the same), it also makes it extremely difficult to prove ownership.

Shouldn’t try to pay them off at all. But a millstone around your neck for 30 years is no fun.
• UK Students Should Not Try To Pay Off Loans Early (G.)
Students should not try to pay off their loans early despite the controversial interest rate rise to 6.1% in September, according to research by money expert Martin Lewis. Lewis says his moneysavingexpert.com website has been “swamped” by graduates terrified by new statements that show their debt spiralling in size after interest is added. He believes most graduates will never repay their debt. Lewis said: “Many graduates are starting to panic. First they look in shock at their student loan statements after noticing interest totalling thousands has been added. Then they read the headline interest rate for the 2017-18 academic year will increase from 4.6% to 6.1%. It’s no surprise I’ve been swamped with people asking if they should be trying to overpay the loans to reduce the interest.”
But after crunching the numbers, Lewis estimates that “overpaying is just throwing money away” unless the graduate is likely to be in very high-paid employment all their lives. Only if the student lands a job earning £40,000 a year on graduation, and then enjoys big pay rises after, should they consider repaying their loan early, said Lewis. A graduate earning £36,000 a year will repay £40,500 of a £55,000 total student loan over 30 years, said Lewis, at the current repayment rates. The remaining debt will be wiped clean after 30 years. If the same graduate cuts the total £55,000 balance to £45,000 with an overpayment of £10,000, they will still have to repay the same amount of student loan over 30 years, making the overpayment entirely pointless.

A Spanish bank doing US subprime liar car loans. What a world.
• Fears Mount Over a New US Subprime Boom – Cars (BBG)
It’s classic subprime: hasty loans, rapid defaults, and, at times, outright fraud. Only this isn’t the U.S. housing market circa 2007. It’s the U.S. auto industry circa 2017. A decade after the mortgage debacle, the financial industry has embraced another type of subprime debt: auto loans. And, like last time, the risks are spreading as they’re bundled into securities for investors worldwide. Subprime car loans have been around for ages, and no one is suggesting they’ll unleash the next crisis. But since the Great Recession, business has exploded. In 2009, $2.5 billion of new subprime auto bonds were sold. In 2016, $26 billion were, topping average pre-crisis levels, according to Wells Fargo. Few things capture this phenomenon like the partnership between Fiat Chrysler and Banco Santander.
Since 2013, as U.S. car sales soared, the two have built one of the industry’s most powerful subprime machines. Details of that relationship, pieced together from court documents, regulatory filings and interviews with industry insiders, lay bare some of the excesses of today’s subprime auto boom. Wall Street has rewarded lax lending standards that let people get loans without anyone verifying incomes or job histories. For instance, Santander recently vetted incomes on fewer than one out of every 10 loans packaged into $1 billion of bonds, according to Moody’s. The largest portion were for Chrysler vehicles.
Some of their dealers, meantime, gamed the loan application process so low-income borrowers could drive off in new cars, state prosecutors said in court documents. Through it all, Wall Street’s appetite for high-yield investments has kept the loans – and the bonds – coming. Santander says it has cut ties with hundreds of dealerships that were pushing unsound loans, some of which defaulted as soon as the first payment. At the same time, Santander plans to increase control over its U.S. subprime auto unit, Santander Consumer USA Holdings, people familiar with the matter said.

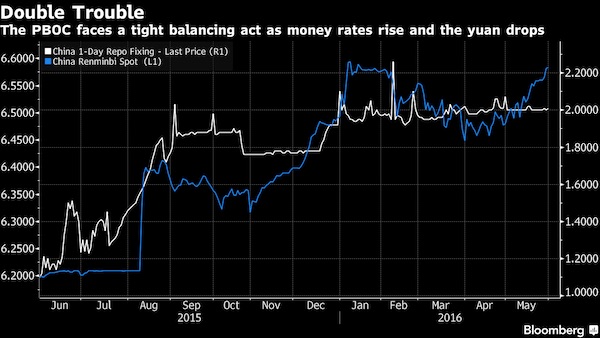
Xi is toying with his credibility.
• When A “Black Swan” Will No Longer Do: China Warns Beware The “Gray Rhino” (ZH)
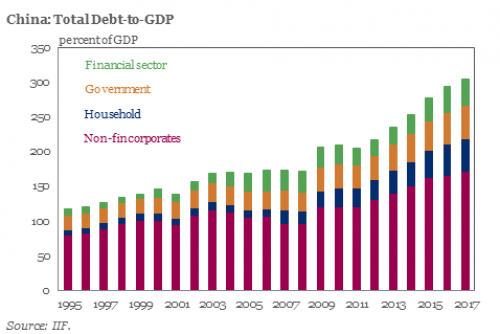
Perhaps the biggest outcome from the weekend Conference was the creation of a financial “super-regultor” meant to tackle the growing threat of a financial crisis, and among its broad conclusions were i) To make finance better serve the real economy; ii) To contain financial risks; and iii) To deepen financial reforms. The proposed reforms are the result of the unprecedented increase in overall Chinese debt, which while promoting growth – in this case China’s latest 6.9% GDP print – is also leading to a relentless buildup of risks. And while until now Chinese regulators had homed in on financial-sector excesses, the latest probe – Bloomberg notes – is now widening to debt in the broader economy, “a shift that prompted a sell-off in domestic stocks.”
There was another reason for the market’s swoon. Earlier on Monday China People’s Daily newspaper warned of potential “gray rhinos” which it defined as “highly probable, high-impact threats that people should see coming, but often don’t.” So in a surprising case of forward-looking prudence, the Chinese government is doing what numerous Fed members have also done in recent weeks, by setting a surprisingly wary tone about risk, demonstrated best by the front page commentary in the People’s Daily, which said China should not only be alert to “black swan” risks that catch people off guard but also more obvious threats, citing cited a term popularized by author Michele Wucker’s book “The Gray Rhino: How to Recognize and Act on the Obvious Dangers We Ignore.”
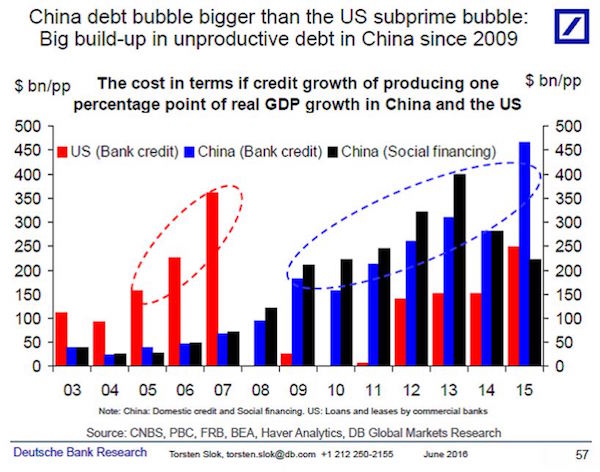
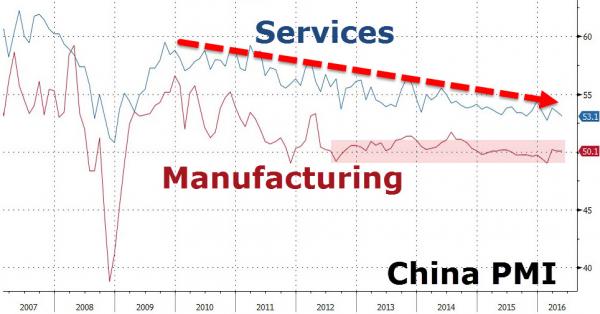
Noting that with the economy still on a slowing-growth trend, the People’s Daily commentary said that China should “strictly prevent risks from liquidity, credit, shadow banking and abnormal capital market fluctuations, as well as insurance market and property bubbles.” And, as Bloomberg adds, the new focus on “deleveraging in the economy” suggests that local-government and state-owned enterprise debt is now very much in the spotlight. In other words, this time Beijing’s crackdown on excess debt may actually be real. Of course, by now it is widely understood that China’s strong (credit-driven) momentum has fueled global economic expansion and boosted sentiment in international markets, and served as the springboard for the global economic rebound in the depths of the financial crisis (when China’s debt load was roughly half the current one).
[..] In a separate commentary by China Daily, the official English-language newspaper added that fending off risks is one of the country’s top priorities, with corporate debt running high, the property market being overheated and excess capacity in some sectors lingering, adding that “only through guarding against financial risks can a sound and stable financial sector better fulfill its duty and purpose of serving the real economy.” While it is admirable that China continues to push for deleveraging, it faces an uphill battle, not least of all because as the IIF recently calculated, China’s debt is not only the biggest contributor to global debt growth, currently at a record $217 trillion, but as of 2017 is at just over 300% debt/GDP. Meanwhile, the marginal benefit of all this debt continues to shrink, with the Chinese economy growing at levels just shy of all time lows.

Cash in your monopoly money before they find out what it’s worth.
• Half of China’s Rich Plan To Move Overseas (CNBC)
Half of Chinese millionaires are considering moving overseas, and the U.S. remains their favorite destination, according to a new survey. Among Chinese millionaires with a net worth of more than $1.5 million, half either plan to or are considering moving abroad, according to a survey from Hurun Report in association with Visas Consulting Group. The survey suggests that the flow of wealthy Chinese and Chinese fortunes into U.S. homes and buildings is likely to continue, helping demand and prices in certain real estate markets — especially in the U.S. The U.S. remains the most popular destination for wealthy Chinese moving their families and fortunes abroad, according to the report. Canada ranks second, overtaking the U.K., which had ranked second but now ranks third. Australia comes in at fourth.
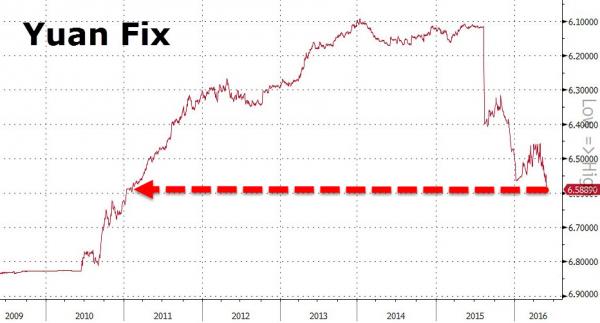
The favorite city for wealthy Chinese moving to the U.S. is Los Angeles, while Seattle ranks second followed by San Francisco. New York ranked fourth. When asked for their main reasons for moving abroad, education was the top reason, followed by the “living environment.” “Education and pollution are driving China’s rich to emigrate,” said Rupert Hoogewerf, chairman and chief researcher of Hurun Report. “If China can solve these issues, then the primary incentive to emigrate will have been taken away.” Yet the fear of a falling Chinese currency is also driving many rich Chinese — and their money — abroad. Fully 84% of Chinese millionaires are concerned about the devaluation of the yuan, up from 50% last year. Half are worried about the exchange rate of the dollar, foreign exchange controls and property bubbles in China.

Australia almost makes America look good. But let’s not make it look like Japan has no problems.
• Household Debt: A Tale of Three Countries (Hail)
In the year 2000, Japan, the USA and Australia all had about the same ratio of household debt to GDP – in each country, this figure was about 70%. In Japan, the ratio fell gradually from 70% to the low 60%, and has remained at about 62% for a while. In the US, household debt surged as financial fragility grew, with the ratio peaking at 98% in the first quarter of 2008. Households deleveraged post GFC, and the ratio fell back to about 80%. Till way too high for another surge in private debt to be allowed to persist, but at least well below its level at the peak of the bubble. What about Australia? Like Japan and the US, our household debt to GDP stood at about 70% at the millennium – well above the levels of previous years. It then grew and grew, mainly due to increasing mortgage debt, standing at 108% in mid-2008.
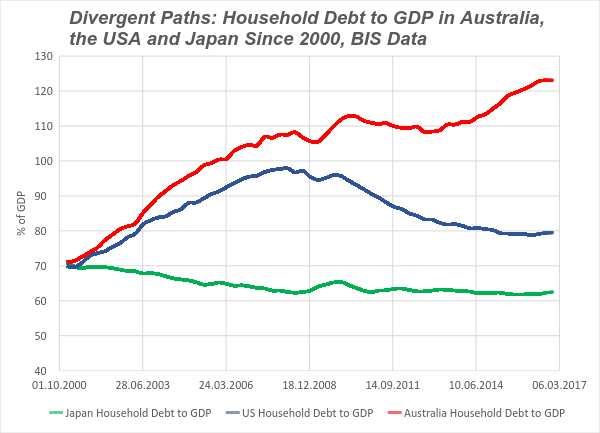
Well above the level in the US when the crash happened there. As we know, Australia missed the worst of the GFC, and propped up its housing market, and household debt just kept growing. By the end of last year it was above 123%, placing Australia very near the top of the global league table. Bound to lead to a crash? Many would say so – Steve Keen and Philip Soos amongst them, and who am I to disagree? Unwise? On that we should all agree. And done at the urging of successive governments which have failed to run appropriate fiscal policies; with the approval, for most of this period, of the RBA; and with the acquiescence of what until quite recently was a very relaxed APRA. Who has the debt problem? Not Japan. Since around 2013, The Bank of Japan began buying up government debt, to become a monopoly supplier of bank reserves, denominated in Yen.
In September 2016 it took the decision to buy unlimited amounts of Japanese government bonds at a fixed-yield, meaning it could control yields across bond maturities from a two-to-40-year output and sets them at whatever level they choose. It also implemented $80 trillion worth of quantitative and qualitative easing while introducing a negative interest rate of minus 0.1% to current accounts held by financial institutions at the bank, driving the bond yield rate down. Bond market dealers queued up to get their hands on as much Japanese government debt as they could, with the promise it would mature within 40 years. To quote Economist Bill Mitchell: “The bond markets do not have the power to set yields unless the government allows them that flexibility. The government rules, not the markets.” Moreover, Japan’s government doesn’t need to issue debt in primary markets in order to spend. Because monetary sovereign government debt is not the problem. Household debt is the problem.

“..any contact between Russians and Americans is ipso facto nefarious vectors into the very beating heart of the “Resistance” itself..”
[..] this blog might be described as anti-Trump, too, in the sense that I did not vote for him and regularly inveigh against his antics as President — but neither is Clusterfuck Nation a friend of the Hillary-haunted Dem-Prog “Resistance,” in case there’s any confusion about where we stand. If anything, we oppose the entirety of the current political regime in our nation’s capital, the matrix of rackets that is driving the aforementioned Limousine-of-State off the cliff of economic collapse. Just sayin’. “Resistance” law professors, such as Lawrence Tribe at Harvard, were quick to holler “treason” over Junior’s meet-up with Russian lawyer Natalia Veselnitskaya and Russian-American lobbyist Rinat Akhmetshin. Well, first of all, and not to put too fine a point on it, don’t you have to be at war with another nation to regard any kind of consort as “treason?”
Last time I checked, we were not at war with Russia — though it sure seems like persons and parties inside the Beltway would dearly like to make that happen. You can’t call it espionage either, of course, because that would purport the giving of secret information, not the receiving of political gossip. Remember, the “Resistance” is not going for impeachment, but rather Section 4 of the 25th Amendment. That legal nicety makes for a very neat-and-clean surgical removal of a whack-job president, without all the cumbrous evidentiary baggage and pain-in-ass due process required by impeachment. All it requires is a consensus among a very small number of high officials, who then send a note to the leaders in both houses of congress stating that said whack-job president is a menace to the polity — and out he goes, snippety-snip like a colorectal polyp, into the hazardous waste bag of history.
And you’re left with a nice clean asshole, namely Vice President Mike Pence. Insofar as Pence appears to be a kind of booby-prize for the “Resistance,” that fateful reach for the 25th Amendment hasn’t happened quite yet. It is hoped, I’m sure, that the incessant piling on of new allegations about “collusion” with the Russians will get the 25thers over the finish line and into the longed-for end zone dance. More interestingly, though, the meme that has led people to believe that any contact between Russians and Americans is ipso facto nefarious vectors into the very beating heart of the “Resistance” itself: the Clintons.
How come the Clintons have not been asked to explain why — as reported on The Hill blog — Bill Clinton was paid half a million dollars to give speech in Russia (surely he offered them something of value in exchange, pending the sure thing Hillary inaugural), or what about the $2.35 million “contribution” that the Clinton Foundation received after Secretary of State Hillary allowed the Russians to buy a controlling stake in the Uranium One company, which owns 20% of US uranium supplies, with mines and refineries in Wyoming, Utah, and other states, as well as assets in Kazakhstan, the world’s largest uranium producer? Incidentally, the Clinton Foundation did not “shut down,” as erroneously reported early this year. It was only its Global Initiative program that got shuttered. The $2.35 million is probably still rattling around in the Clinton Foundation’s bank account. Don’t you kind of wonder what they did with it? I hope Special Prosecutor Robert Mueller wants to know.

“..techno-industrial society consumed more energy and resources during the most recent doubling (the past 35 years or so) than in all previous history..”
• Staving Off the Coming Global Overshoot Collapse (Rees)
Humans have a virtually unlimited capacity for self-delusion, even when self-preservation is at stake. The scariest example is the simplistic, growth-oriented, market-based economic thinking that is all but running the world today. Prevailing neoliberal economic models make no useful reference to the dynamics of the ecosystems or social systems with which the economy interacts in the real world. What truly intelligent species would attempt to fly spaceship Earth, with all its mind-boggling complexity, using the conceptual equivalent of a 1955 Volkswagen Beetle driver’s manual? Consider economists’ (and therefore society’s) near-universal obsession with continuous economic growth on a finite planet.
A recent ringing example is Kaushik Basu’s glowing prediction that “in 50 years, the world economy is likely (though not guaranteed) to be thriving, with global GDP growing by as much as 20% per year, and income and consumption doubling every four years or so.” Basu is the former chief economist of the World Bank, senior fellow at the Brookings Institution and professor of economics at Cornell University, so he is no flake in the economics department. But this does not prevent a display of alarming ignorance of both the power of exponential growth and the state of the ecosphere. Income and consumption doubling every four years? After just 20 years and five doublings, the economy would be larger by a factor of 32; in 50 years it will have multiplied more than 5000-fold! Basu must inhabit some infinite parallel universe.
In fairness, he does recognize that if the number of cars, airplane journeys and the like double every four years with overall consumption, “we will quickly exceed the planet’s limits.” But here’s the thing — it’s 50 years before Basu’s prediction even takes hold and we’ve already shot past several important planetary boundaries. Little wonder. Propelled by neoliberal economic thinking and fossil fuels, techno-industrial society consumed more energy and resources during the most recent doubling (the past 35 years or so) than in all previous history. Humanity is now in dangerous ecological overshoot, using even renewable and replenishable resources faster than ecosystems can regenerate and filling waste sinks beyond capacity. (Even climate change is a waste management problem — carbon dioxide is the single greatest waste by weight in all industrial economies.)
Meanwhile, wild nature is in desperate retreat. One example: from less than one% at the dawn of agriculture, humans and their domestic animals had ballooned to comprise 97% of the total weight of terrestrial mammals by the year 2000. That number is closer to 98.5% today, with wild mammals barely clinging to the margins. The “competitive displacement” of other species is an inevitable byproduct of continuous growth on a finite planet. The expansion of humans and their artefacts necessarily means the contraction of everything else. [..] Ignoring overshoot is dangerously stupid — we are financing growth, in part, by irreversibly liquidating natural resources essential to our own long-term survival.