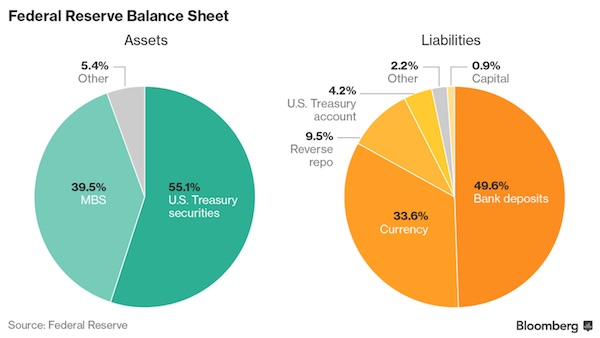
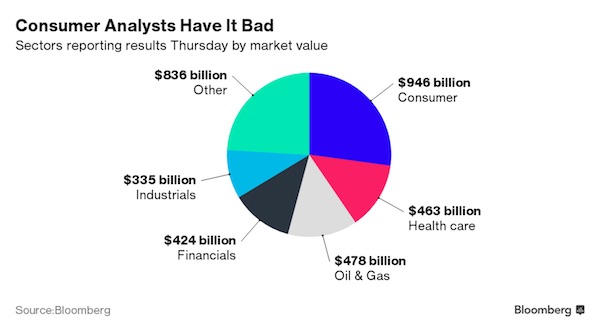
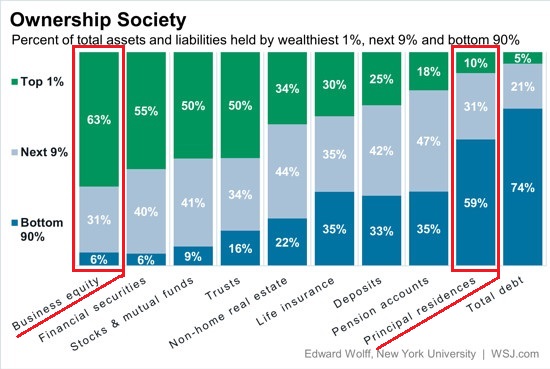
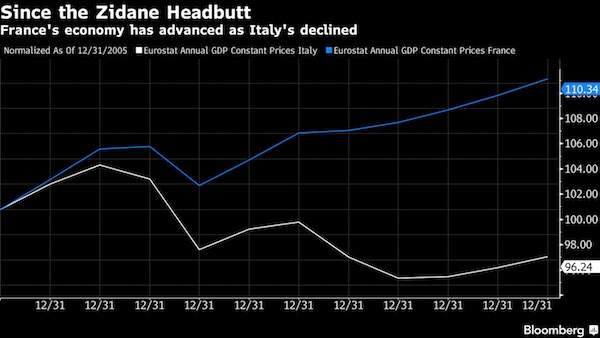
Egon Schiele Meadow, Church and Houses 1912

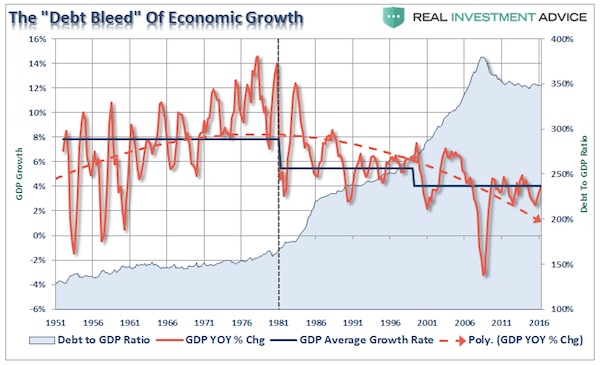
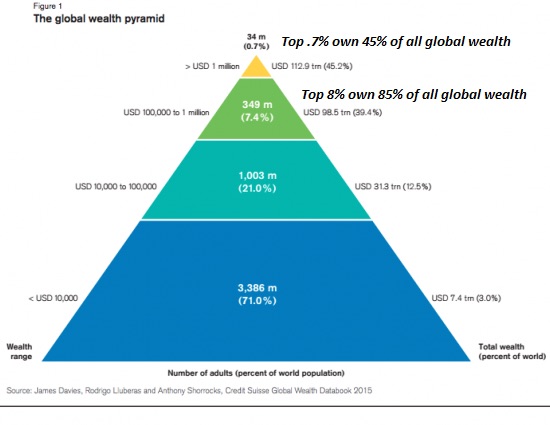
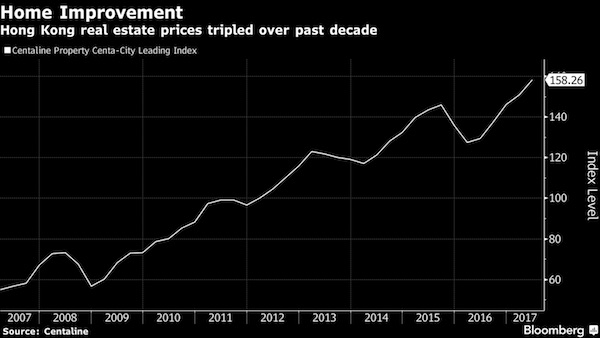
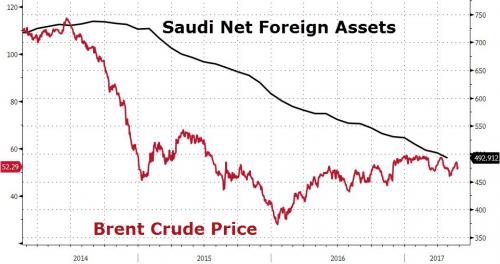
More cycles.
• Wall Street Banks Warn Downturn Is Coming (BBG)
HSBC, Citigroup and Morgan Stanley see mounting evidence that global markets are in the last stage of their rallies before a downturn in the business cycle. Analysts at the Wall Street behemoths cite signals including the breakdown of long-standing relationships between stocks, bonds and commodities as well as investors ignoring valuation fundamentals and data. It all means stock and credit markets are at risk of a painful drop. “Equities have become less correlated with FX, FX has become less correlated with rates, and everything has become less sensitive to oil,” Andrew Sheets, Morgan Stanley’s chief cross-asset strategist, wrote in a note published Tuesday. His bank’s model shows assets across the world are the least correlated in almost a decade, even after U.S. stocks joined high-yield credit in a selloff triggered this month by President Donald Trump’s political standoff with North Korea and racial violence in Virginia.
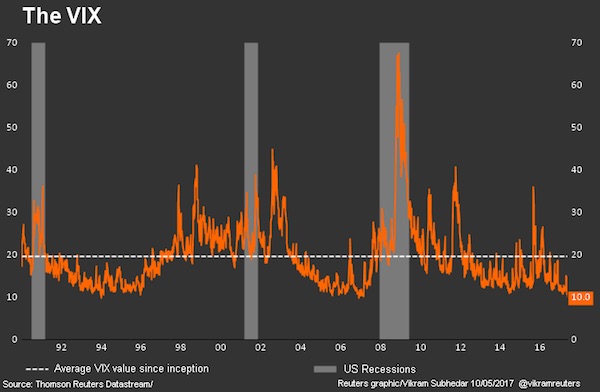
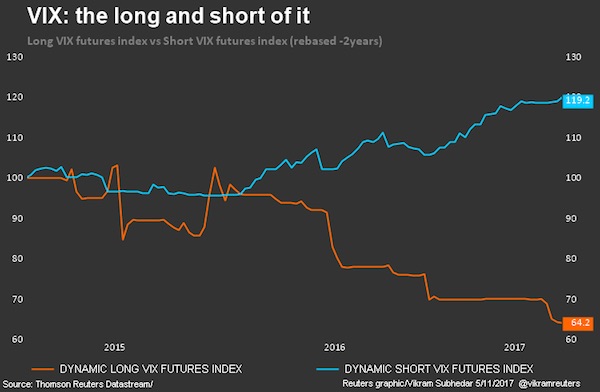
Just like they did in the run-up to the 2007 crisis, investors are pricing assets based on the risks specific to an individual security and industry, and shrugging off broader drivers, such as the latest release of manufacturing data, the model shows. As traders look for excuses to stay bullish, traditional relationships within and between asset classes tend to break down. “These low macro and micro correlations confirm the idea that we’re in a late-cycle environment, and it’s no accident that the last time we saw readings this low was 2005-07,” Sheets wrote. He recommends boosting allocations to U.S. stocks while reducing holdings of corporate debt, where consumer consumption and energy is more heavily represented. That dynamic is also helping to keep volatility in stocks, bonds and currencies at bay, feeding risk appetite globally, according to Morgan Stanley. Despite the turbulent past two weeks, the CBOE Volatility Index remains on track to post a third year of declines.
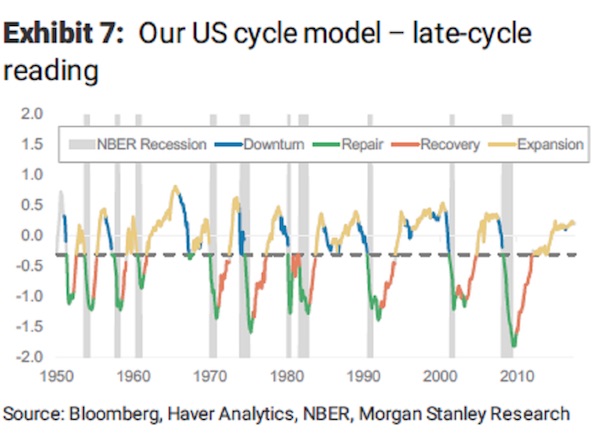
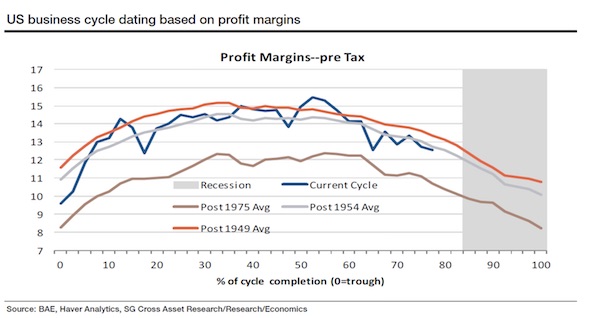
Oxford Economics macro strategist Gaurav Saroliya points to another red flag for U.S. equity bulls. The gross value-added of non-financial companies after inflation – a measure of the value of goods after adjusting for the costs of production – is now negative on a year-on-year basis. “The cycle of real corporate profits has turned enough to be a potential source of concern in the next four quarters,” he said in an interview. “That, along with the most expensive equity valuations among major markets, should worry investors in U.S. stocks.” The thinking goes that a classic late-cycle expansion – an economy with full employment and slowing momentum – tends to see a decline in corporate profit margins. The U.S. is in the mature stage of the cycle – 80% of completion since the last trough – based on margin patterns going back to the 1950s, according to Societe Generale.

They warn about a downturn, but not for themselves. Their asses are covered.
• Big US Banks Could See Profit Jump 20% With Deregulation (BBG)
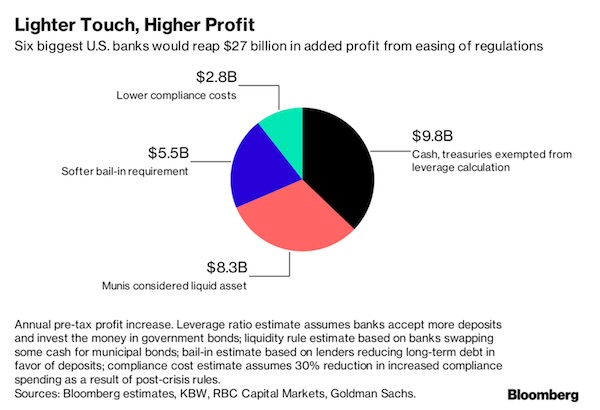
The deregulation winds blowing through Washington could add $27 billion of gross profit at the six largest U.S. banks, lifting their annual pretax income by about 20%. JPMorgan Chase and Morgan Stanley would benefit most from changes to post-crisis banking rules proposed by Donald Trump’s administration, with pretax profit jumping 22%, according to estimates by Bloomberg based on discussions with analysts and the banks’ own disclosures. Goldman Sachs would have the smallest percentage increase, about 16%. Bloomberg’s calculations are based largely on adjustments banks could make to the mix of securities they hold and the interest they earn from such assets. The proposed changes would allow the largest lenders to take on more deposits, move a greater portion of their excess cash into higher-yielding Treasuries and municipal bonds, and issue a lower amount of debt that costs more than customer deposits.
Of the changes proposed in June by Treasury Secretary Steven Mnuchin, the one that would probably have biggest impact on profit is allowing banks to buy U.S. government bonds entirely with borrowed money. Three others could also boost income: counting municipal bonds as liquid, or easy-to-sell, assets; requiring less debt that won’t have to be paid back if a bank fails; and making it easier to comply with post-crisis rules. Regulators appointed by Trump could make these changes without congressional approval. Doing so would reverse their agencies’ efforts since 2008 to strengthen capital and liquidity requirements for U.S. banks beyond international standards. While bringing U.S. rules in line with global ones probably wouldn’t threaten bank safety, some analysts and investors worry the pendulum could swing even further.
“Since the crisis, we’ve had the luxury of excess capital buildup in the banking system and regulators reining in risky activities,” said William Hines at Standard Life Aberdeen. “If there’s too much pullback on minimum capital requirements, too much relaxation of restraints, we’re concerned there’ll be more risk-taking by banks, and the system will become vulnerable.”

Blowing bubbles everywhere and claiming they bring strength. It’s Orwell.
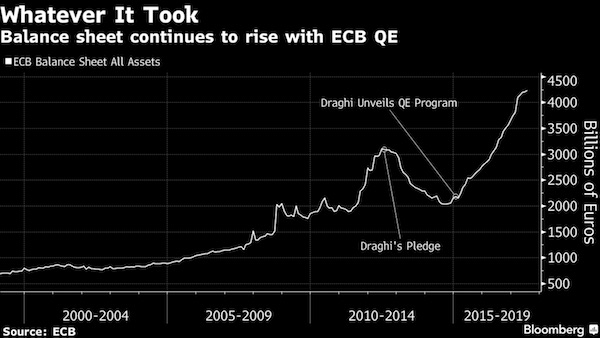
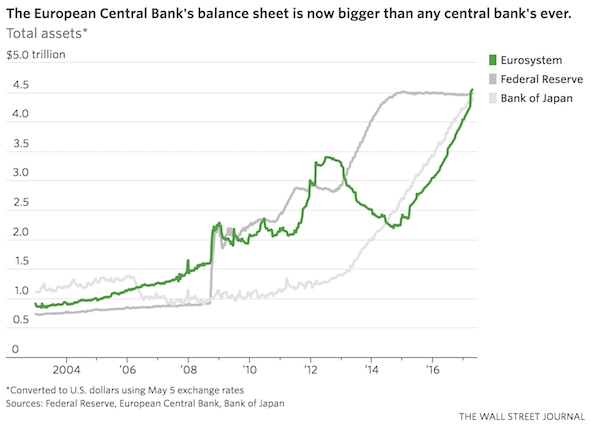
• ECB Chief Draghi: QE Has Made Economies More Resilient (BBC)
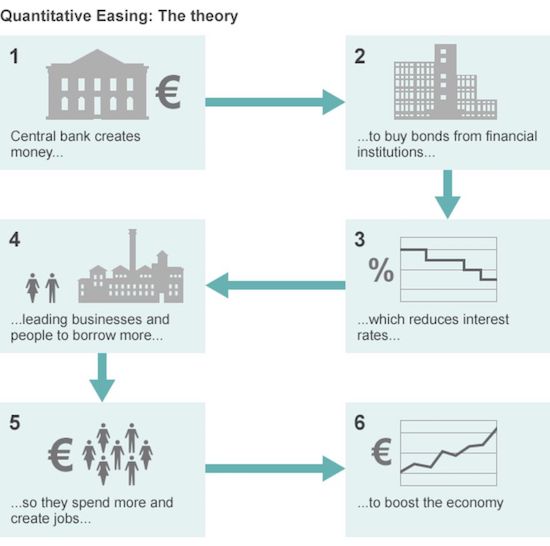
European Central Bank President Mario Draghi has said unconventional policies like quantitative easing (QE) have been a success both sides of the Atlantic. QE was introduced as an emergency measure during the financial crisis to pump money directly into the financial system and keep banks lending. A decade later, the stimulus policies are still in place, but he said they have “made the world more resilient”. But he also said gaps in understanding these relatively new tools remain. As the economic recovery in the eurozone gathers pace, investors are watching closely for when the ECB will ease back further on its €60bn a month bond-buying programme. Central bankers, including Mr Draghi, are meeting in Jackson Hole, Wyoming, later this week, where they are expected to discuss how to wind back QE without hurting the economy.
On Monday, a former UK Treasury official likened the stimulus to “heroin” because it has been so difficult to wean the UK, US and eurozone economies off it. In a speech in Lindau, Germany on Wednesday, Mr Draghi defended QE and the ECB’s policy of forward guidance on interest rates. “A large body of empirical research has substantiated the success of these policies in supporting the economy and inflation, both in the euro area and in the United States,” he said. The ECB buying relatively safe assets such as government bonds means that banks can lend more and improve access to credit for riskier borrowers, Mr Draghi said. He added: “Policy actions undertaken in the last 10 years in monetary policy and in regulation and supervision have made the world more resilient. But we should continue preparing for new challenges.”

End the Fed.
• Yellen’s Coming Speech Could Mark The ‘End Of An Era’ (BI)
Janet Yellen could be on her way out as chair of the Federal Reserve. On Friday, she’s set to deliver a speech on financial stability at the Fed’s annual economic symposium in Jackson Hole, Wyoming. It could be her last, following months of speculation that President Donald Trump plans to nominate a different candidate when her four-year term ends in February. And Yellen’s successor could have a very different approach to the job. Yellen’s Jackson Hole showing could be the last one, for now, under a Fed chair who takes a technocratic approach to monetary policy, according to Luke Bartholomew, an investment strategist at Aberdeen Standard Investments. “There could be an end-of-an-era feel to Jackson Hole this year,” Bartholomew told Business Insider.
The Fed chair could be replaced by someone who’s “probably not the sort of academic economist that’s been leading it through the Bernanke/Yellen period,” he said, adding that there’s “a broader feeling that under the Trump administration, the technocratic approach of the Fed is increasingly out of favor.” Yellen, 71, was a career economist and academic before President Barack Obama nominated her to replace Ben Bernanke in 2014. Trump told The Wall Street Journal last month that Gary Cohn, Yellen, and “two or three” other candidates were in the running for the job. One of those other people could be Kevin Warsh, a former Fed governor who is now a fellow at the Hoover Institution. But Cohn, the National Economic Council director and Trump’s top economic adviser, is reportedly the top contender. He’s the “archetype of Wall Street, given his job at Goldman in the past,” Bartholomew said. “He certainly brings financial acumen to the job. I’m not sure that’s what the job of Fed chairman is, but he’s a fine candidate.”
Walsh brings some years of Fed experience to the table. But he has worked for seven years in investment banking, at Morgan Stanley, and isn’t an academic policymaker like Yellen or Bernanke. That’s not the only red flag Yellen’s exit would raise. On one extreme, Yale School of Management’s Jeffrey Sonnenfeld thinks markets would crash if Cohn were to leave the White House for the Fed. Stocks dipped last week as rumors spread that he was leaving the administration following Trump’s response to the white-nationalist rally in Charlottesville, Virginia. “I don’t want to be an alarmist, but there is a lot of faith that he is going to help carry through the tax reform that people are looking for,” Sonnenfeld told CNBC last week.

“Long term, the new home median price has been mostly 10% to 20% above the existing home median since 1990. Since 2011, however, new home prices have been at a 35% to 40% premium over resale prices..”
• Here’s Why New Home Sales Tanked (CNBC)
Newly built homes are more expensive than they’ve ever been before. They are also more expensive when compared to similar existing homes than they’ve ever been before. And that is why sales are suffering, dropping an unexpected 9.4% in July compared to June, according to the U.S. Census. They are simply out of reach for too many potential buyers. You don’t have to do a lot of math to see it. The median sale price of a newly built home in July jumped more than 6% compared to July 2016, to $313,700. That marks the highest July price ever. Last December, the median price hit the highest of any month on record. In addition, the price premium for newly built homes compared to comparable existing homes has more than doubled since 2011, according to John Burns Real Estate Consulting.
“Long term, the new home median price has been mostly 10% to 20% above the existing home median since 1990. Since 2011, however, new home prices have been at a 35% to 40% premium over resale prices,” John Burns wrote in a recent note to clients. “While the exact percentages aren’t perfect due to ‘apples and oranges’ comparisons, our consultants have been confirming for years that new home sales have been slowed by larger than usual new home premiums.” The supply of existing homes for sale is still extremely low, but the supply of newly built homes moved higher in July to 5.8 months of inventory. “The scars of the housing bust are still fresh in the minds of many homebuilders, so it is not surprising that many are taking a cautious approach to ramping up production,” noted Aaron Terrazas, a senior economist at Zillow, in reaction to the July report.
Homebuilders are feeling slightly better about their business lately, but they continue to complain about the costs of land, labor, materials and regulation. They claim that is why they cannot build cheaper homes. Unfortunately, the lower end of the market is where most of the demand is and where supply is weakest. “There is still no pickup in sales for homes priced below $300,000, and this is where most of the first time households would be shopping in,” wrote Peter Boockvar, chief market analyst at The Lindsey Group in a note following the Census release on new home sales. “I repeat that the housing industry needs a moderation in home price gains in order to better compete with renting where rents increases are now moderating.”

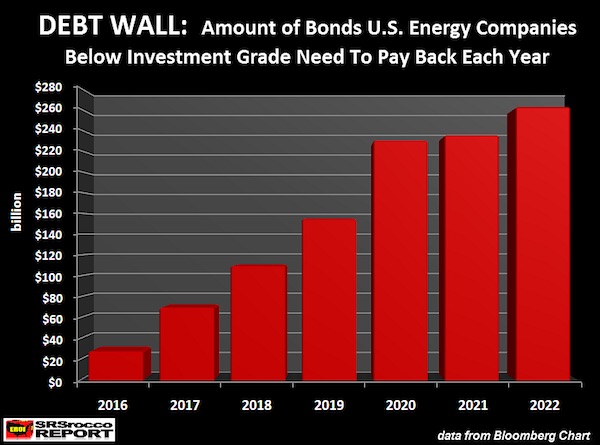
Auto loans are a huge part of money creation.
• Autos Put Economic Downside Risks on Full Display (DDMB)
Federal Reserve data released last week on July industrial production offered little more than more of the same. Despite post-election optimism for a rebound in activity on the nation’s factory floors, the data reveal a continued throttling down in the growth rate to just over 2% compared with this time last year. The main drag on activity – the auto sector – should come as no surprise to investors. Rather than rising by 0.2% over June as projected, manufacturing production contracted by 0.1%, marking the third decline in five months. Motor vehicles and parts production fell by 3.6% on the month, taking the year-over-year slide to 5%. Evidence continues to build that a sampling error may be to blame for the surprising strength in June and July car sales.
Inventory continues to pile up, suggesting more production cuts are in the offing: As of June, the latest data on hand, auto inventories were up 7.4% over last year, leaving manufacturers choking for air. In July, General Motors alone was sitting on 104 days of supply, well above its target of 70 days. Industry-wide, the July/August average of 69 days ties the August 2008 record and sits above the historic average of 56 days of supply. In all, automakers have 3.9 million units of unsold light vehicles, up 324,600 from last August and the highest on record for the month. For context, July and August tie for the leanest stock levels of the year. The decline in July sales was already the steepest this year. Fresh loan delinquency data suggest more pain ahead.
“Deep subprime” borrowers have been a big boost at the margin, propelling back-to-back record years of sales in 2015 and 2016 as lending standards loosened sufficiently to allow millions with credit scores below 530 to access financing. Equifax, the consumer credit reporting firm, didn’t hold back in its second-quarter update, saying the performance of recent vintages of deep subprime loans was “awful.” While industry insiders are quick to point out that the overall pace of defaults across all borrowers remains in check, up just marginally over last year, there is growing concern that deep subprime delinquencies are back at 2007 levels. “The bottom line is excess auto inventories are clearly evident and the auto sector is now in recession,” said The Lindsey Group’s Peter Boockvar.

We’re about to winess the political power of German carmakers. How many execs are being prosecuted? Right.
• Merkel Aide Says Germany Has ‘Vital Interest’ in Diesel Survival (BBG)
Chancellor Angela Merkel’s chief of staff said Germany has a “vital interest” in ensuring diesel engines survive, defending the embattled technology as the industry comes under fire for cheating on emissions tests. Excessive pollution from diesel, as well as traditionally close ties between the government and auto industry, have emerged as a campaign issue in the run up to the country’s federal election in September. Merkel has been confronted by voters on the campaign trail, who accused the government of being too lenient on automakers, prompting the chancellor to question high bonuses for auto executives embroiled in Volkswagen’s cheating scandal. “We have a vital interest in preserving diesel as a technology because it emits far less CO2 than other technologies,” Peter Altmaier, Merkel’s chief of staff, said in a Bloomberg TV interview in Berlin.
“At the same time we have to make sure that all the rules are respected and all the regulations are fully implemented.” Car bosses and government officials reached a compromise deal earlier this month to lower pollution that calls for software updates on million of vehicles instead of more costly hardware fixes. Volkswagen, Daimler and BMW also agreed to a trade-in bonus for cars with outdated emissions controls. The measures have been criticized as a slap on the wrist for Germany’s biggest industry. “We have the responsibility to fight for a good deal but also to preserve the strength and the performance of the automobile industry,” Altmaier said in the interview late on Tuesday. “I’m very optimistic that we will overcome this.”Diesel software updates alone are “insufficient” for many cities to meet the legal limit for nitrogen oxides in the air, Environment Minister Barbara Hendricks told reporters on Wednesday, citing ministry tests conducted this month.
Excessive pollution impacts 70 German towns and cities, and the fixes agreed earlier this month would cut car emissions by a maximum of 6%, she said. Hendricks – a member of Merkel’s junior coalition partner, the Social Democrats – said her ministry and others will ascertain in the coming weeks whether hardware changes in diesels currently on the road are necessary to further lower emissions and will present their findings after the election. “Nobody wants to ban diesels from our cities,” she said. Merkel, who has so far largely steered clear of the debate, is hosting a meeting on Sept. 4 with representatives of the major cities, including the hometowns of BMW, Mercedes-Benz and Porsche, struggling to lower their pollution levels. A number of cities and courts continue to evaluate potential diesel driving bans as the most effective means to meet regulation quickly.

China exports its Ponzi.
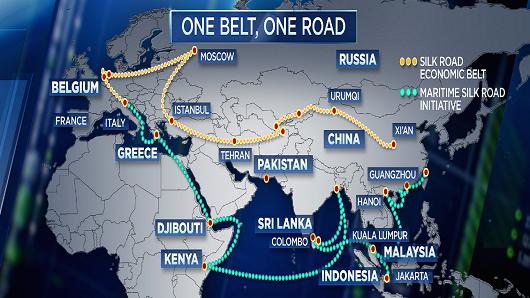
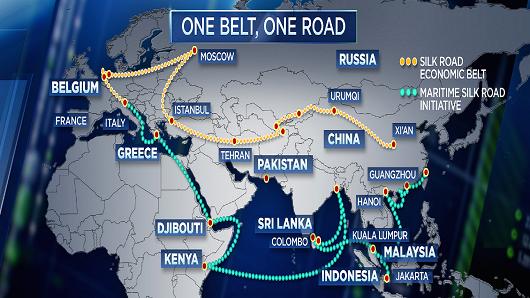
• China’s ‘Belt And Road’ Could Be Next Risk To Global Financial System (CNBC)
China has pitched its mammoth, pan-Eurasian “Belt and Road” infrastructure initiative as a means of promoting economic prosperity and fostering diplomatic ties on a global scale. That rhetoric may win plaudits at a time when other global powers are voicing increasingly protectionist agendas, but it also comes with risks, and increasing levels of state-backed funding have raised concerns about just how safe of a gamble it is. Reports on Tuesday claimed that some of China’s biggest state-owned commercial banks will begin raising capital to fund investments into the initiative, also known as “One Belt, One Road,” which aims to connect more than 60 countries across Asia, Europe and Africa with physical and digital infrastructure. China Construction Bank, the country’s second-largest bank by assets, has been conducting roadshows to raise at least 100 billion yuan ($15 billion) from on- and offshore investors.
Bank of China, Industrial and Commercial Bank of China, and Agricultural Bank of China are also said to be raising tens of billions of dollars. The news highlights the risk that the state could amass hundreds of billions of dollars in nonperforming loans if the projects fail. For Xu Chenggang, professor of economics at Cheung Kong Graduate School of Business in Beijing, it was not a surprise. “It supports my concerns,” Xu told CNBC over the phone. “The impact could be damaging not just for China, but for the global financial system.” “These loans are being extended to governments in risky countries to fund risky infrastructure projects. If the projects were launched by private firms we wouldn’t have to worry because they would know they had to bear the consequences. But here we are talking about government-to-government lending and, ultimately, intergovernmental relations.”
[..] It took decades of economic reforms and loss-making firms before it succeeded in what Xu termed a process of “quiet privatization” at the turn of the 21st century. However, the process has lost momentum over the past 10 years, and the state remains burdened with issues of overcapacity and myriad “zombie firms,” especially within the metals and construction and materials sectors. Xu said that has partially been the motivation for the “Belt and Road” initiative: “Instead of solving the overcapacity problems, they are expanding the problem to projects overseas.” “They (China) are proposing lending money to foreign governments, who will then use the Chinese funds to pay the Chinese companies,” he explained.

“.. one might say Mr. Trump represents a triumph of democracy..”
It should not surprise anyone that Western societies are becoming restless. Trump, Brexit, Charlottesville and, arguably, even radical Islamic terrorism are bi-products of global economic distortions largely created by the unwillingness of the Western political dimension to let the global factors of production naturally settle global prices and wages. (Sorry, it had to be said.) Donald Trump is a sideshow. His ascension, or someone like him, was inevitable. He may have official authority to behave like the leader of the free world (even if he is unable to do so), but so far he has only shown that virtually anyone can become president. Indeed, one might say Mr. Trump represents a triumph of democracy. Behold the robustness of America: the most powerful nation on Earth is unafraid to elect a cross between P.T. Barnum and Chauncey Gardner!
This is not to say a US president cannot raise and emphasize truly meaningful economic goals and mobilize countries around the world to help achieve them; but it is to say that this President seems to not know or be interested in what those goals might be. As discussed, the biggest challenges facing the US economy and US labor stem from a distorted global price and wage scale. Mr. Trump’s domestic fiscal, regulatory, tax and immigration goals seek only to raise US output and wages. This cannot be achieved without the participation of global commerce. There is no such thing anymore as a US business that makes US products sold only in the US without being influenced by global prices, wages and exchange rates. The romantic, patriotic “made in the USA” theme does not comport with the reality that the US also seeks to keep the dollar the world’s reserve currency and that maintaining America’s power requires the US to control the world’s shipping lanes.
Mr. Trump and his base cannot have one without the other. (Do we really have to articulate this?) Mr. Trump’s “Being There” presidency is reflecting an inconvenient truth back on a society that has, until maybe now, successfully deluded itself into believing government is functionally the glue holding society together. Though he does not mean to, Mr. Trump is single-handedly demonstrating to groups ranging from idealistic Washington elites to social media zombies to southern white supremacists that Madisonian government has become a dignified cover for the financial, commercial and national security interests that control it. We suspect those interests would rather the reach of their power be less visible.

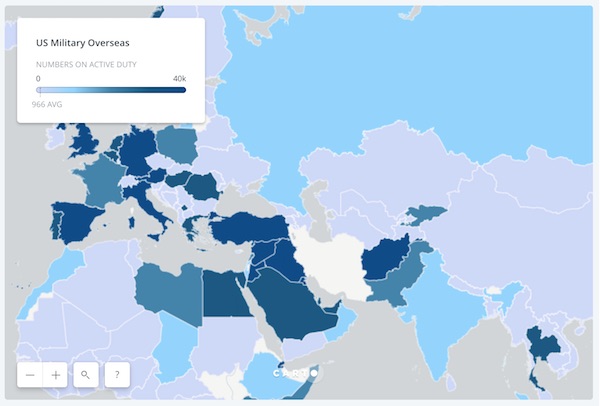
Two maps, actually. Click the link for fully interactive versions.
• All The Countries The USA Has Invaded, In One Map (Indy)
From Montezuma to the shores of Tripoli, the US has had a military presence across the world, from almost day one of her independence. What constitutes invasion? As one map below shows, the US has a military presence in much of the world without being an occupying force (though some would dispute that definition). For instance, although the Confederacy considered the US to be a hostile invading power, indy100 are not counting the Civil War or any annexation within the continental United States as an ‘invasion’. Using data on US military interventions published by the Evergreen State College, in Olympia Washington, indy100 has created this map (below). The data was compiled by Dr Zoltan Grossman, a professor of Geography and Native Studies. The map documents a partial list of occasions, since 1890, that US forces were used in a territory outside the US.
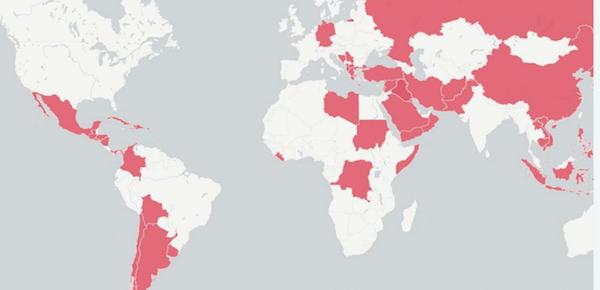
Caveats: This includes: Deployment of the military to evacuate American citizens, Covert military actions by US intelligence, Providing military support to an internal opposition group, Providing military support in one side of a conflict (e.g. aiding Iraq during the Iran-Iraq War 1988-89), Use of the army in drug enforcement actions (e.g. Raids on the cocaine region in Bolvia in 1986 It does not include threats of nuclear weapons against a territory, such as during the Berlin Air Lift (1948-49). It also excludes any time US military personnel were deployed to a foreign country for an exclusively humanitarian purpose – e.g. sending troops to the Democratic Republic of the Congo to provide assistance to refugees fleeing the Rwandan genocide (1996-97).

The demise of a society. Not because of marriages declining, but because of why they are.
• America, Home of the Transactional Marriage (Atlantic)
Over the last several decades, the proportion of Americans who get married has greatly diminished—a development known as well to those who lament marriage’s decline as those who take issue with it as an institution. But a development that’s much newer is that the demographic now leading the shift away from tradition is Americans without college degrees—who just a few decades ago were much more likely to be married by the age of 30 than college graduates were. Today, though, just over half of women in their early 40s with a high-school degree or less education are married, compared to three-quarters of women with a bachelor’s degree; in the 1970s, there was barely a difference. The marriage gap for men has changed less over the years, but there the trend lines have flipped too: 25% of men with high-school degrees or less education have never married, compared to 23% of men with bachelor’s degrees and 14% of those with advanced degrees.
Meanwhile, divorce rates have continued to rise among the less educated, while staying more or less steady for college graduates in recent decades. The divide in the timing of childbirth is even starker. Fewer than one in 10 mothers with a bachelor’s degree are unmarried at the time of their child’s birth, compared to six out of 10 mothers with a high-school degree. The share of such births has risen dramatically in recent decades among less educated mothers, even as it has barely budged for those who finished college. (There are noticeable differences between races, but among those with less education, out-of-wedlock births have become much more common among white and nonwhite people alike.)
[..] Autor, Dorn, and Hanson found that in places where the number of factory jobs shrank, women were less likely to get married. They also tended to have fewer children, though the share of children born to unmarried parents, and living in poverty, grew. What was producing these trends, the researchers argue, was the rising number of men who could no longer provide in the ways they once did, making them less attractive as partners. Furthermore, many men in these communities became no longer available, sometimes winding up in the military or dying from alcohol or drug abuse. (It’s important to point out that this study and similar research on employment and marriage focus on opposite-sex marriages, and a different dynamic may be at work among same-sex couples, who tend to be more educated.)